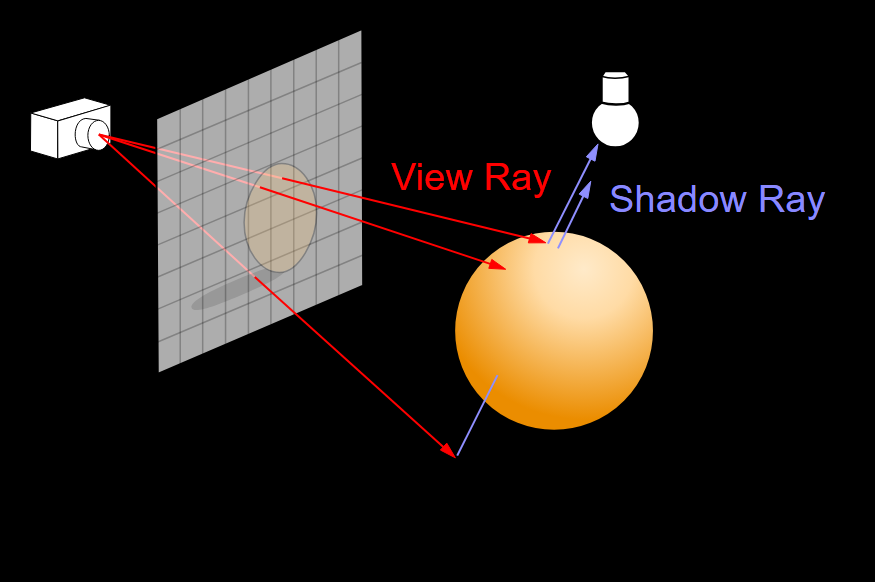
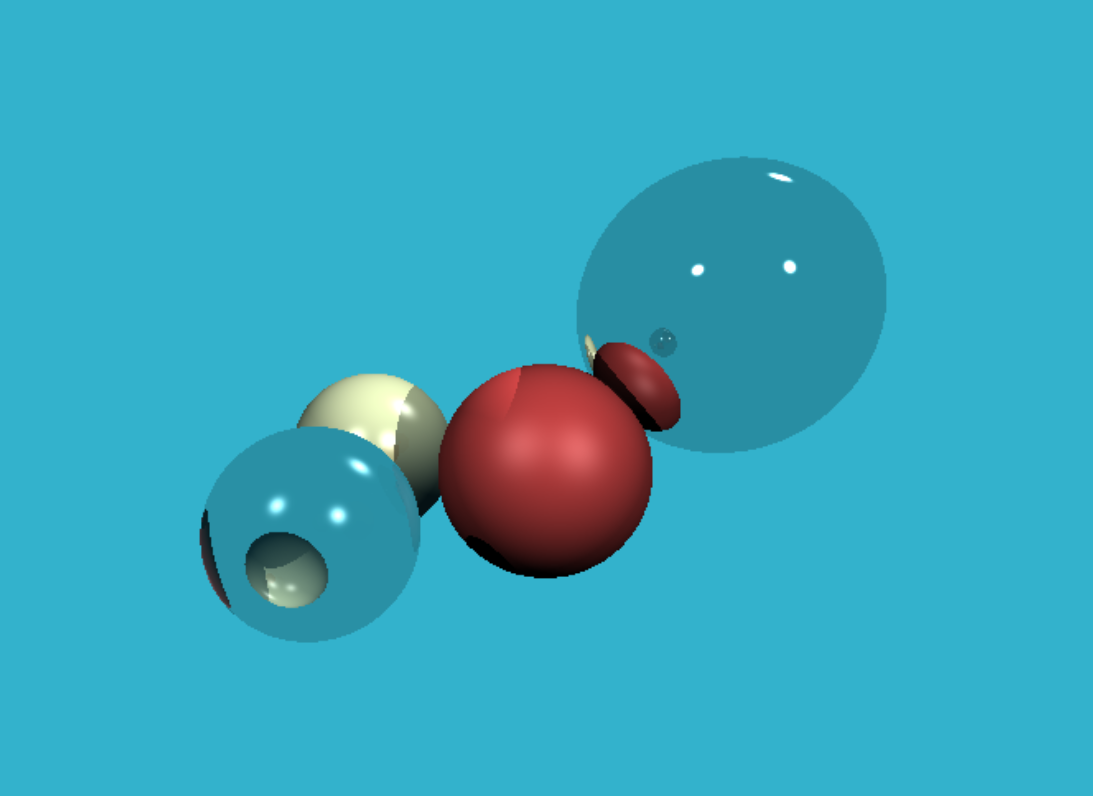
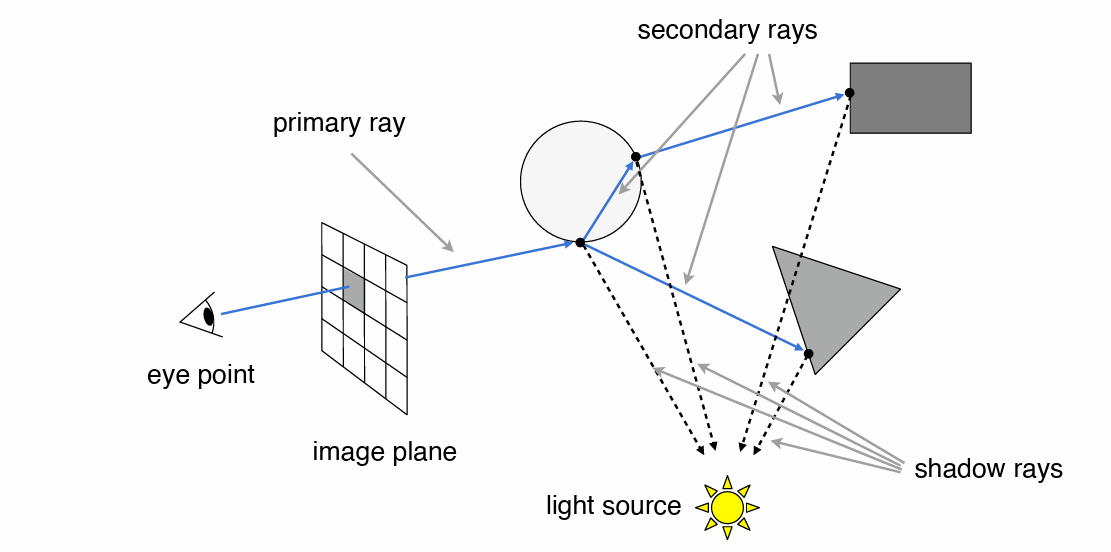
Tinyraytracer
- Whitted 风格光线追踪
基本框架搭建¶
- 球体类型
ray_interset用于判断球与源点为 orig 方向为 dir 的光线是否相交,如果相交距离是多少struct Sphere { Vec3f center; float radius; Sphere(const Vec3f &c, const float &r) : center(c), radius(r) {} /*@param orig: origin of the ray @param dir: direction of the ray @param t0: distance from the origin to the first intersection point*/ bool ray_intersect(const Vec3f &orig, const Vec3f &dir, float &t0) const { Vec3f L = center - orig; float tca = L*dir; float d2 = L*L - tca*tca; if (d2 > radius*radius) return false; float thc = sqrtf(radius*radius - d2); t0 = tca - thc; float t1 = tca + thc; if (t0 < 0) t0 = t1; if (t0 < 0) return false; return true; } };
- 光线追踪的基本形式
- 光线追踪发射光线的基本实现
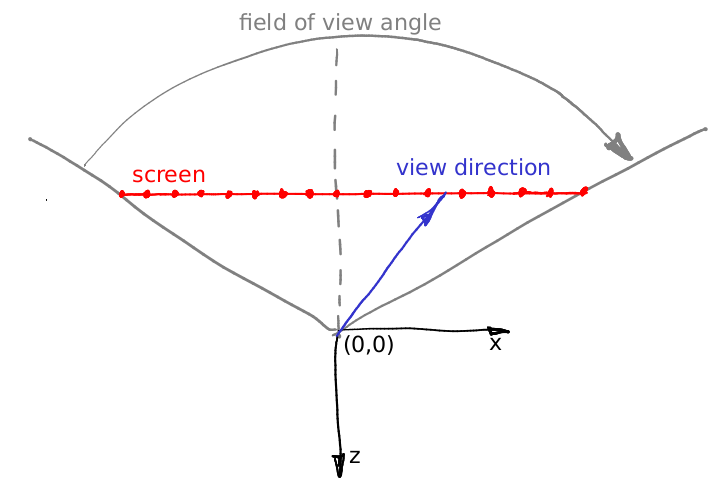
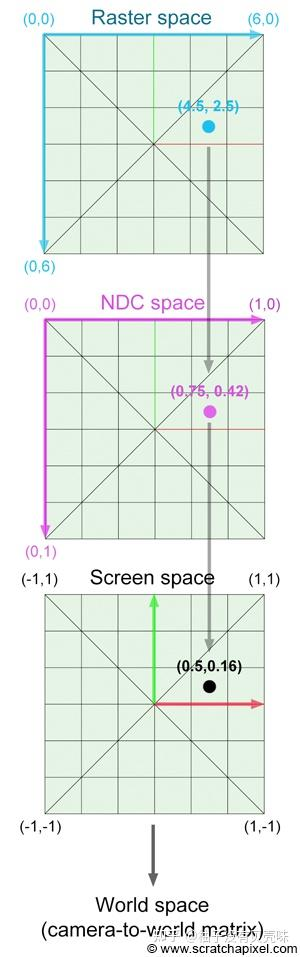
for (int j = 0; j<height; j++) { for (int i = 0; i<width; i++) { float x = (2*(i + 0.5)/(float)width - 1)*tan(fov/2.)*width/(float)height; float y = -(2*(j + 0.5)/(float)height - 1)*tan(fov/2.); Vec3f dir = Vec3f(x, y, -1).normalize(); framebuffer[i+j*width] = cast_ray(Vec3f(0,0,0), dir, sphere); } } - 默认相机位于 (0,0,0)屏幕位于(0,0,-1),向 -z 方向看
-
float x = (2*(i + 0.5)/(float)width - 1)*tan(fov/2.)*width/(float)height;- 先将屏幕空间投影到 (-1,1)上的标准空间,之后根据视角映射到真实坐标(默认这个间距是 1,因此直接乘以 tan(FOV/2))
- 即将像素点映射到了真实的空间坐标
-
检测发出涉嫌是否打到球体,并且可能存在多个球体
bool intersect(const Vec3f &orig, const Vec3f &dir, const std::vector<Sphere> &spheres, Vec3f &hit_p, Vec3f &normal, Material &material) { float spheres_dist = std::numeric_limits<float>::max(); for (size_t i=0; i<spheres.size(); i++) { float dist_i; //击中更近的球体 if (spheres[i].ray_intersect(orig, dir, dist_i) && dist_i < spheres_dist) { spheres_dist = dist_i; hit_p = orig + dir*dist_i; normal = (hit_p - spheres[i].center).normalize(); material = spheres[i].material; } } return spheres_dist<1000; } Vec3f cast_ray(const Vec3f &orig, const Vec3f &dir, const std::vector<Sphere> &spheres) { Vec3f hit_p, normal; Material material; if (!intersect(orig, dir, spheres, hit_p, normal, material)) { return backgroud.color; } return material.color; } - 对一个方向发射线条之后,检测所有球体,寻找最近的碰撞点作为结果,并记录材质,坐标以及法线等信息
灯光与基本反射¶
- 一个简单的思路,将像素点与光源的连线,以及像素点的法线比较,计算光照强度。(类似布林冯里的漫反射强度影响因素之一)
float diffuse_intensity = 0; for(PointLight light: lights) { Vec3f light_dir = (light.position - hit_p).normalize(); diffuse_intensity += light.intensity * std::max(0.f, light_dir*normal); } return material.color*diffuse_intensity; 
- 镜面反射
- 首先为材质添加反射率,镜面指数等不同属性
struct Material { Vec3f color; Vec2f albedo; float specular_exponent; Material(const Vec2f &a, const Vec3f &color, const float &spec) : albedo(a), color(color), specular_exponent(spec) {} Material() : albedo(1,0), color(), specular_exponent() {} };
- 首先为材质添加反射率,镜面指数等不同属性
- 除了漫反射带来的亮度外添加镜面反射的亮度(phong 模型那样)
Vec3f reflect(const Vec3f &I, const Vec3f &N) { return I - N*2.f*(I*N); } Vec3f cast_ray(const Vec3f &orig, const Vec3f &dir) { Vec3f hit_p, normal; Material material; if (!intersect(orig, dir, hit_p, normal, material)) { return backgroud.color; } float diffuse_intensity = 0, specular_intensity = 0; for(PointLight light: lights) { Vec3f light_dir = (light.position - hit_p).normalize(); diffuse_intensity += light.intensity * std::max(0.f, light_dir*normal); specular_intensity += powf(std::max(0.f, -reflect(-light_dir, normal)*dir), material.specular_exponent)*light.intensity; } return material.color*diffuse_intensity*material.albedo[0] + Vec3f(1., 1., 1.)*specular_intensity*material.albedo[1]; }
阴影¶
- 额外进行一次判断,判断点到光源的连线上是否被其他物体
遮挡
Vec3f shadow_orig = hit_p + light_dir*1e-3; Vec3f shadow_p, shadow_n; Material tmpmaterial; if (intersect(shadow_orig, light_dir, shadow_p, shadow_n, tmpmaterial) && (shadow_p-shadow_orig).norm() < dis) { continue; }
多次反射¶
- 递归调用 cast_ray
if (depth>max_depth||!intersect(orig, dir, hit_p, normal, material)) { return backgroud.color; } float diffuse_intensity = 0, specular_intensity = 0; Vec3f reflect_dir = reflect(dir, normal).normalize(); Vec3f reflect_orig = reflect_dir*normal < 0 ? hit_p - normal*1e-3 : hit_p + normal*1e-3; Vec3f reflect_color = cast_ray(reflect_orig, reflect_dir, depth+1);
折射¶
- 斯涅耳定律计算折射出射角度
Vec3f refract(const Vec3f &I, const Vec3f &N, const float &refractive_index) { float cosi = - std::max(-1.f, std::min(1.f, I*N)); //假定光线从空气(折射率为1)进入另一种介质 float etai = 1, etat = refractive_index; Vec3f n = N; if (cosi < 0) {//从介质进入空气 cosi = -cosi; std::swap(etai, etat); n = -N; } float eta = etai/etat; float k = 1 - eta*eta*(1 - cosi*cosi);//是否全反射 return k<0 ? Vec3f(0, 0, 0) : I*eta + n*(eta*cosi - sqrtf(k)); } - 完整的 cast_ray:漫反射+镜面反射+多次反射(递归)+折射
// 定义一个光线投射函数,用于计算从原点 orig 沿方向 dir 发出的光线的颜色。 // 参数 depth 用于限制递归的深度,避免无限递归。 Vec3f cast_ray(const Vec3f &orig, const Vec3f &dir, int depth=0) { Vec3f hit_p, normal; // 定义交点位置和交点处的法线向量 Material material; // 定义在交点处的材质信息 // 如果递归层级超过最大深度或者光线与场景中的物体不相交,则返回背景色 if (depth > max_depth || !intersect(orig, dir, hit_p, normal, material)) { return backgroud.color; } // 初始化漫反射和镜面反射强度 float diffuse_intensity = 0, specular_intensity = 0; // 计算反射光方向,并对反射方向进行归一化处理 Vec3f reflect_dir = reflect(dir, normal).normalize(); // 根据反射方向和法线确定反射光的起始位置,避免精度问题导致的自我交叉 Vec3f reflect_orig = reflect_dir * normal < 0 ? hit_p - normal * 1e-3 : hit_p + normal * 1e-3; // 递归计算反射光颜色 Vec3f reflect_color = cast_ray(reflect_orig, reflect_dir, depth + 1); // 计算折射光方向,并对折射方向进行归一化处理 Vec3f refract_dir = refract(dir, normal, material.refractive_index).normalize(); // 根据折射方向和法线确定折射光的起始位置 Vec3f refract_orig = refract_dir * normal < 0 ? hit_p - normal * 1e-3 : hit_p + normal * 1e-3; // 递归计算折射光颜色 Vec3f refract_color = cast_ray(refract_orig, refract_dir, depth + 1); // 遍历所有光源进行照明计算 for (PointLight light : lights) { // 计算光源到交点的距离和方向,并对方向进行归一化 float dis = (light.position - hit_p).norm(); Vec3f light_dir = (light.position - hit_p).normalize(); // 计算阴影的起始位置,避免交点自身遮挡(自阴影问题) Vec3f shadow_orig = hit_p + light_dir * 1e-3; Vec3f shadow_p, shadow_n; Material tmpmaterial; // 检查从交点到光源的路径是否被其他物体遮挡 if (intersect(shadow_orig, light_dir, shadow_p, shadow_n, tmpmaterial) && (shadow_p - shadow_orig).norm() < dis) { continue; // 如果被遮挡,则跳过当前光源的计算 } // 计算漫反射光强度 diffuse_intensity += light.intensity * std::max(0.f, light_dir * normal); } // 根据材质属性和计算出的光照强度,计算最终颜色 return material.color * diffuse_intensity * material.albedo[0] + Vec3f(1., 1., 1.) * specular_intensity * material.albedo[1] + reflect_color * material.albedo[2] + refract_color * material.albedo[3]; }