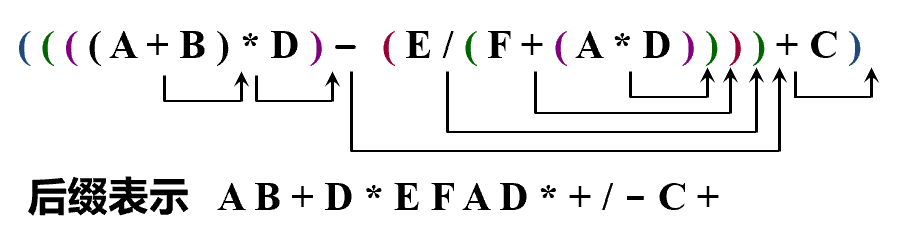线性表¶
- \(n(\ge0)\) 个表项的有限序列 \(L=(a_1,\dots,a_n)\)
- 顺序表:顺序存储方式
- 存储利用率高,存取速度快
- 插入、删除等操作时需要移动大量数据
- 链表:链表存储方式
- 适应表的动态增长和删除
- 需要额外的指针存储空间
顺序表¶
顺序表类的定义
#include <iostream.h> //定义在“seqList.h”中
#include <stdlib.h>
#include “linearList.h"
const int defaultSize = 100;
template < class E>
class SeqList: public LinearList<E> {
protected:
E *data; //存放数组
int maxSize; //最大可容纳表项的项数
int last; //当前已存表项的最后位置
void reSize(int newSize); //改变数组空间大小
public:
SeqList(int sz = defaultSize); //构造函数
SeqList(SeqList<E>& L); //复制构造函数
~SeqList() {delete[ ] data;} //析构函数
int Size() const {return maxSize;} //求表最大容量
int Length() const {return last+1;} //计算表长度
int Search(E& x) const;
//搜索x在表中位置,函数返回表项序号
int Locate(int i) const;
//定位第 i 个表项,函数返回表项序号
bool getData(int i, E& x) const; //取第i个表项的值
bool Insert(int i, E x); //插入
bool Remove(int i, E& x); //删除
};
#include <stdlib.h> //操作“exit”存放在此
#include “seqList.h” //操作实现放在“seqList.cpp”
template <class E>
SeqList<E>::SeqList(int sz) {
if (sz > 0) {
maxSize = sz; last = -1;
data = new E[maxSize]; //创建表存储数组
if (data == NULL){ //动态分配失败
cerr << "存储分配错误!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
};
template <class E>
SeqList<E>::SeqList ( SeqList<E>& L ) {
maxSize = L.Size();
last = L.Length()-1;
E value;
data = new E[maxSize]; //创建存储数组
if (data == NULL) //动态分配失败
{cerr << "存储分配错误!" << endl; exit(1);}
for (int i = 1; i <= last+1; i++) //传送各个表项
{L.getData(i, value); data[i-1] = value;}
};
template <class E>
int SeqList<E>::Search(E & x) const {
//在表中顺序搜索与给定值 x 匹配的表项,找到则
//函数返回该表项是第几个元素,否则函数返回0
for (int i = 0; i <= last; i++) //顺序搜索
if ( data[i] == x )
return i+1; //表项序号和表项位置差1
return 0; //搜索失败
};
template <class E>
bool SeqList<E>::Insert (int i, E x) {
//将新元素x插入到表中第i (1≤i≤last+2) 个表项位
//置。
if (last == maxSize-1) return false; //表满
if (i < 1 || i > last+2) return false; //参数i不合理
for (int j = last; j >= i-1; j--) //依次后移
data[j+1] = data[j];
data[i-1] = x; //插入(第 i 表项在data[i-1]处)
last++;
return true; //插入成功
};
template <class E>
bool SeqList<E>::Remove (int i, E& x) {
//从表中删除第 i (1≤i≤last+1) 个表项,通过引用型
//参数 x 返回被删元素。
if (last == -1) return false; //表空
if (i < 1 || i > last+1) return false;//参数i不合理
x = data[i-1];
for (int j = i; j <= last; j++) //依次前移,填补
data[j-1] = data[j];
last--;
return true;
};
- 实现集合运算
void Union ( SeqList<int> & LA,SeqList<int> & LB ) { int n = LA.Length ( ); int m = LB.Length ( ); int x; for ( int i = 1; i <= m; i++ ) { LB.getData(i, x); //在LB中取一元素 int k = LA.Search (x); //在LA中搜索它 if ( k == 0 ) //若未找到插入它 {n++; LA.Insert (n, x);} } } void Intersection ( SeqList<int> & LA, SeqList<int> & LB ) { int n = LA.Length ( ); int m = LB.Length ( ); int i = 1; int x; while ( i <= n ) { LA.getData (i, x); //在LA中取一元素 int k = LB.Search (x); //在LB中搜索它 if ( k == 0 ) { LA.Remove (i,x); n--;} //未找到,在LA中删除它 else i++; } }
链表¶
-
插入元素:头中尾三种情况
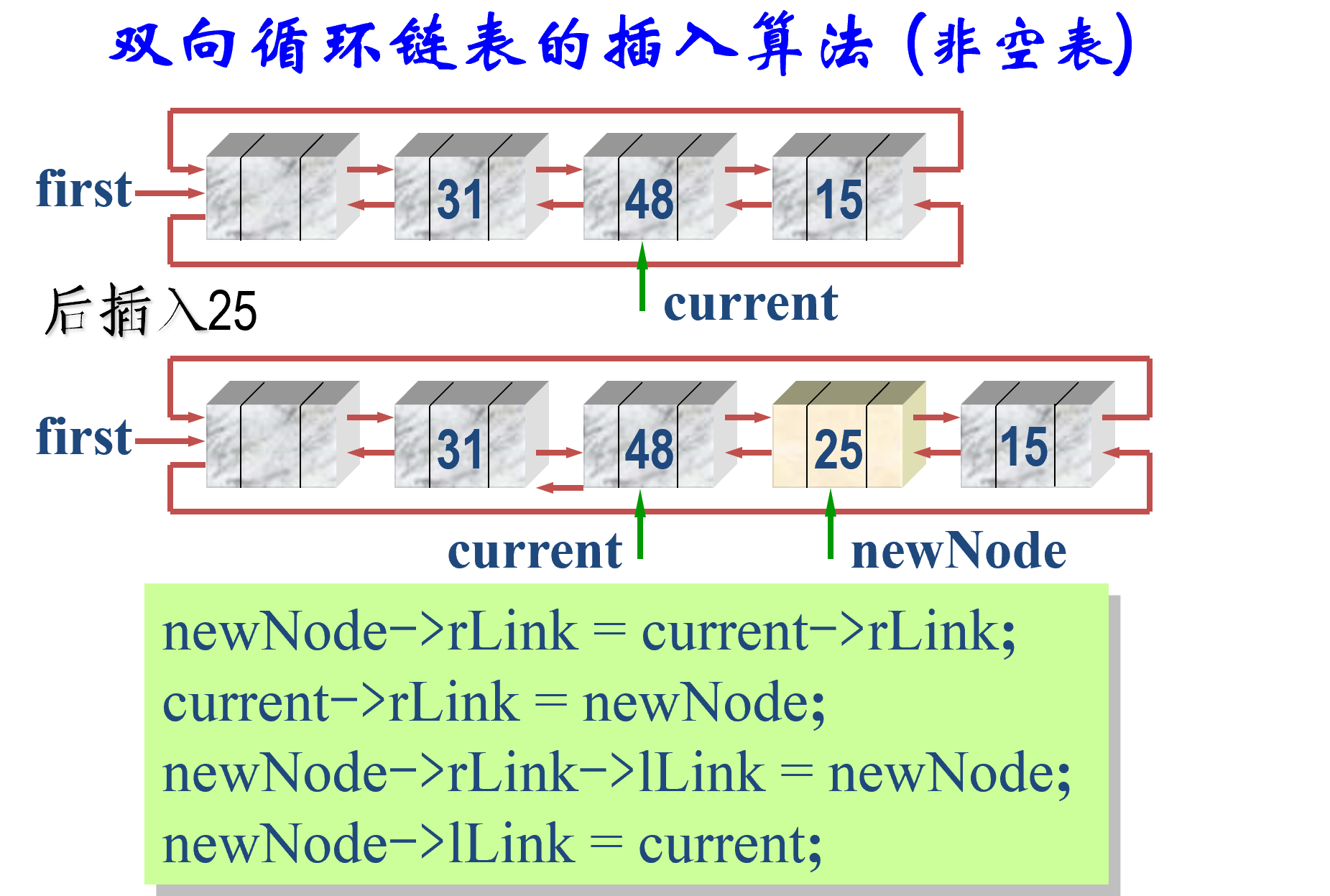
bool List::Insert(int i, int x) { //将新元素 x 插入到第 i 个结点之后。i 从1开始, //i = 0 表示插入到首元结点之前。 if (first == NULL || i == 0) { //空表或首元结点前 LinkNode *newNode = new LinkNode(x); //建立一个新结点 newNode->link = first; first = newNode; //新结点成为首元结点 } else { //否则,寻找插入位置 LinkNode *current = first; int k = 1; while (k < i && current != NULL) //找第i结点 { current = current->link; k++; } if (current == NULL && first != NULL) //链短 {cerr << “无效的插入位置!\n”; return false;} else { //插入在链表的中间 LinkNode *newNode = new LinkNode(x); newNode->link = current->link; current->link = newNode; } } return true; }; -
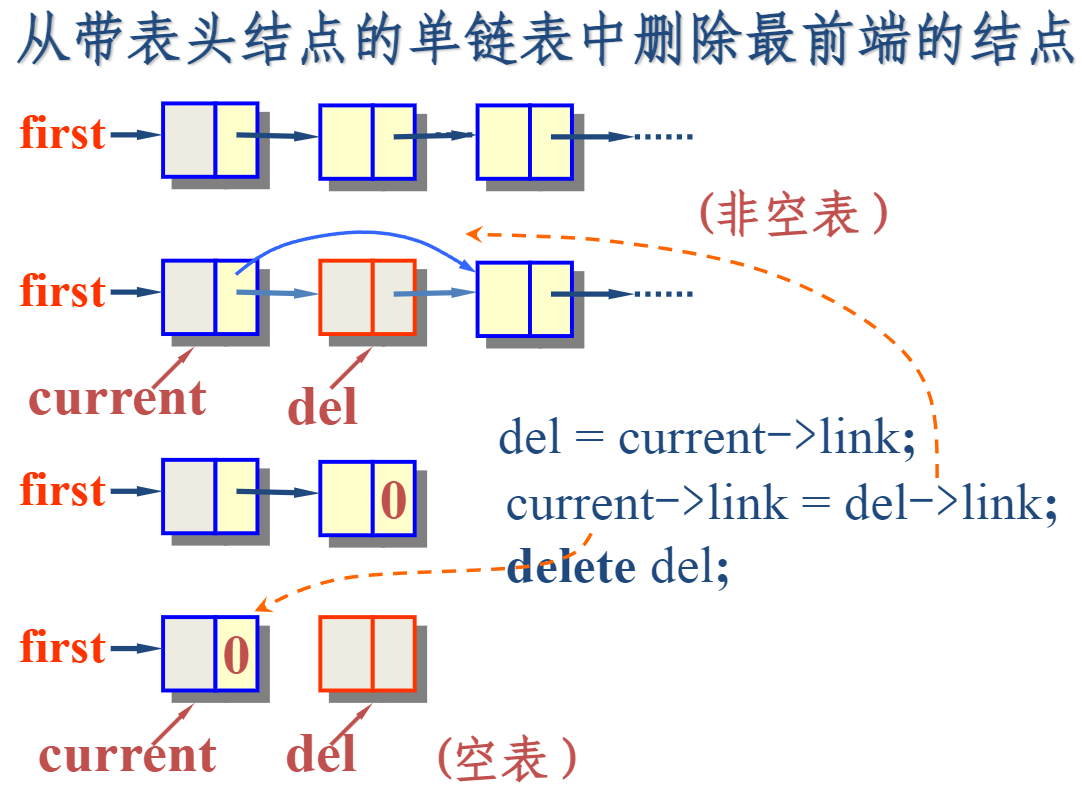
删除元素:两种情况,头节点或其它节点
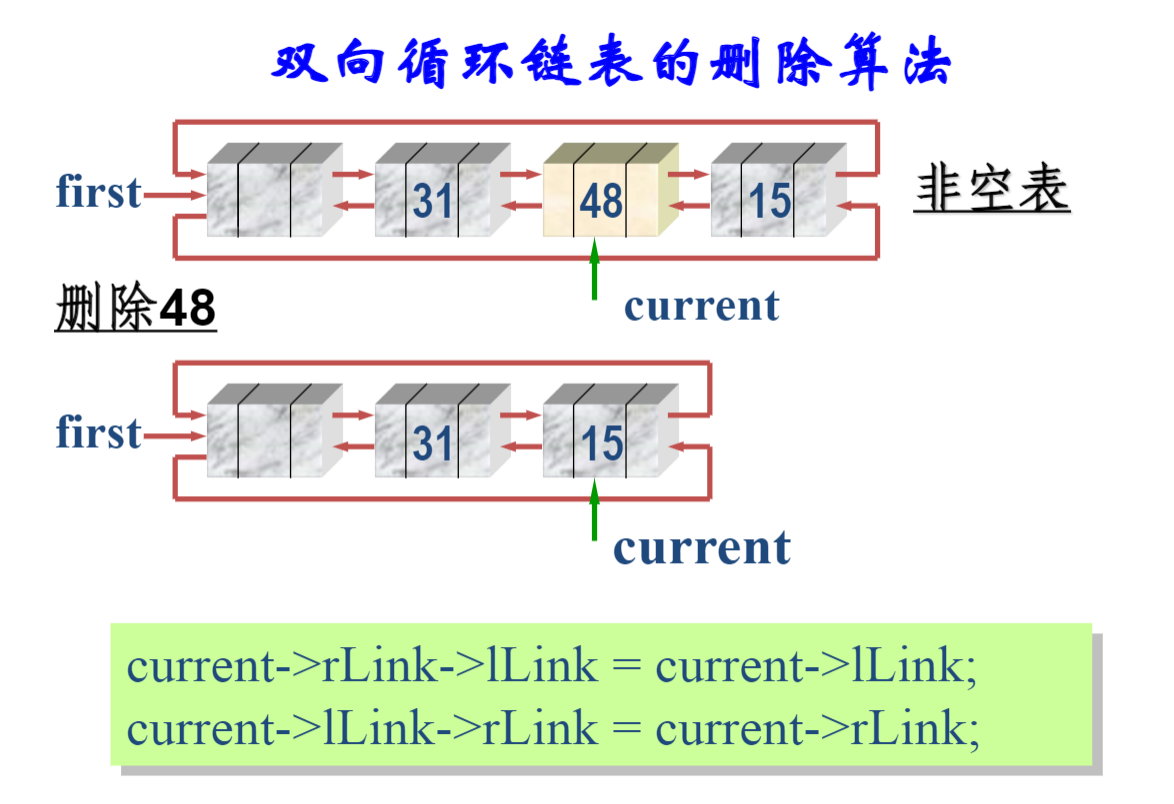
bool List::Remove (int i, int& x) { //将链表中的第 i 个元素删去, i 从1开始。 LinkNode *del; //暂存删除结点指针 if (i <= 1) { del = first; first = first->link; } else { LinkNode *current = first; k = 1; //找i-1号结点 while (k < i-1 && current != NULL) { current = current->link; k++; } if (current == NULL || current->link == NULL) { cout << “无效的删除位置!\n”; return false; } del = current->link; //删中间/尾结点 current->link = del->link; } x = del->data; delete del; //取出被删结点数据 return true; }; -
使用附加头节点统一操作
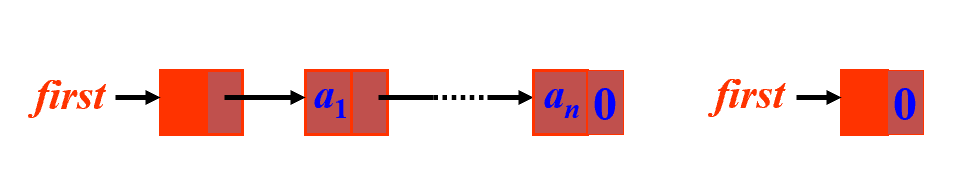
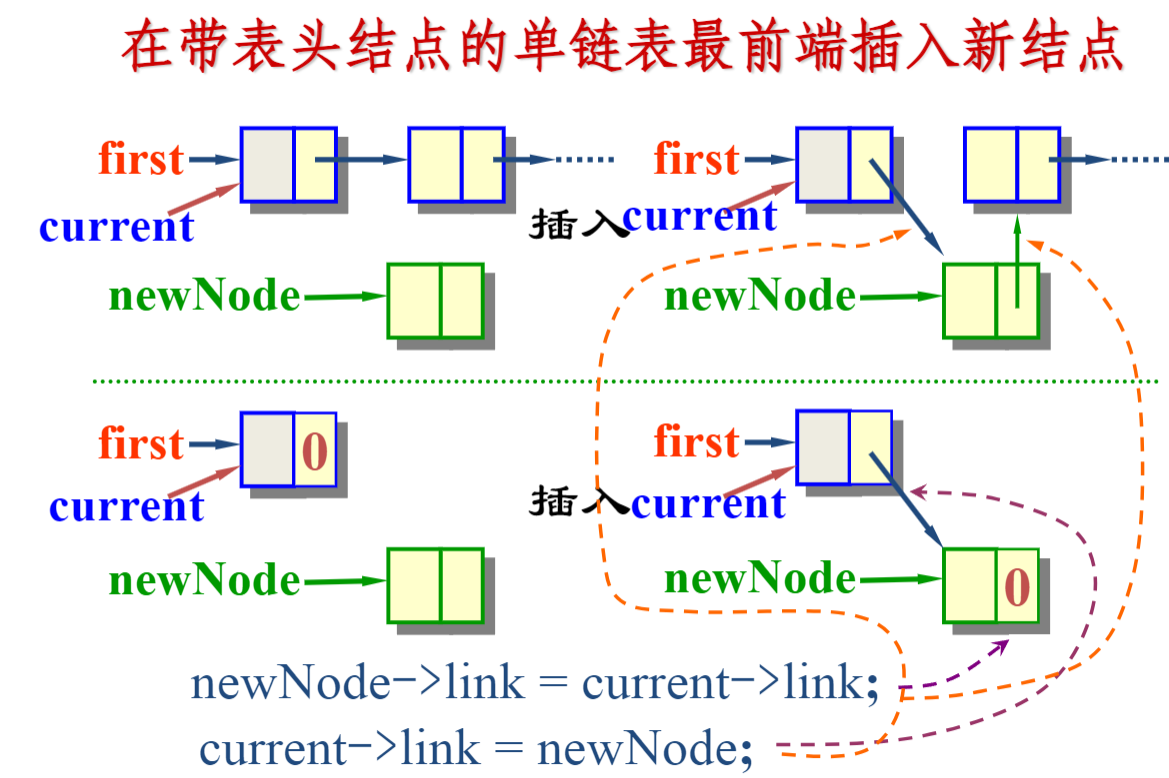
-
-
循环链表
- 搜索:从表头出发,再次回到表头是终止
-
带头节点的双向循环链表
-
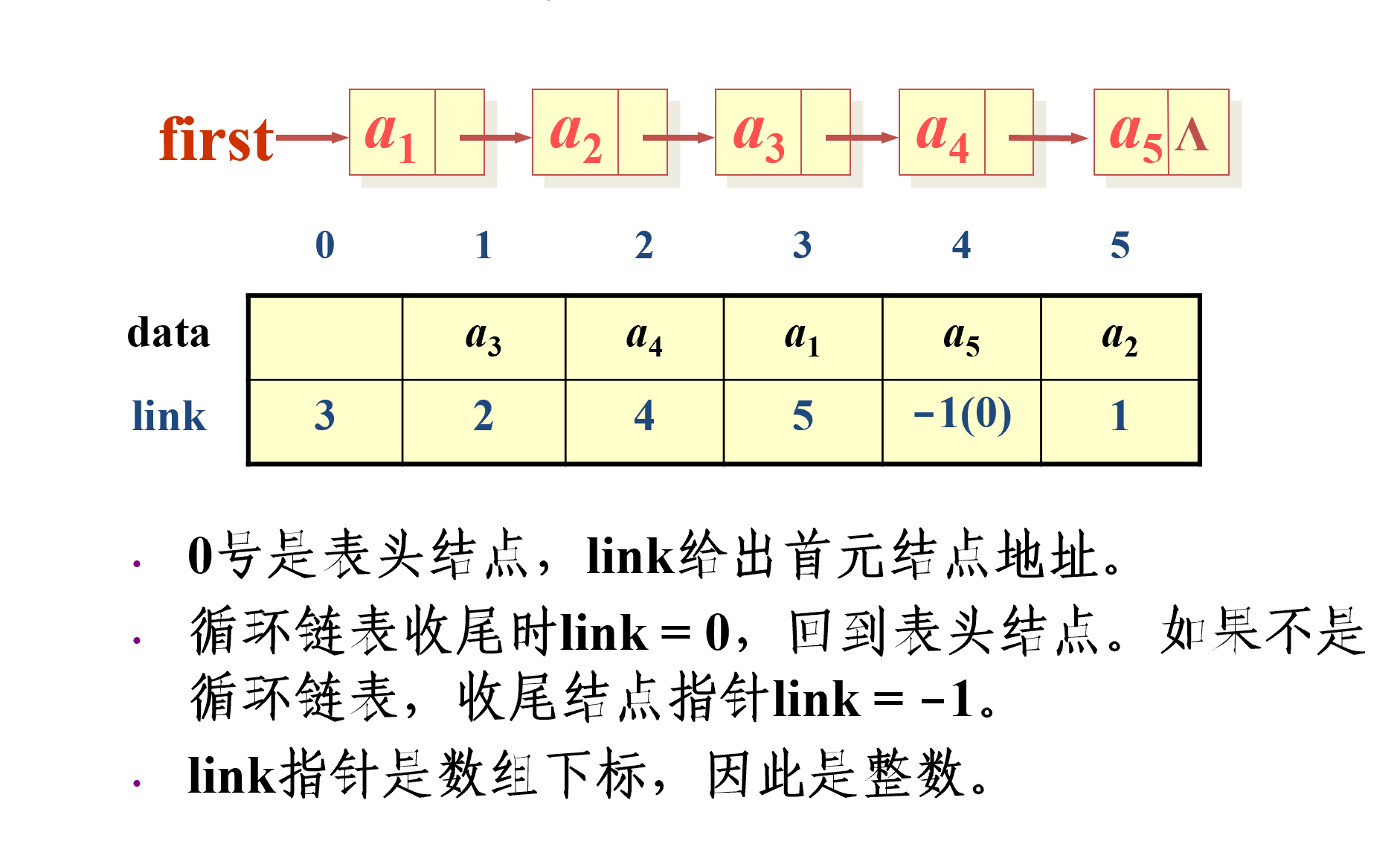
静态链表 图论#链式前向星
- 为数组中每一个元素附加一个链接指针,就形成静态链表结构。
-
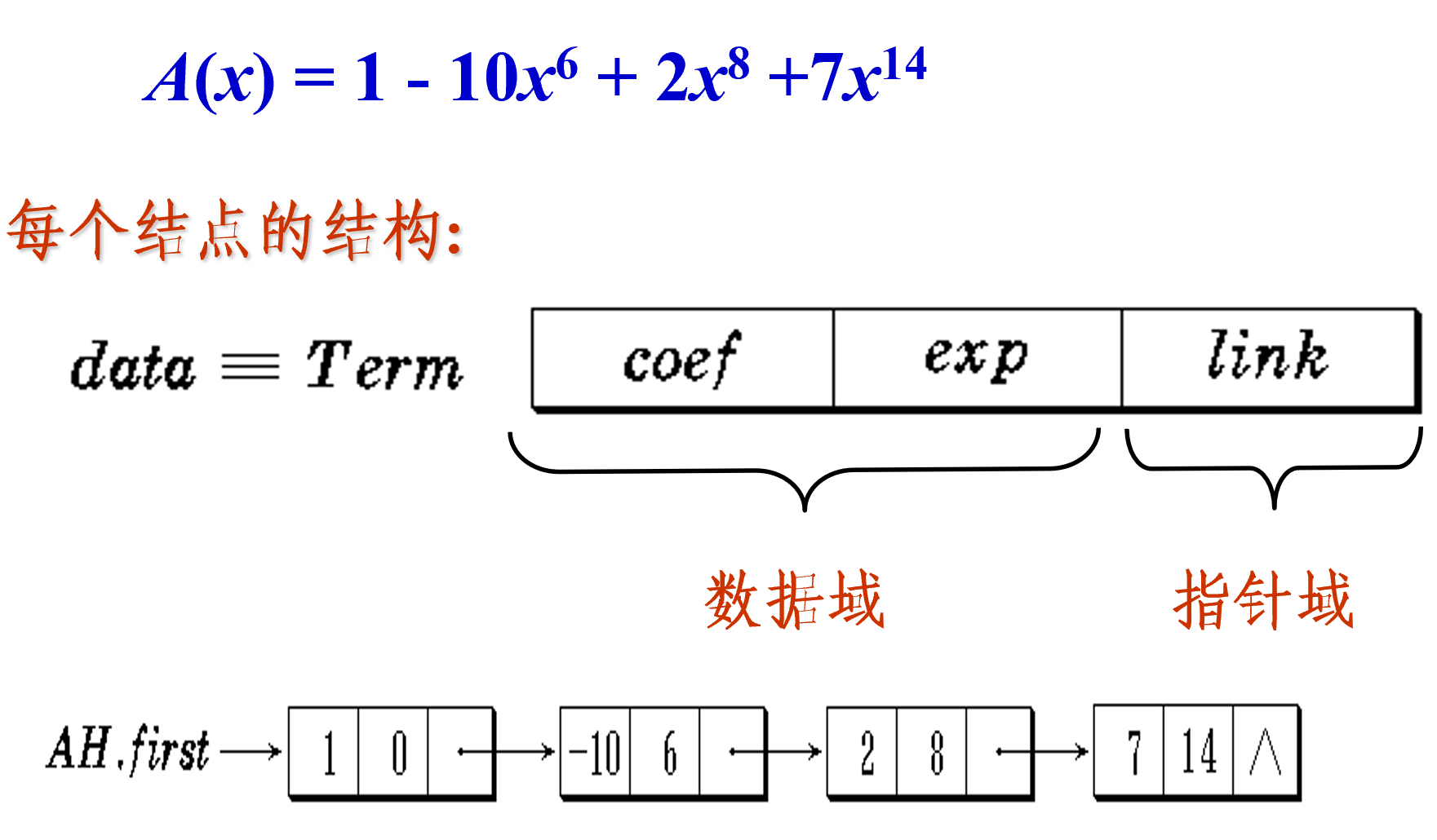
应用:多项式计算
- 使用链表可以更好地处理(阶差别较大的)1多项式
栈¶
-
栈和队列都是限制存取位置的线性结构
-
n 个元素入栈,可能的出栈顺序数目:
- 枚举第一个元素的出栈时间,分治 \(f(n) = \sum_{i=1}^{i=n}{f(i-1)*f(n-i)}\)(卡特兰数),通项为 \(f(n) = \frac{C_{2n}^{n}}{n+1}\)
-
在第一个元素入栈之后出栈之前有 i-1 个元素入栈又出栈,这可以作为一个类似的子问题
-
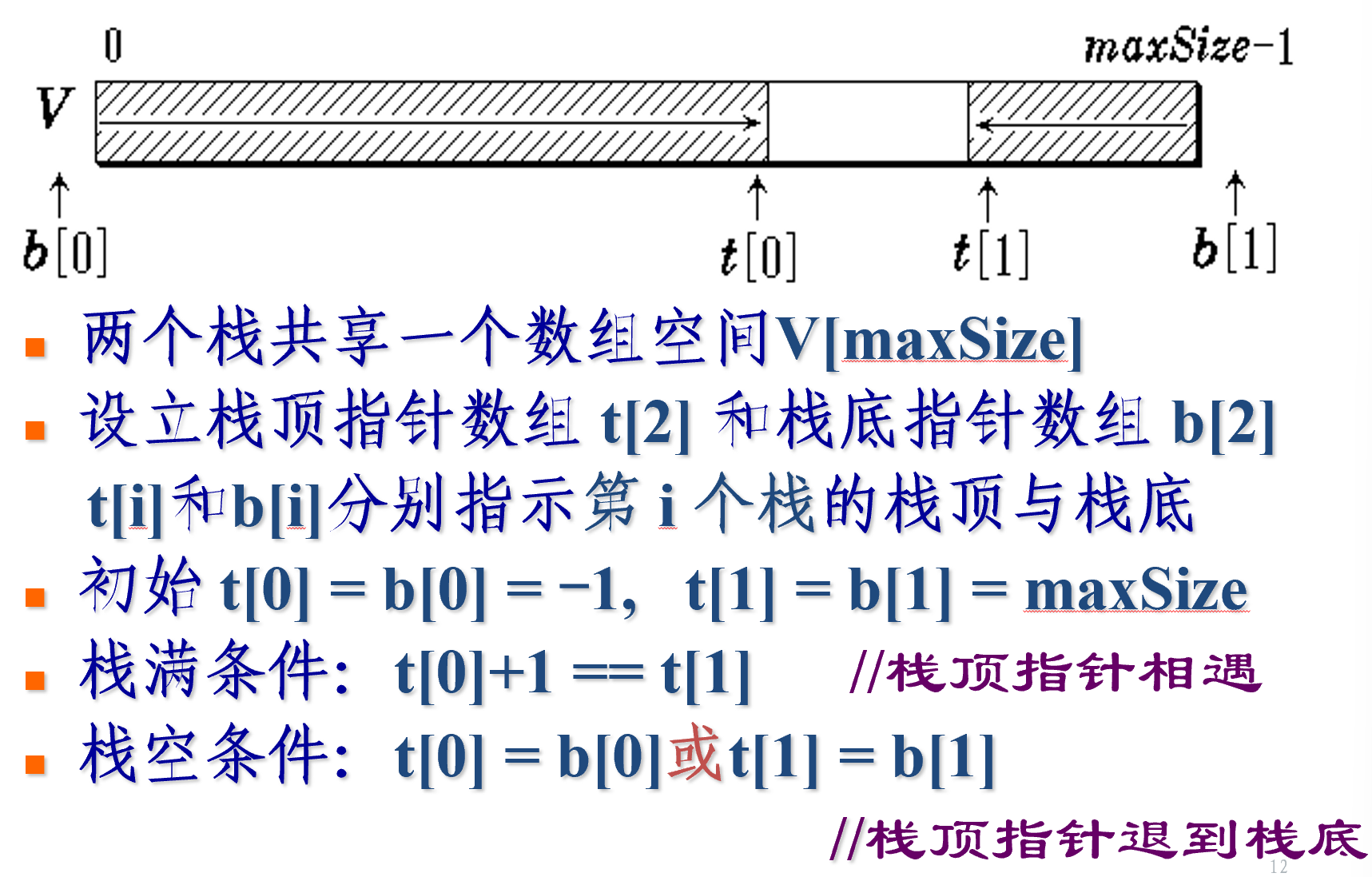
双栈共享空间
-
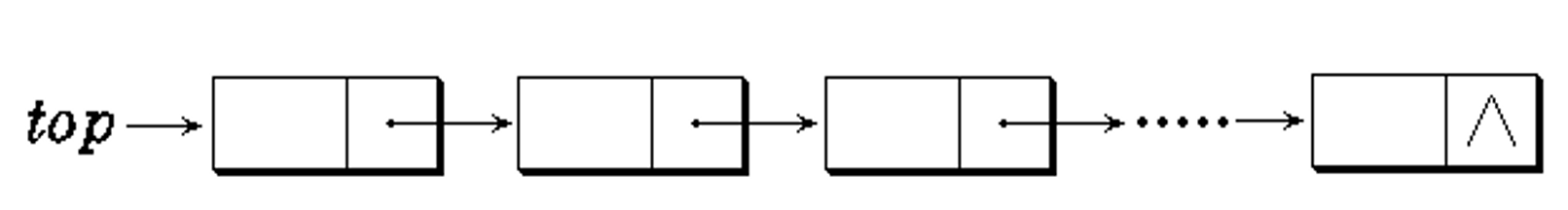
链式栈
- 栈顶在链头,插入与删除仅在栈顶处执行
应用:表达式求值¶
难点¶
-
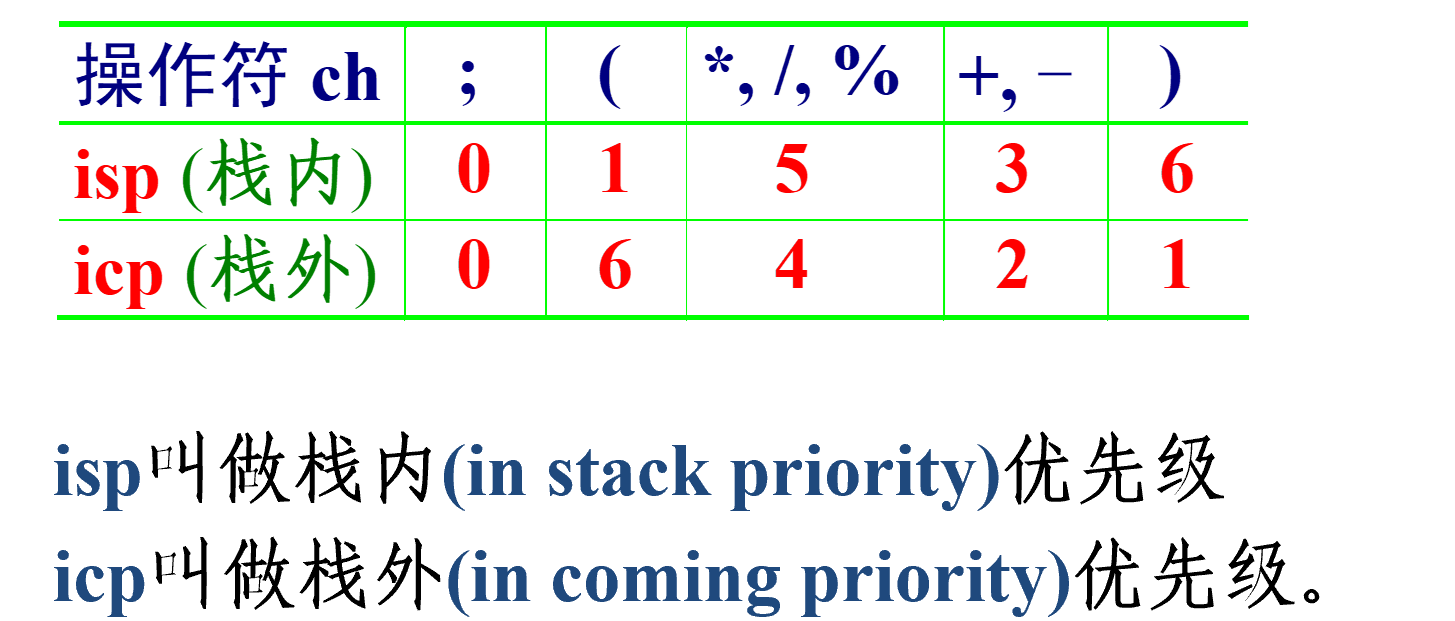
中缀转化为后缀
A + B * (C - D) - E / F->ABCD-*+EF/-- 手动转化:先对中缀表达式按运算优先次序加上括号,再把操作符后移到右括号的后面并以就近移动为原则,最后将所有括号消去。

- 如果是数字直接输出
;用作标识,开始之前先将;入栈,并且中缀表达式末尾也有一个;(用作结束时清空栈)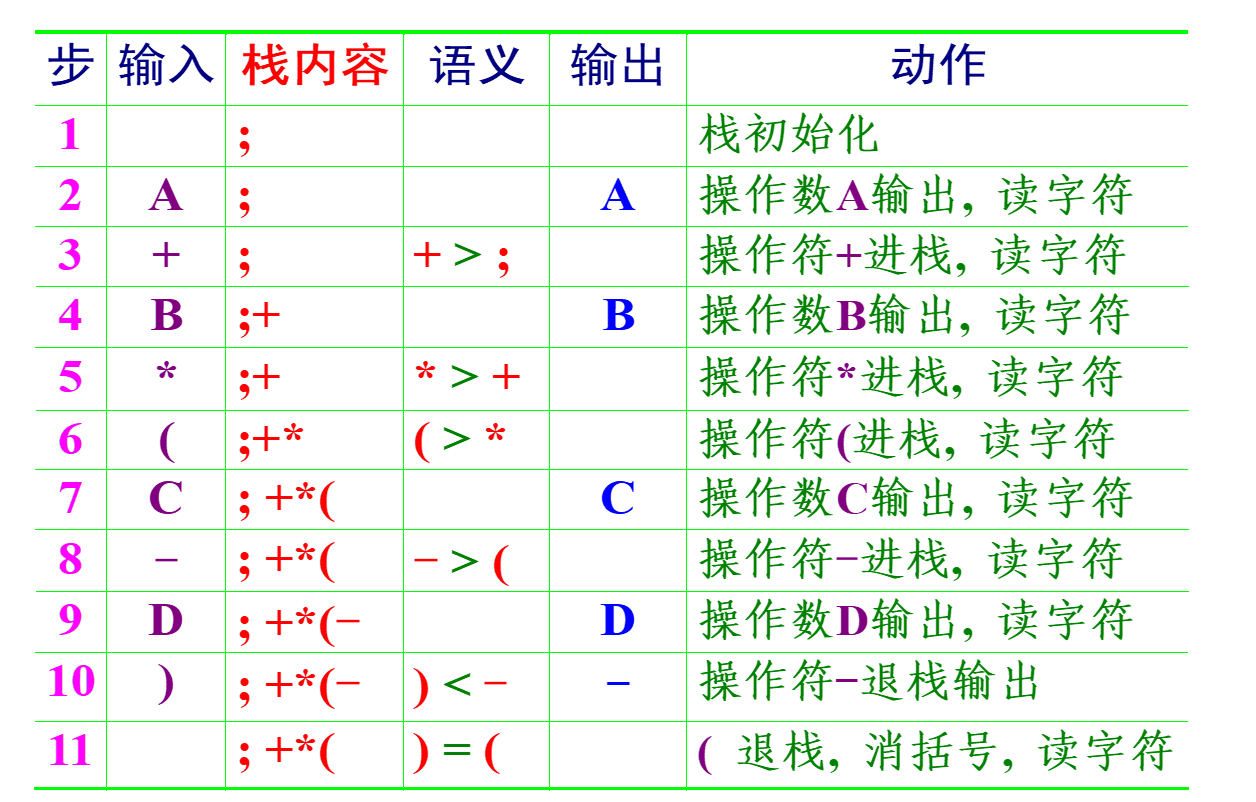
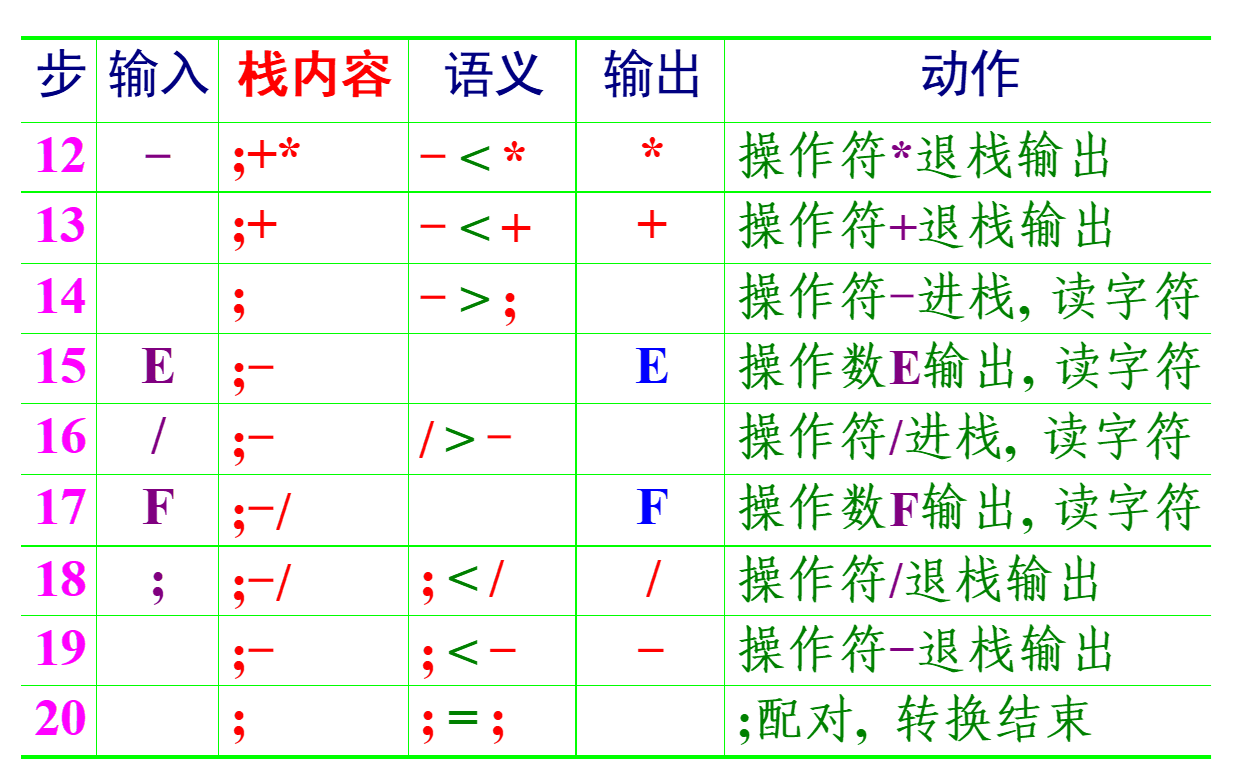
-
后缀表达式求值
- 遍历后缀表达式,遇到数就压栈,遇到操作复就从栈中取数进行计算,再放回栈中
- 栈中剩下的最后一个元素就是计算结果
应用:栈与递归¶
- 单向递归和尾递归可直接用迭代实现其非递归过程其他情形必须借助栈实现非递归过程
- 单向递归:如求解斐波那契数列(类似动态规划)
- 尾递归:如求解阶乘
队列¶
-
顺序队列(数组表示)
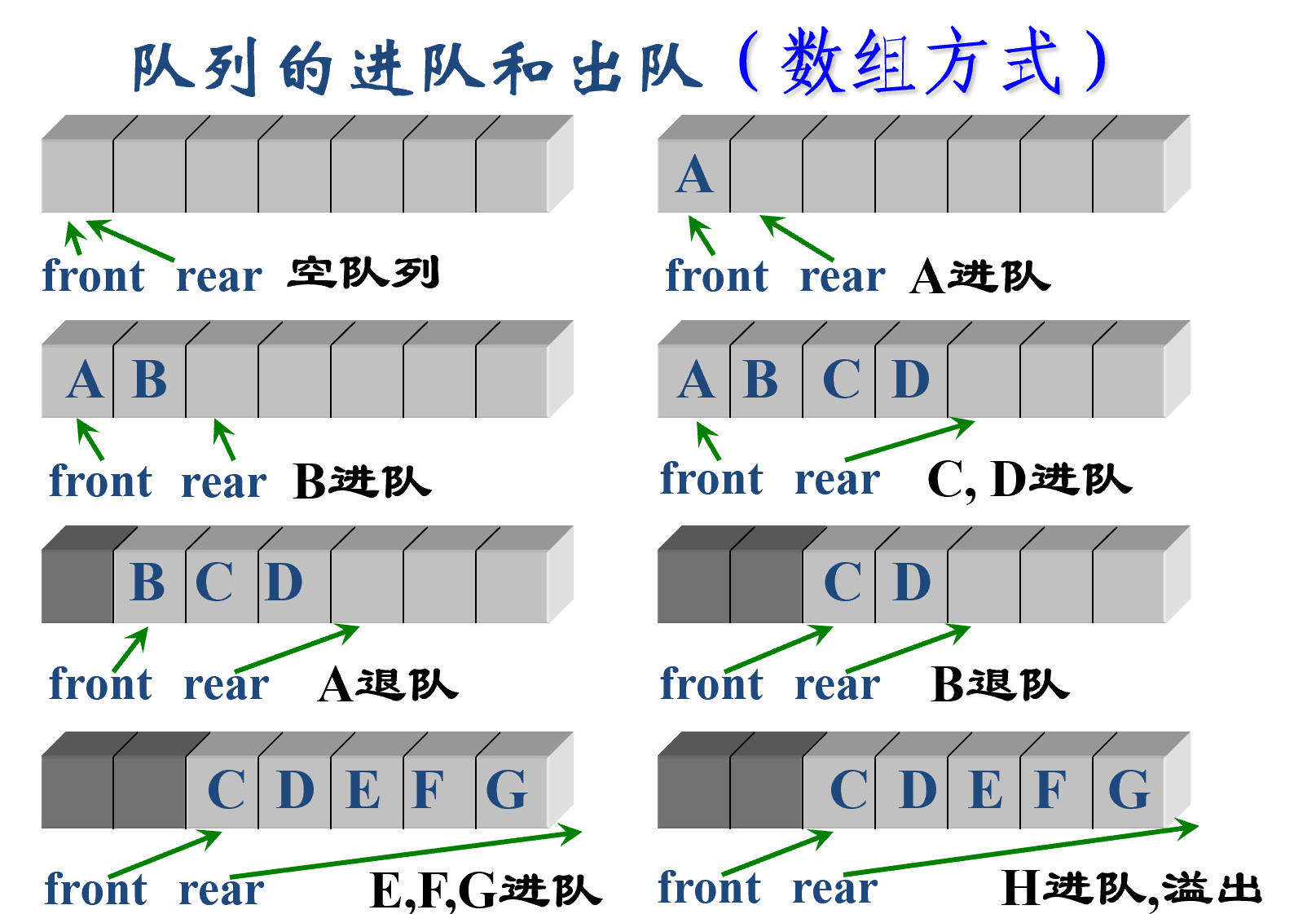
- 进队:rear++;出队:front++
- 队空时:rear=front;队满时:rear=maxSize
- 随着元素进入与弹出,逐渐无法使用,出现假溢出(使用环形队列解决)
-
循环队列
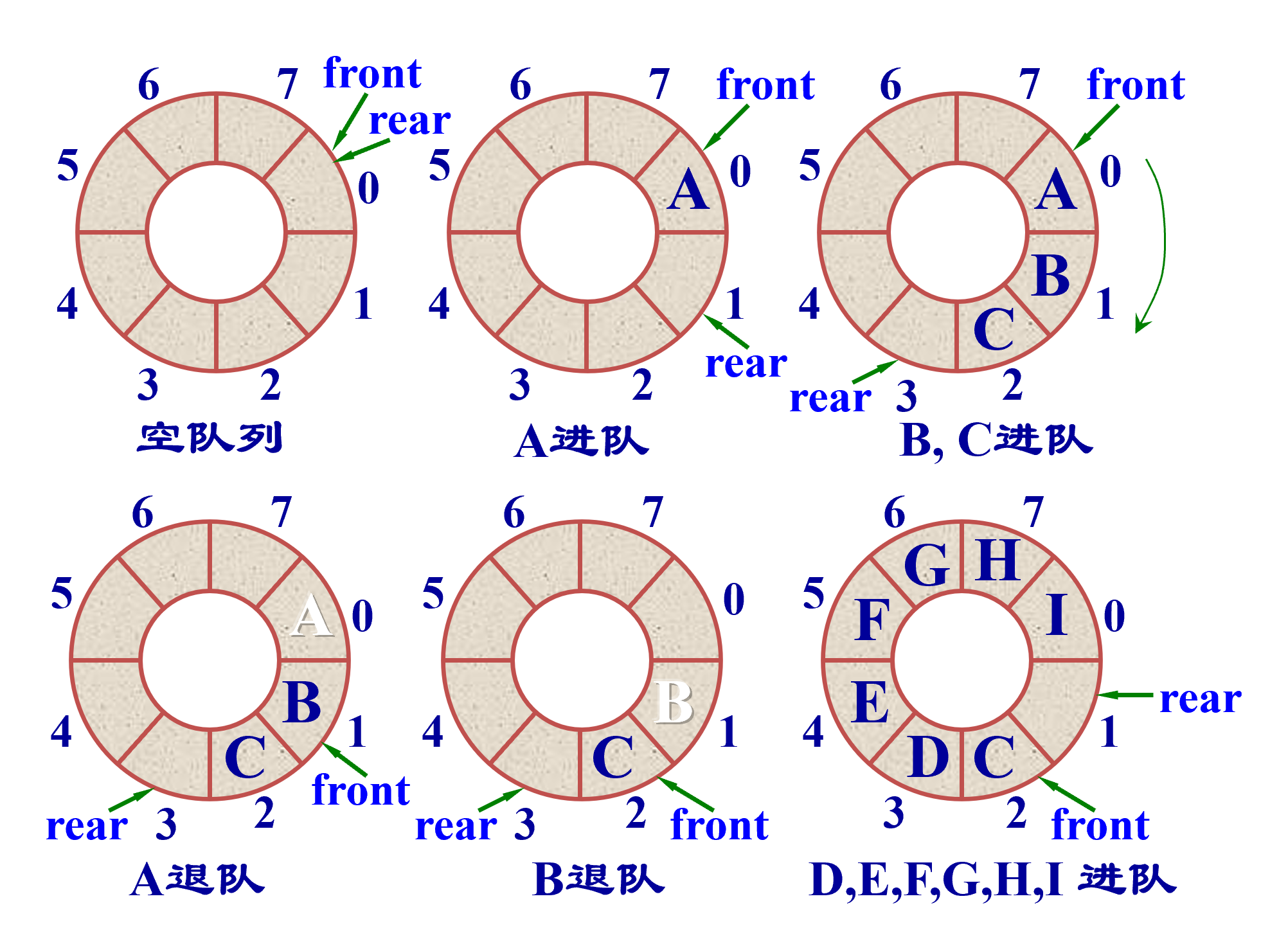
- 队头指针进 1: front = (front+1) % maxSize;
- 队尾指针进 1: rear = (rear+1) % maxSize;
- 队列初始化:front = rear = 0;
- 队空条件:front == rear;
- 队满条件:(rear+1) % maxSize == front
-
链式队列
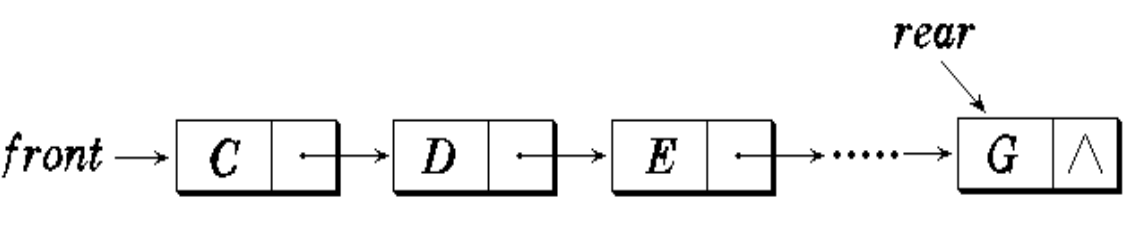
- 队头在链头,队尾在链尾。
- 注意操作时需要讨论是否为空
-
优先级队列
- 每次从队列中取出的是具有最高优先权 (优先级)的元素
- 数组实现:每次插入到相应位置维护顺序
-
应用:计算杨辉三角
- 从前一行的数据可以计算得到下一行的数据(类似一个 BFS 的过程)
- 在每一行左右加上零统一递推式
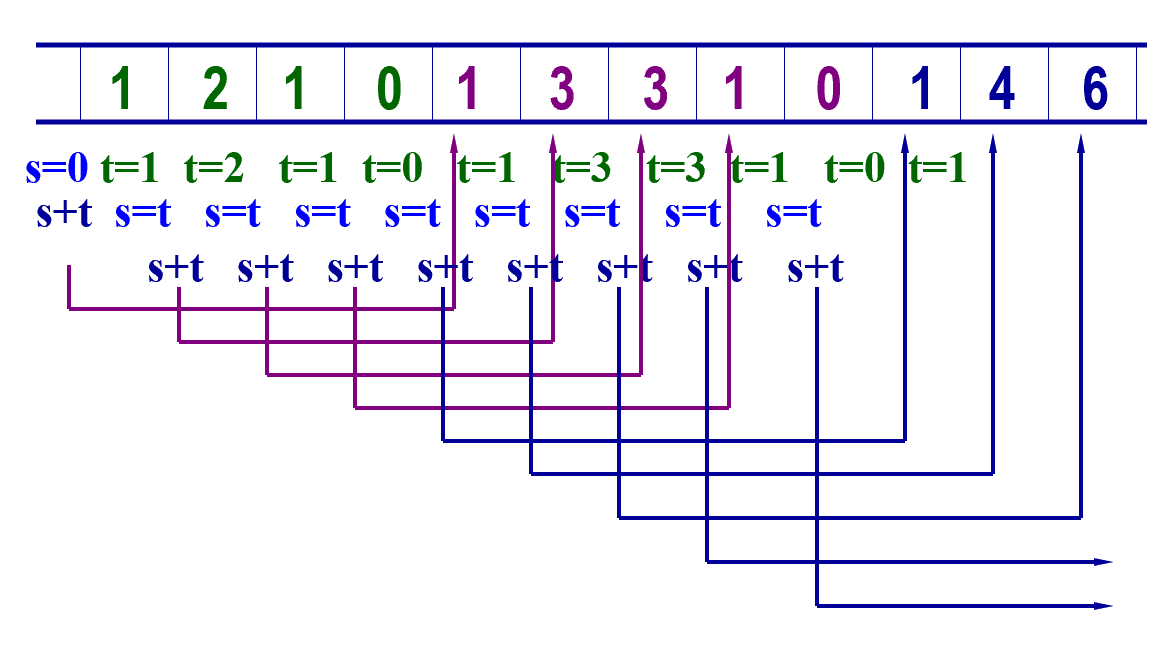
void YANGHVI(int n) { Queue q(n+3); //队列初始化 q.makeEmpty(); q.EnQueue(1); q.EnQueue(1); int s = 0, t; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { //逐行计算 cout << endl; q.EnQueue(0); for (int j = 1; j <= i+2; j++) { //下一行 q.DeQueue(t); q.EnQueue(s + t); s = t; if (j != i+2) cout << s << ' '; } } }
数组¶
- 数组是相同类型的数据元素的集合
-
n 维数组元素存储地址 \(a+(\sum_{j=1}^{n-1}(i_j*\prod^n_{k=j+1}m_{k})+i_n)*l\)
- i 表示对应下标的值,m 表示对应维度的容量
-
对称矩阵(一定是方阵)
- 只需要存储为上三角矩阵/下三角矩阵
- 总共需要存储 \(n*(n+1)/2\) 个元素
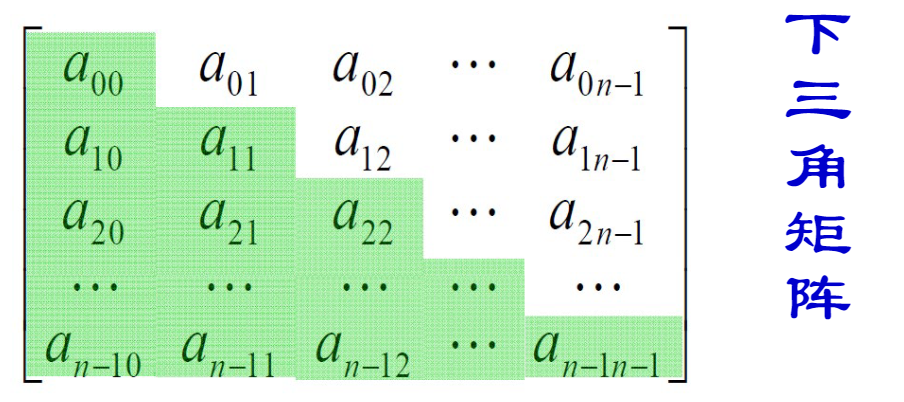
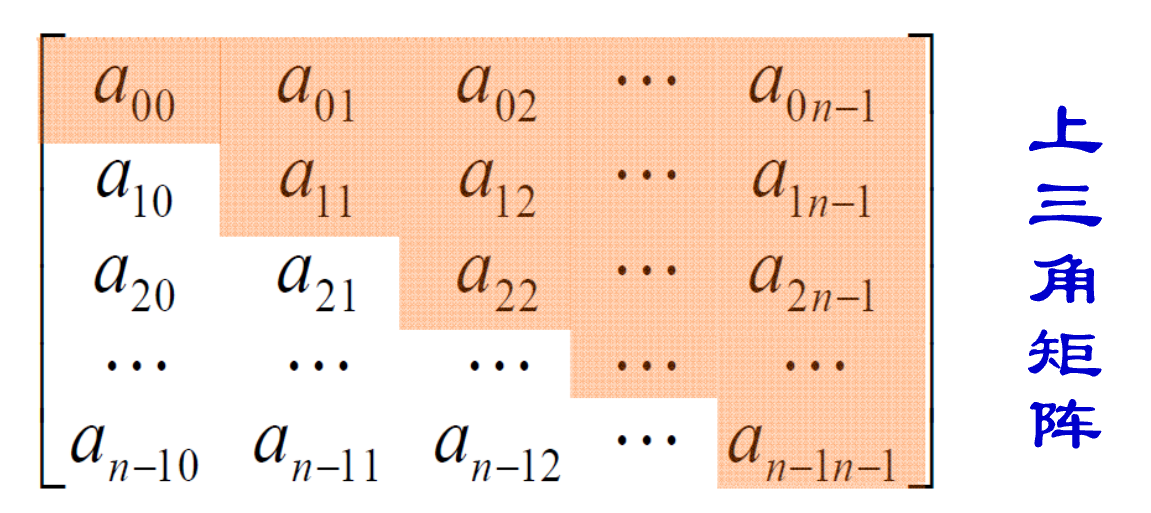
- 下三角矩阵中,对于 \(i>=j\) (否则找对称元素即可)数组元素 \(A[i][j]\) 在数组中存放位置为 \(1+2+\cdots+i+j=(i+1)*i/2+j\)
- 已知位于位置 k,则 \(i*(i+1)/2<=k<(i+1)*(i+2)/2\) 的 i 及 \(j=k-i*(i+1)/2\) 的到元素的下标
- 对于上三角矩阵\(A[i][j]\) (i<=j)位于 \(n+(n-1)+\dots+(n-i+1)+j-i=(2*n-i-1)*i/2+j\)
-
三对角矩阵

- 有 \(3n-2\) 个非0元素, \(0<=i<=n-1 \ i-1<=j<=i+1\)
- \(A[i][j]\) 位于 \(k=2*i+j\)
-
\[\begin{aligned}&{i=}{\left\lfloor(k+1)/3\right\rfloor}\\&{j=k-2}{*}{i}\end{aligned}\]
稀疏矩阵¶
- 稀疏因子 \(e=s/(m*n)\) 通常认为 \(e<=0.05\) 为稀疏矩阵
- 存储稀疏矩阵时一般只存储非零元素,使用三元组 \((i,j,a_{ij})\) 表示矩阵的元素在稀疏矩阵的三元组表中
- 存储时三元组按照字典序进行排列
-
非空元素三元组加上矩阵的长宽就可以确定唯一的稀疏矩阵
-
转置(关键是要维护矩阵元素三元组的排列顺序)
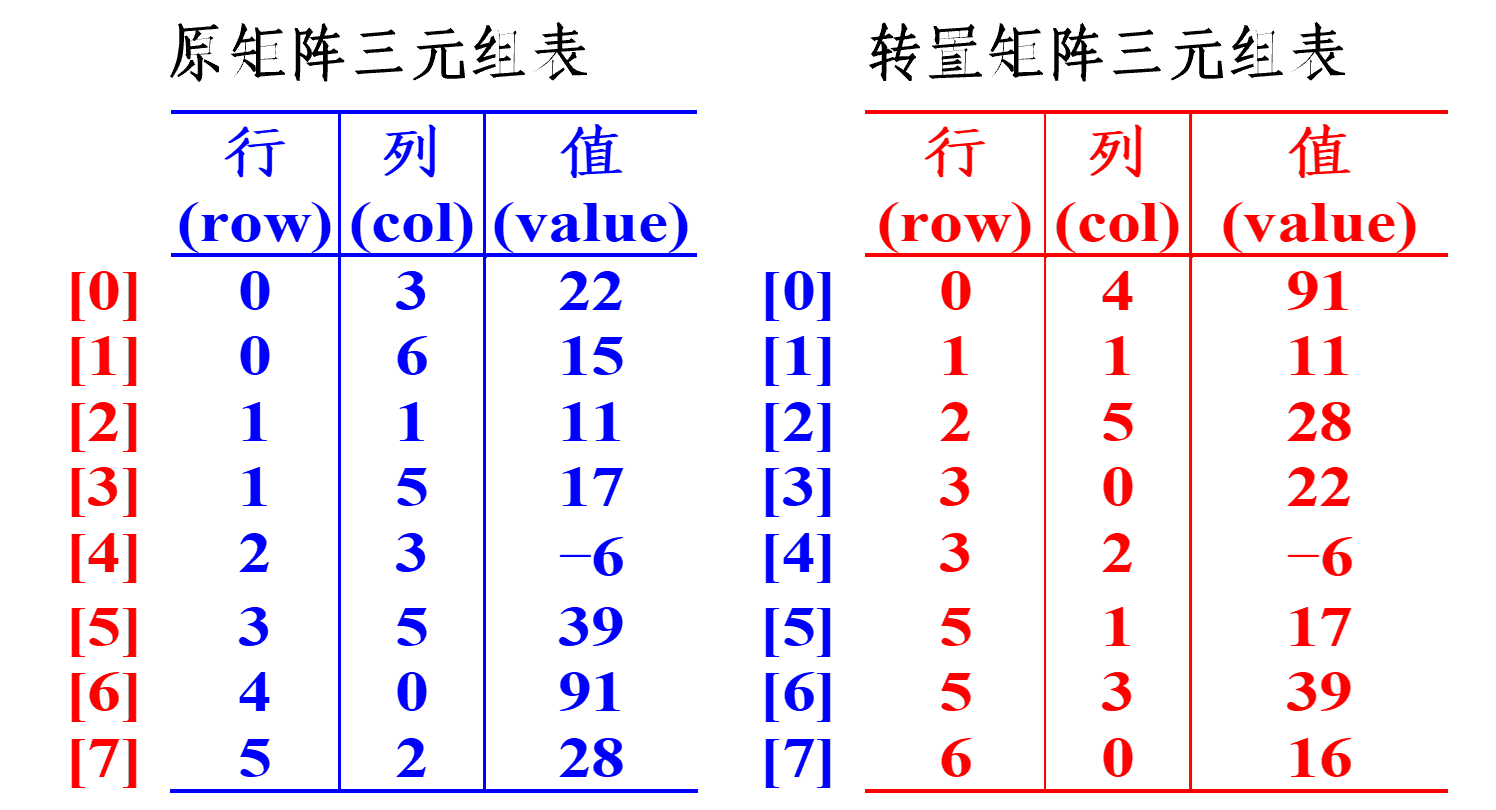
- 设矩阵列数为 Cols,对矩阵三元组表扫描 Cols 次。第 k 次扫描找寻所有列号为 k 的项,将其行号变列号、列号变行号,顺次存于转置矩阵三元组表。
- 主要关注转置之前的列,因为转置之前的行是单调的,因此只需要从上向下扫描即可实现有序
-
快速转置
- 对原矩阵 A 扫描一遍(实际为两遍,建辅助数组需扫描一遍),按 A 中每一元素的列号,立即确定在转置矩阵 B 三元组表中的位置,并装入它。
- rowSize 记录矩阵转置前各列,即转置矩阵各行非零元素个数;
- rowStart 记录转置矩阵各行非零元素在转置三元组表中开始存放位置。
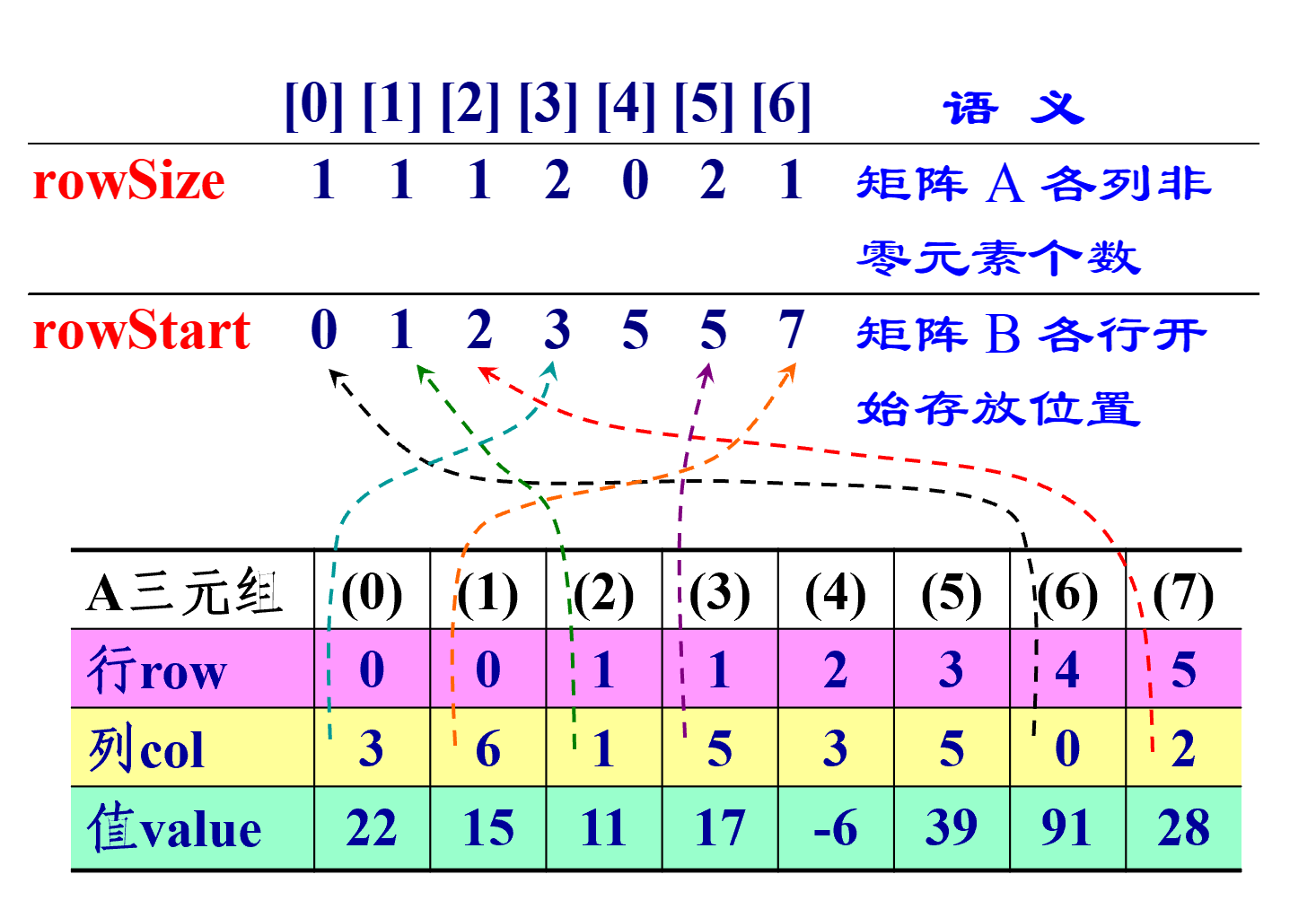
-
带行指针的二元组
- 用带行指针数组的二元表白哦是稀疏矩阵(利用链表表示行)
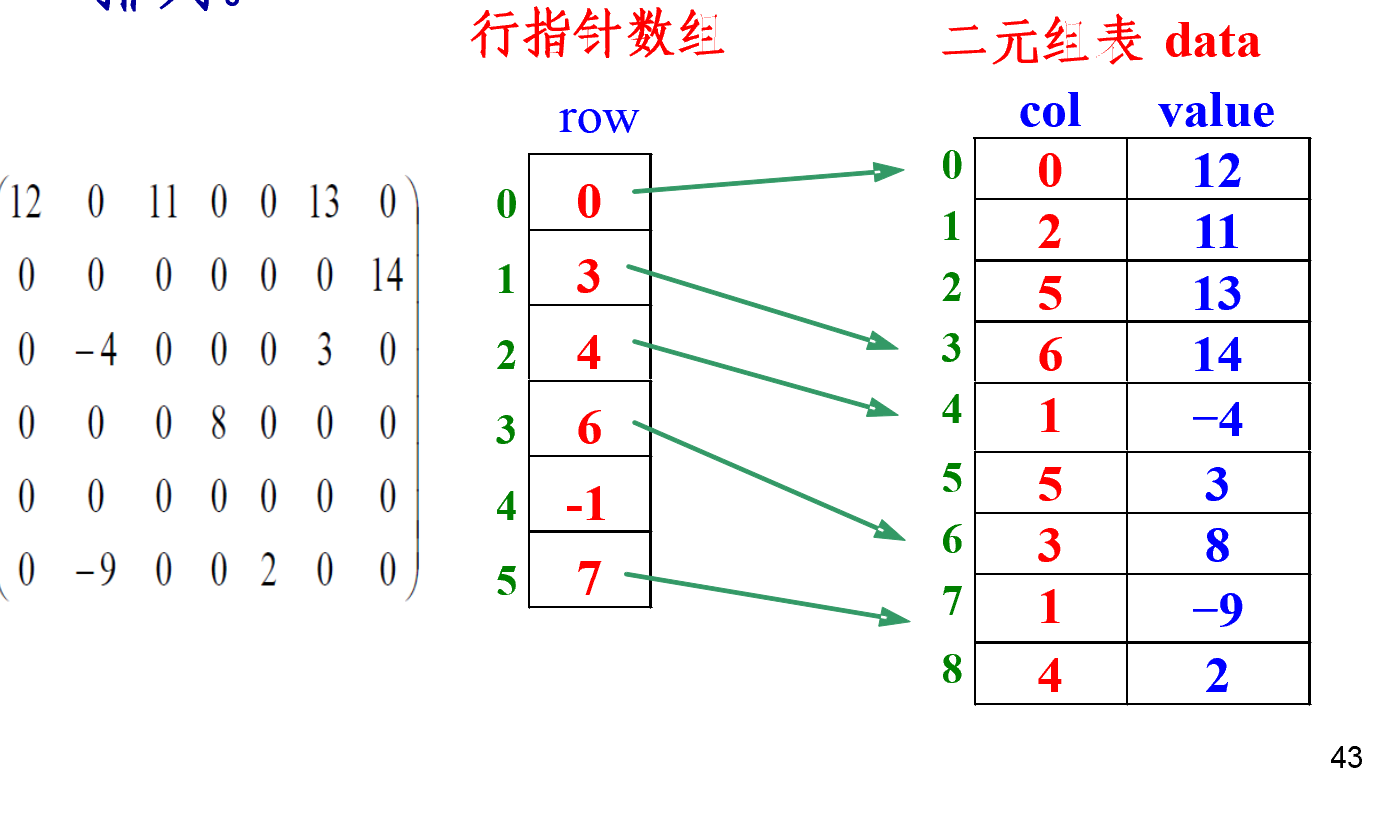
-
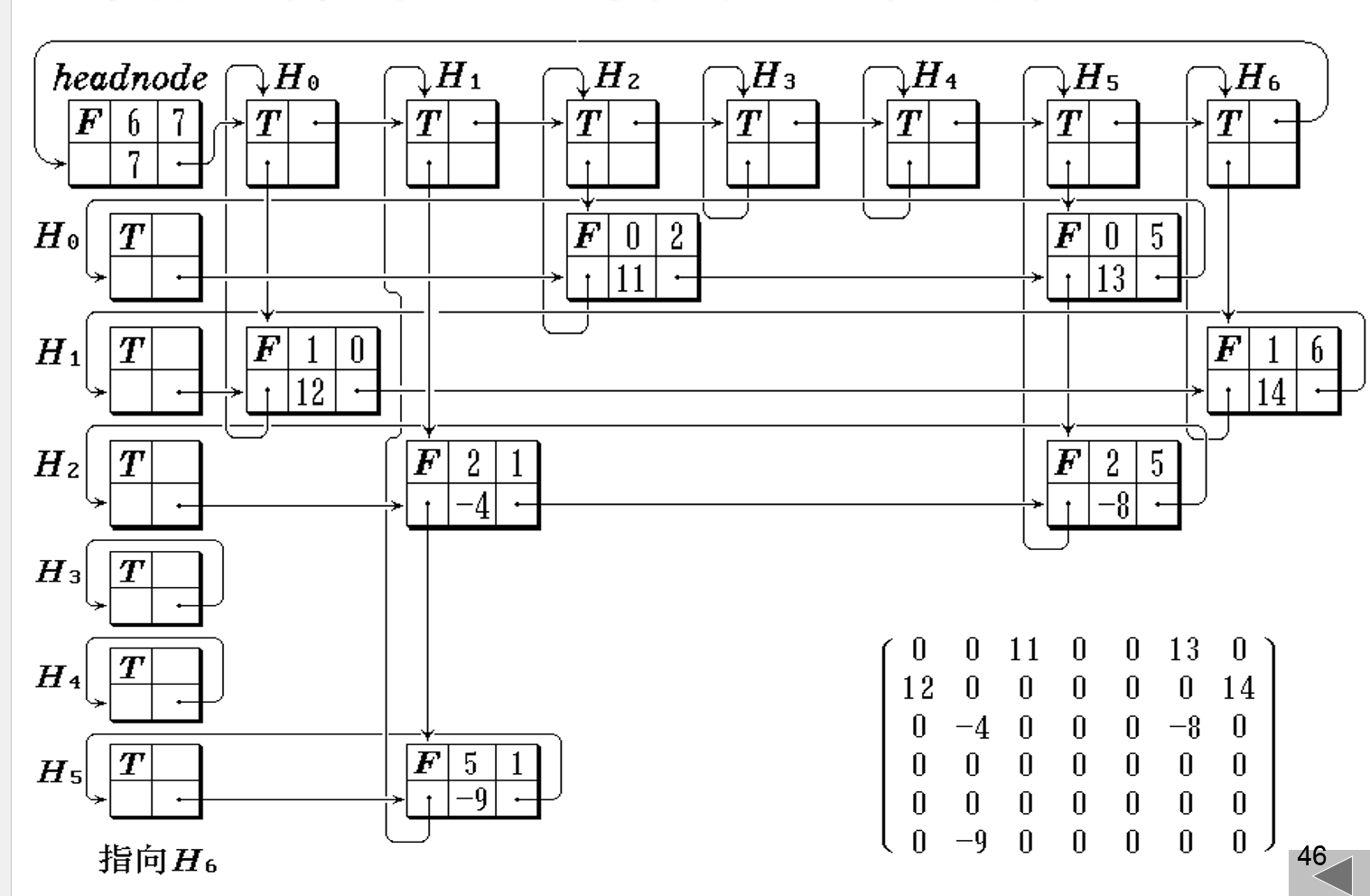
正交链表示稀疏矩阵
- 适应矩阵操作时(+-*)时矩阵非零元素的动态变化
- 如上面的"带行指针的二元组"相比,行列访问更为便捷
字符串¶
- 朴素的模式匹配 \(O(n\cdot m)\)
难点¶
KMP¶
- 复杂度 \(O(n)\)
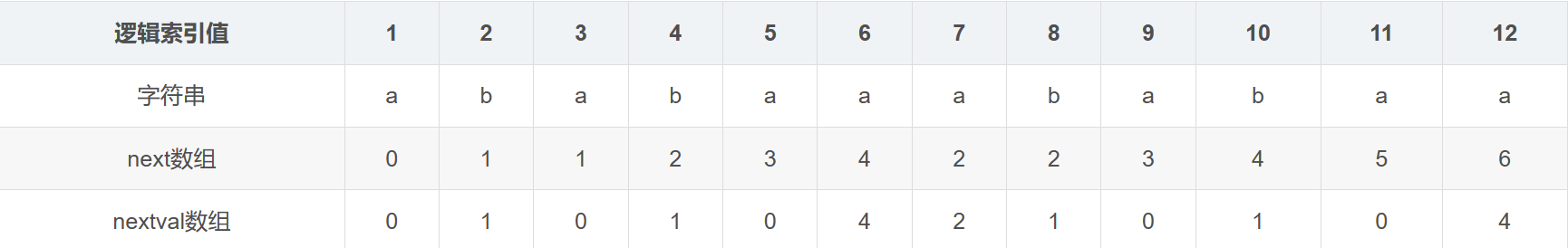
- 由模式串计算,\(next[i]\) 表示 \(pat[0,i-1]\) 的最长共同前后缀的长度
- 书上定义(注意书上定义实际上是之前版本的next[i-1])
-
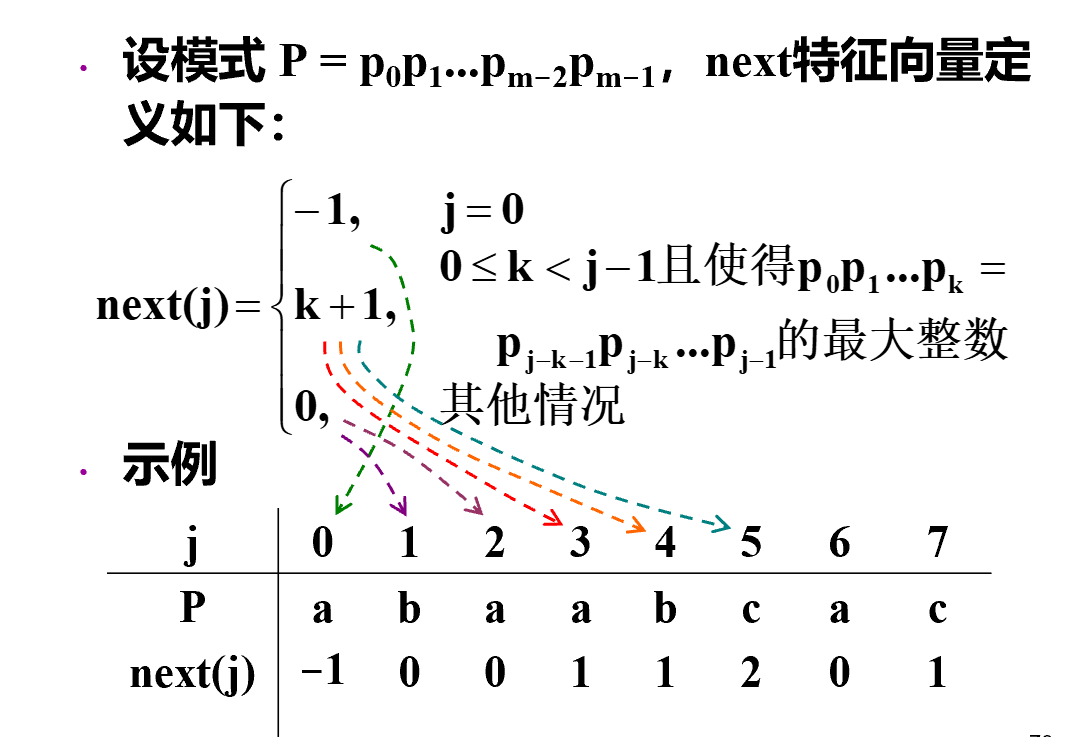
-
匹配时
- 如果 j > 0,那么在下一趟比较时模式串 P 的起始比较位置是 next(j),目标串 T 的指针不回溯,仍指向上一趟失配的字符;
- 如果 j = 0,则目标串指针 T 进一,模式串指针 P 回到 p0,继续进行下一趟匹配比较
vector<int> build_next(string s)//构建next数组 { vector<int>next{-1};//第一位一定为零(因为规定前后缀不能为自身) int i=1,len=0;//len记录当前位置最大重合长度 while(i<s.size()) { if(s[len]==s[i-1]&&len!=i-1) { len++; next.push_back(len); i++; } else { if(len==0) { next.push_back(0); i++; } else len=next[len];//找到对应的前缀的末尾位置(一种递归思想,长的匹配不上则逐渐缩短去找) } } return next; } int kmp(string fs,string ss)//ss为待匹配的子串 { vector<int>next=build_next(ss); int i=0,j=0; while(i<fs.size()) { if(fs[i]==ss[j]) { i++; j++; } else if(j>0) j=next[j];//前next[j-1]位仍相同,在这之后继续匹配 else i++; if(j==ss.size()) return i-j; } return -1; } -
有的题目会将所有项加 1(即第一项不是 -1 而是 0)
-
nextval 计算:
- 问题比如子串是 \(aaaab\) 待匹配串 \(aaabaa\)
- 那么第 4 为比较失败了会依次尝试 \(next[4],next[3]\dots\) 这实际上没有必要,因为子串中这些位置都相同,后面不匹配,前面相同的位置也不会成功
- 因此,如果 \(p[j]=p[next[j]]\to next[j]=next[next[j]]\)
难点¶
广义表¶
-
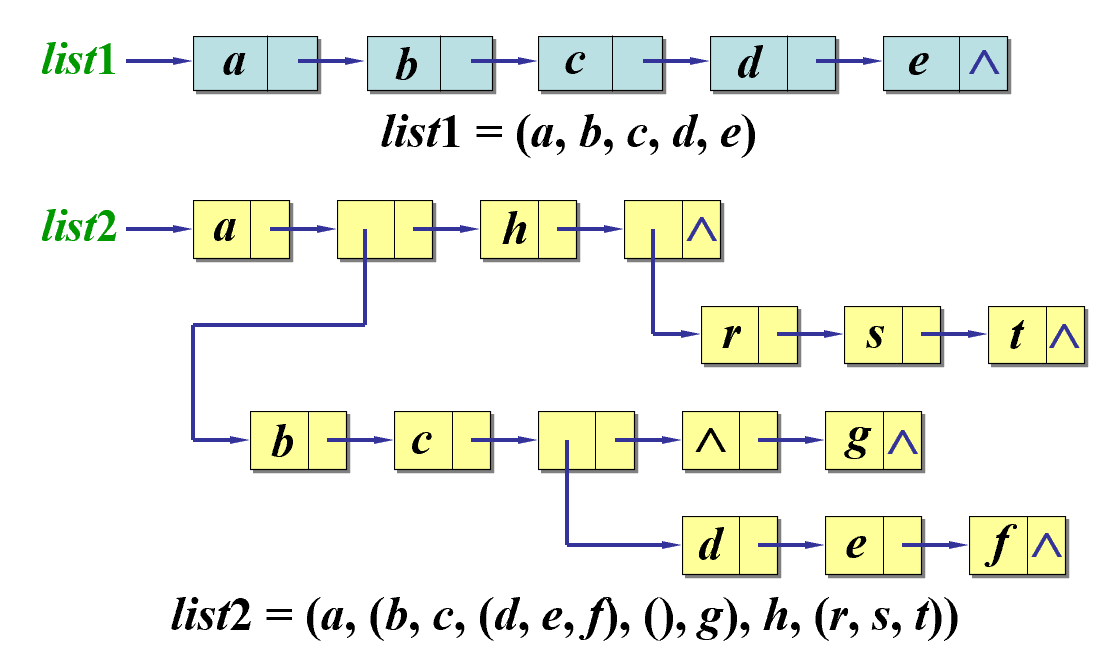
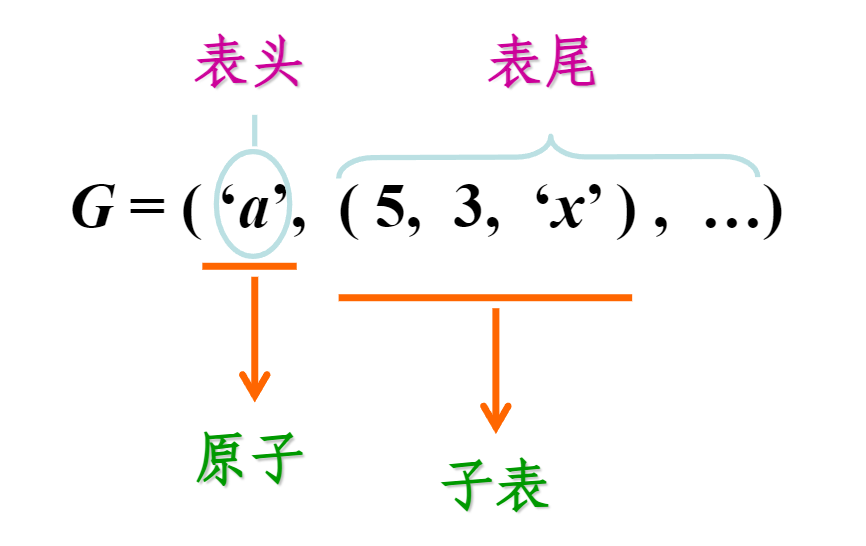
广义表是 n 个元素组成的有限序列 \(LS(a_1,\dots,a_n)\)
- 元素可以为数据元素或子表
-
n > 0 时表的第一个元素为广义表的表头,其他元素为表尾
- 可以通过嵌套 head、tail 访问广义表中任意一个元素
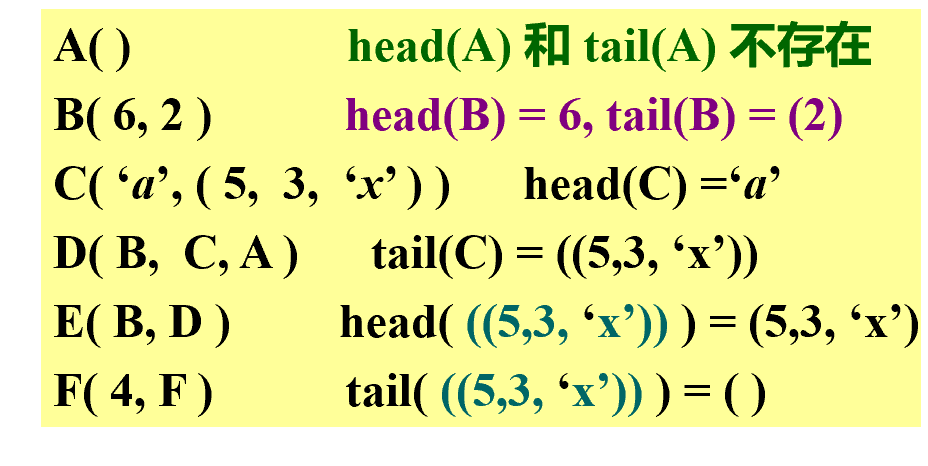
- 返回的尾元素的元组,即要在外面加一组括号,而 head 返回表头(单个元素)不会加上一组额外括号
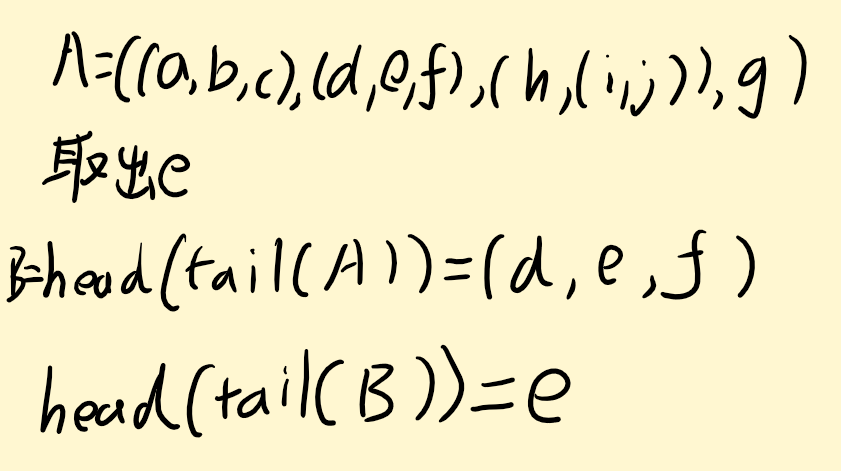
-

-
广义表视图
-
广义表结点的定义
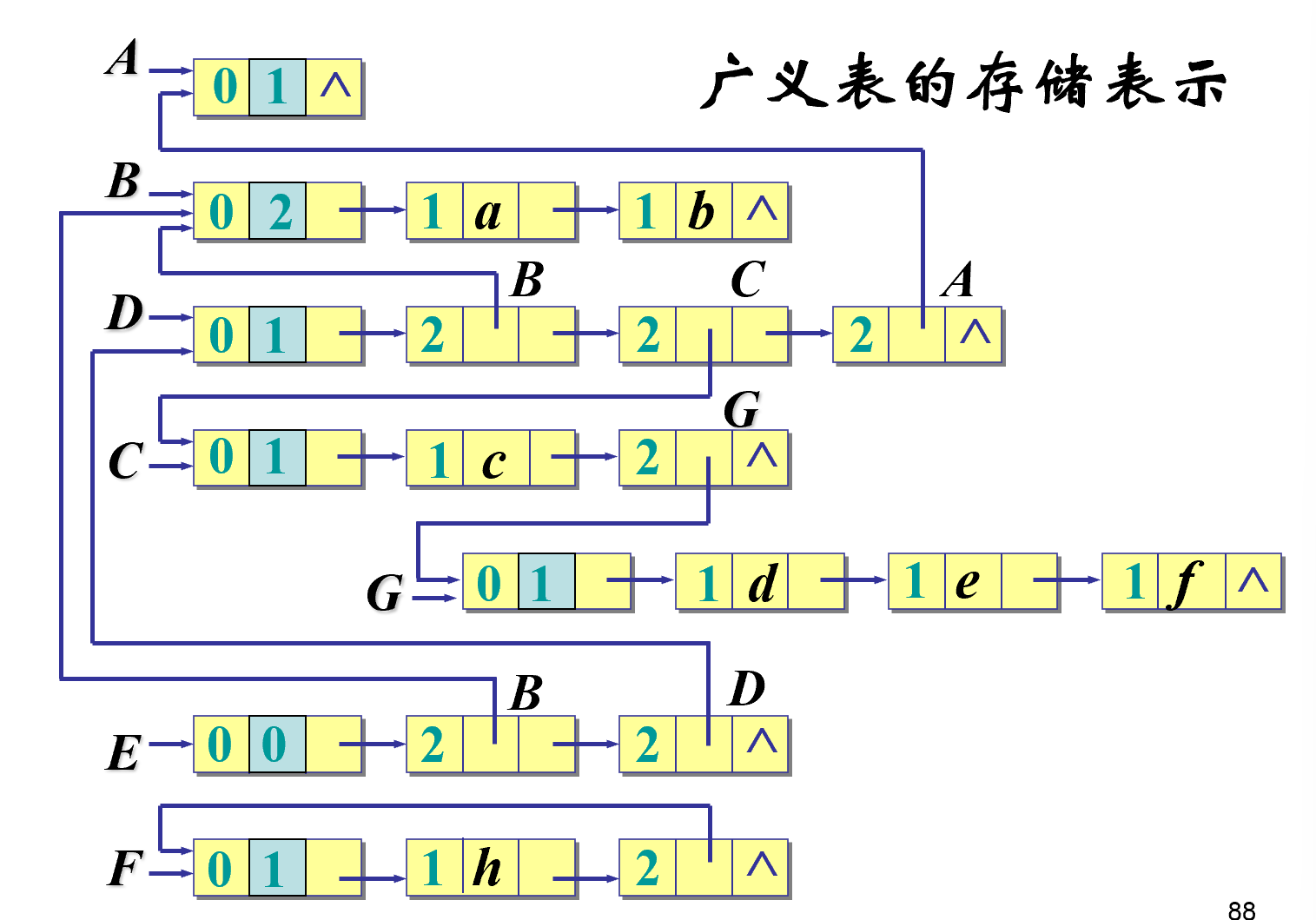
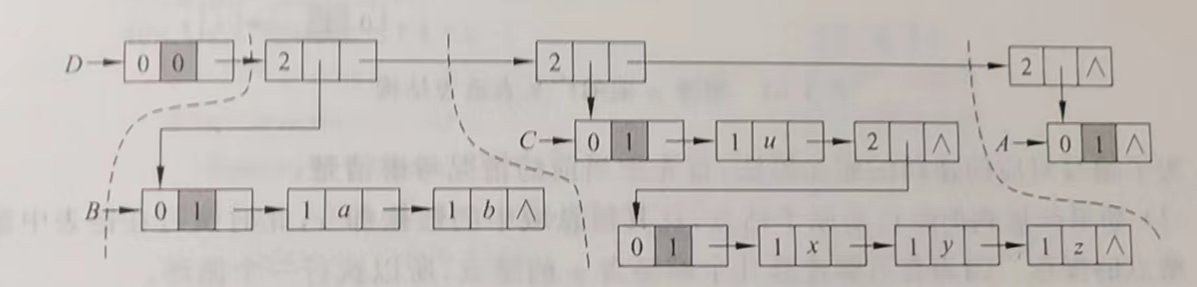
utype | info | tlink- 节点类型 utype:广义表专用的附加头节点 0(并不是广义表的第一个元素表头,而是一个附加的头节点,类似于表的标识符 ABCD(表名));原子数据 1;子表2;
- 信息 info:utype=0 时存储引用计数;等于 1 时存储数据值;等于 2 时存储子表表头指针
- 尾指针 tlink:utype=0 时指向第一个节点;utype!=0 时指向同一层下一个节点
- 存储表示
*广义表的实现¶
-
定义:
template <class T> struct GenListNode { //广义表结点类定义 int utype; //=0 / 1 / 2 GenListNode<T> *tlink; //同层下一结点指针 union { //等价变量 int ref; //存放引用计数 T value; //存放数值 GenListNode<T> *hlink; //存放子表指针 } info; GenListNode() //构造函数 : utype(0), tlink(NULL), info.ref(0) {} GenListNode(GenListNode<T>& R) { //复制构造函数 utype = R.utype; tlink = R.tlink; info = R.info; } }; template <class T> class GenList { //广义表类定义 public: Genlist(); //构造函数 ~GenList(); //析构函数 bool Head (GenListNode<T>& x); //x 返回表头 bool Tail (GenList<T>& lt); //lt 返回表尾 GenListNode<T> *First(); //返回第一个元素地址(尾元素中) GenListNode<T> *Next (GenListNode<T> *elem); //返回表元素elem的直接后继元素 void Copy ( const GenList<T>& R); //广义表的复制 int Length(); //计算广义表长度 int Depth(); private: GenListNode<T> *first; //广义表头指针 GenListNode<T> *Copy (GenListNode<T> *ls); //复制一个ls指示的无共享非递归表 int Length (GenListNode<T> *ls); //求由ls指示的广义表的长度 int Depth (GenListNode<T> *ls); //计算由ls指示的非递归表的深度 bool Equal (GenListNode<T> *s, GenListNode<T> *t); //判以s和t为表头的两个表是否相等 void Remove (GenListNode<T> *ls); //释放以ls为附加头结点的广义表 void CreateList (istream &in, GenListNode<T> *& ls, SeqList<T>& L1, SeqList <GenListNode<T> *>& L2); //从输入流对象输入广义表的字符串描述, //建立一个带头结点的广义表结构 friend istream& operator >> (istream& in, GenList<T>& L); }; template <class T> Genlist<T>::GenList() { //构造函数 GenListNode<T> * first = new GenListNode; if (first == NULL) { cerr << “存储分配失败!\n”; exit(1); } }; template <class T> bool GenList<T>::Head (GenListNode <T>& x) { //若广义表非空,则通过x返回其第一个元素的值 //否则函数没有定义 if (first->tlink == NULL) return false; //空表 else { //非空表 x.utype = first->tlink->utype; x.info = first->tlink->info; return true; //x返回表头的值 } }; template <class T> bool GenList<T>::Tail(GenList<T>& lt) { //若广义表非空,则通过lt返回广义表除表头元素 //以外其他元素组成的表,否则函数没有定义 if (first->tlink == NULL) return false; //空表 else { //非空表 lt.first->utype = 0; //设置头结点 lt.first->info.ref = 0;//相当于又嵌套了一层括号 lt.first->tlink = Copy(first->tlink->tlink); return true; } }; template <class T> GenListNode<T> *GenList<T>::First() { //返回广义表的第一个元素(若表空,则返回一个 //特定的空值NULL) if (first->tlink == NULL) return NULL; //空表 else return first->tlink; //非空表 }; template <class T> GenListNode<T> *GenList<T>::Next(GenListNode<T> *elem) { //返回表元素elem的直接后继元素 if (elem->tlink == NULL) return NULL; else return elem->tlink; }; -
复制
template <class T> //公有函数 void GenList<T>::Copy(const GenList<T>& R) first = Copy(R.first); //调用私有函数 }; template <class T> //私有函数 GenListNode<T>* GenList<T>::Copy(GenListNode <T> *ls) {//复制一个 ls 指示的无共享子表的非递归表 GenListNode<T> *q = NULL; if (ls != NULL) { q = new GenListNode<T>; //处理当前的结点q q->utype = ls->utype; //复制结点类型 switch (ls->utype) { //根据utype传送信息 case 0: q->info.ref = ls->info.ref; break; case 1: q->info.value = ls->info.value; break; case 2: q->info.hlink = Copy(ls->info.hlink); break; } q->tlink = Copy(ls->tlink); //处理同层下一结点 } return q; }; -
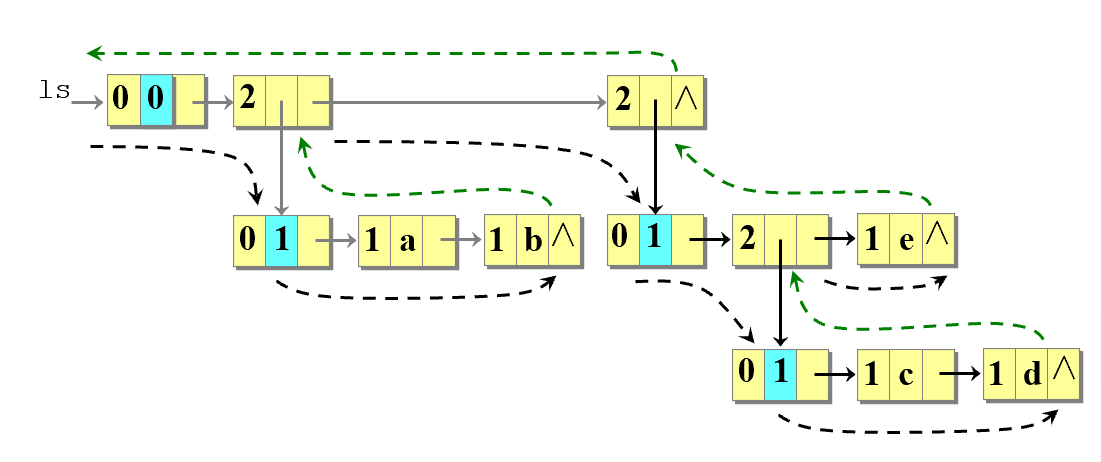
-
长度:
-
求广义表的长度就是求同一层次中 tlink 连接起来的单链表的长度
template<class T> int GenList<T>::Length(){ return Length(first); }; template<class T> int GenList<T>::Length(GenListNode<T>*ls){ if(ls!=NULL)return 1+Length(ls->tlink); else return 0; } -
深度:
-
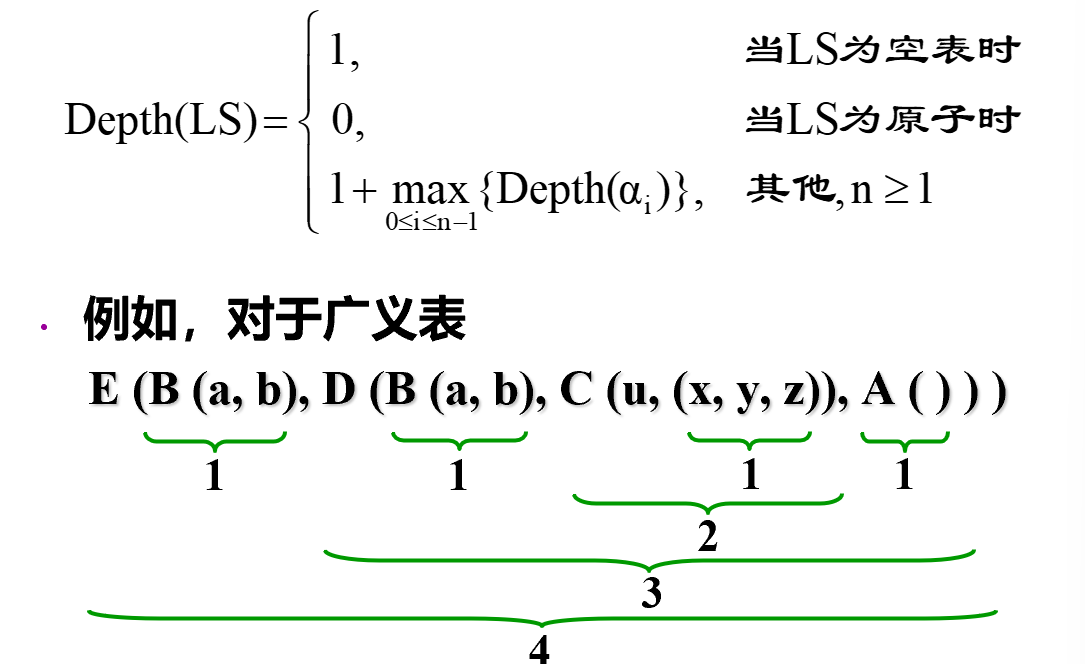
template <class T> int GenList<T>::Depth() { //公有函数 //计算一个非递归表的深度 return Depth(first); }; template <class T> //私有函数 int GenList<T>::Depth(GenListNode<T> *ls) { if (ls->tlink == NULL) return 1; // ls->tlink ==NULL, 空表,深度为1 GenListNode<T> *temp = ls->tlink; int m = 0, n; while (temp != NULL) { //在广义表顶层横扫 if (temp->utype == 2) { //扫描到表结点 n = Depth(temp->info.hlink); //递归计算以子表深度 if (m < n) m = n; //取最大深度 } temp = temp->tlink; } return m+1; //返回深度 }; -
比较相等
template<class T> bool equal(GenList<T>*s,GenListNode<T>*t){ int x; if(s->tlink==NULL&&t->tlink==NULL)return true; if(s->tlink!=NULL&&t->tlink!=NULL&&s->tlink->utype==t->tlink->utype){ if(s->tlink->utype==1){ x=(s->tlink->info.value==t->tlink->info.value)?1:0; } else if(s->tlink->utype==2){ x=equal(s->tlink->info.hlink,t->tlink->info.hlink); } if(x==1)return equals(s->tlink,t->tlink); } return false; } -
删除元素
-
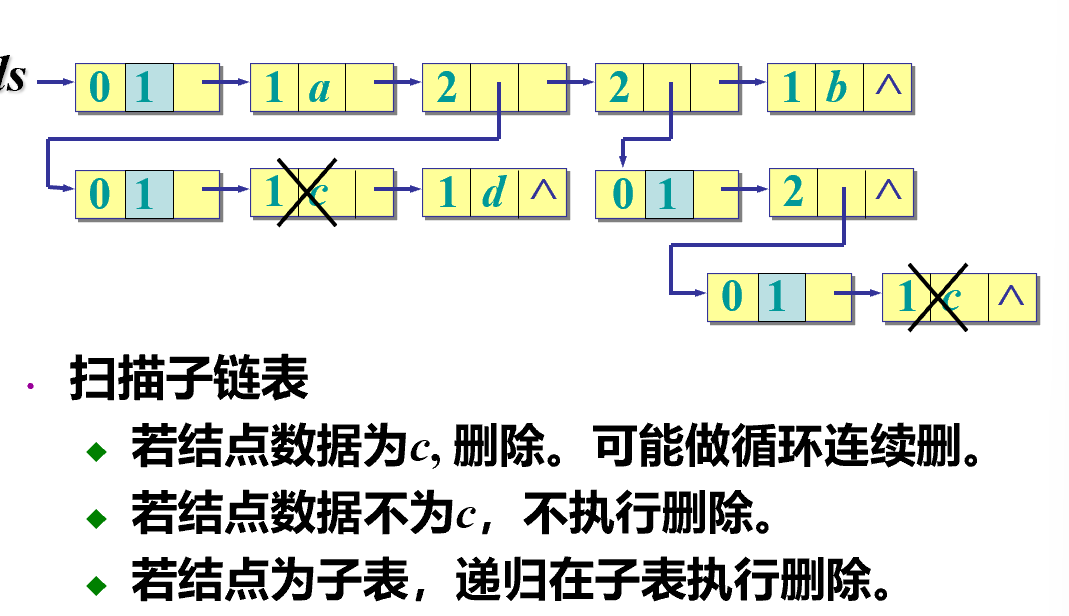
template <class T> void delvalue(GenListNode<T> *ls, T x) { if (ls->tlink != NULL) { //非空表 GenListNode<T> * p = ls->tlink; //第一个结点 while (p != NULL && (p->utype == 1 && p->info.value == x)) { ls->tlink = p->tlink; delete p; p = ls->tlink; //p指向同层下一结点 } if (p != NULL) {//遇到表元素 if (p->utype == 2) delvalue(p->info.hlink, x);//递归在子表中删除 delvalue(p, x); //在该表行中继续删除 } } }; -
对于共享表来说,如果一个表元素有多个地方使用它,贸然删去它会造成其他地方使用出错。因此,当要做删除时,先把该表的头结点中的引用计数 ref 减 1,当引用计数减到 0 时才能执行结点的真正释放。
template <class T> GenList<T>::~GenList() { //广义表的析构函数, 每个头结点都有引用计数 Remove(first); if(first.info.ref<=0) delete first; //first要额外处理 }; template <class T> void GenList<T>::Remove(GenListNode<T> *ls) { //私有函数:释放以ls为表头指针的广义表 ls->info.ref--; //头结点的引用计数减1 if (ls->info.ref <= 0) { //如果减到0 GenListNode<T> *q; while (ls->tlink != NULL) { //横扫表顶层 q = ls->tlink; //到第一个结点 if (q->utype == 2) { //递归删除子表 Remove(q->info.hlink); if (q->info.hlink->info.ref <= 0) delete q->info.hlink; //删子表头结点 } ls->tlink = q->tlink; delete q; } } }; -
由字符串建立广义表
- 字符串描述
S(A ( ‘b’, ‘c’ ), B(‘#’), ‘d’ ); - 检测从输入流对象输入的一个字符,如果遇到表名(用大写字母表示),首先检查这个表名是否已经存在,如果是,说明该表是共享表,只要将相应头结点的引用计数加一即可;如果不是,保存该表名并建立相应广义表。表名后面一定是左括号‘(’,不是则输入错,是则递归建立广义表结构。
- 注意:ABCD 是表的标识符(指向表的外部指针),与表头区分
- 如果遇到用小写字母表示的原子,则建立原子结点;如果遇到右括号‘)’,子表链收尾并退出递归。
- 空表情形括号里应夹入一个非英文字母,如字符'#',不能一个字符也没有。整个广义表描述字符串以';'结束
template<class T> void Genlist<T>::CreateList(istream &in,GenListNode<T>*&ls,SeqList<T>&L1,SeqList<GenListNode<T>*>&L2)//L1存储大写字母的表名,L2存储表名对应子表节点的地址 { T chr; in>>chr; if(isalpha(chr)&&isupper(chr)||chr=='(')//大写字母或( { ls=new GenListNode<T>; ls->utype=2; if(isalpha(chr)&&isupper(chr)){ int n=L1.Length(); int m=L1.Search(chr); if(m!=0){//表已经建立 GenListNode<T>*p=L2.Locate(m); p->ref++; ls->info.hlink=p;//可以直接使用 return; } else{ ls->info.hlink=new GenListNode<T>;//新的外头界点 ls->info.hlink->utype=0; ls->info.hlink->ref=1; L1.insert(n,chr); L2.insert(n,ls->hlink); } in>>chr; if(chr!='(') exit(-1); } CreateList(in,ls->info.hlink->tlink,L1,L2);//继续处理子表 CreateList(in,ls,L1,L2);//子表处理完成,继续处理 } else if(isalpha(chr)&&islower(chr)){ ls=new GenListNode<T>; ls->utype=1; ls->info.value=chr; CreateList(in,ls,L1,L2); } else if(chr==',') CreateList(in,ls->tlink,L1,L2); else if (chr == ')') ls->tlink = NULL; else if (chr == '#') ls = NULL; } template <class T> istream& operator >> (istream& in, GenList<T>& L) { int n; cout << “输入广义表串的字符个数:”<< endl; in >> n; SeqList<T> Ls1(n); SeqList <GenListNode<T> *> Ls2 (n); CreateList (in, L.first, Ls1, Ls2); //建立存储结构 };