SQL基本语法
概述¶
- 数据库:存储数据的仓库
- 数据库管理系统:操纵和管理数据库的大型软件(如 MySql)
-
SQL:操作关系型数据库的编程语言,定义操作的统一标准
-
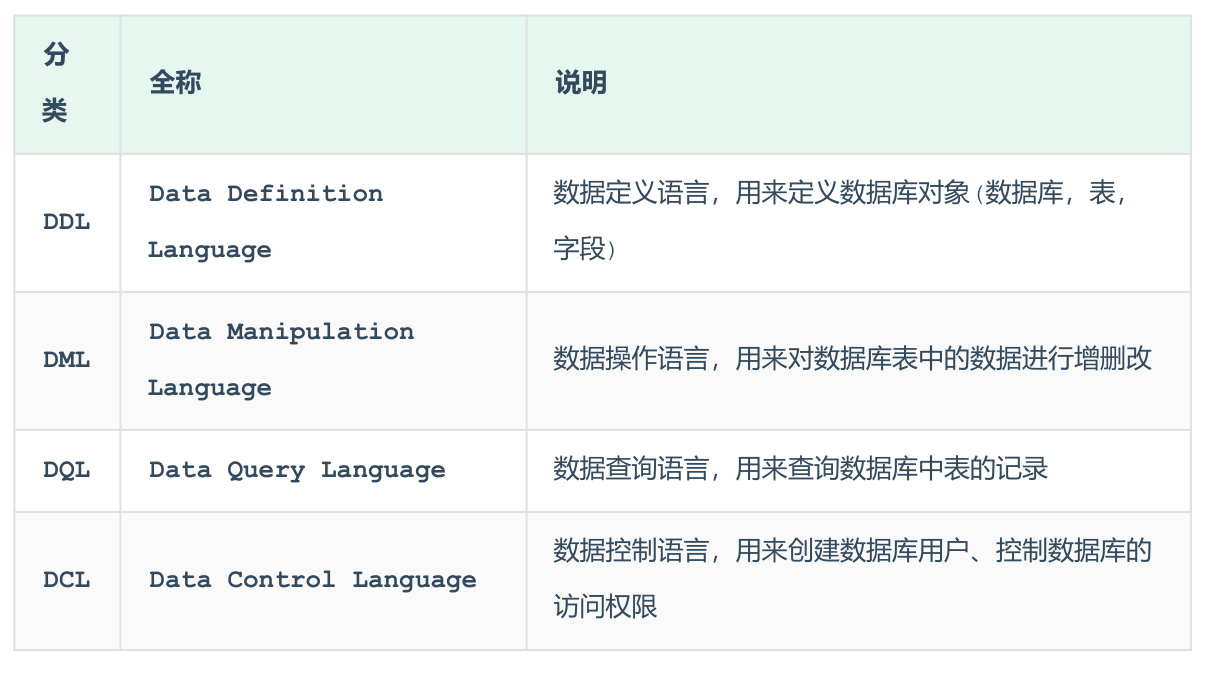
分类
基本语法¶
-
SQL 语句可以换行,使用分号作为结尾,不区分大小下,一般关键词使用大写
-
注释
- 单行注释:-- 注释内容或 # 注释内容
- 多行注释:/* 注释内容 */
DDL¶
数据库操作¶
- 查询现有数据库
show databases ; - 创建数据库
create database [ if not exists ] 数据库名 [ default charset 字符集 ] [ collate 排序规则 ] ; - 切换数据库
use 数据库名- 在操作数据库中的表之前需要先切换到改数据库下
- 删除数据库
drop database [ if exists ] 数据库名 ;
表操作¶
- 查询当前数据库所有的表
show tables; - 查看指定表的结构
desc 表名 ; -
查看指定表的建表语句
show create table 表名 ; -
建表
CREATE TABLE 表名( 字段1 字段1类型 [ comment 字段1注释 ], 字段2 字段2类型 [comment 字段2注释 ], 字段3 字段3类型 [comment 字段3注释 ], ...... 字段n 字段n类型 [comment 字段n注释 ] ) [ comment 表注释 ] ; create table tb_user( id int comment '编号', name varchar(50) comment '姓名', age int comment '年龄', gender varchar(1) comment '性别' ) comment '用户表' -
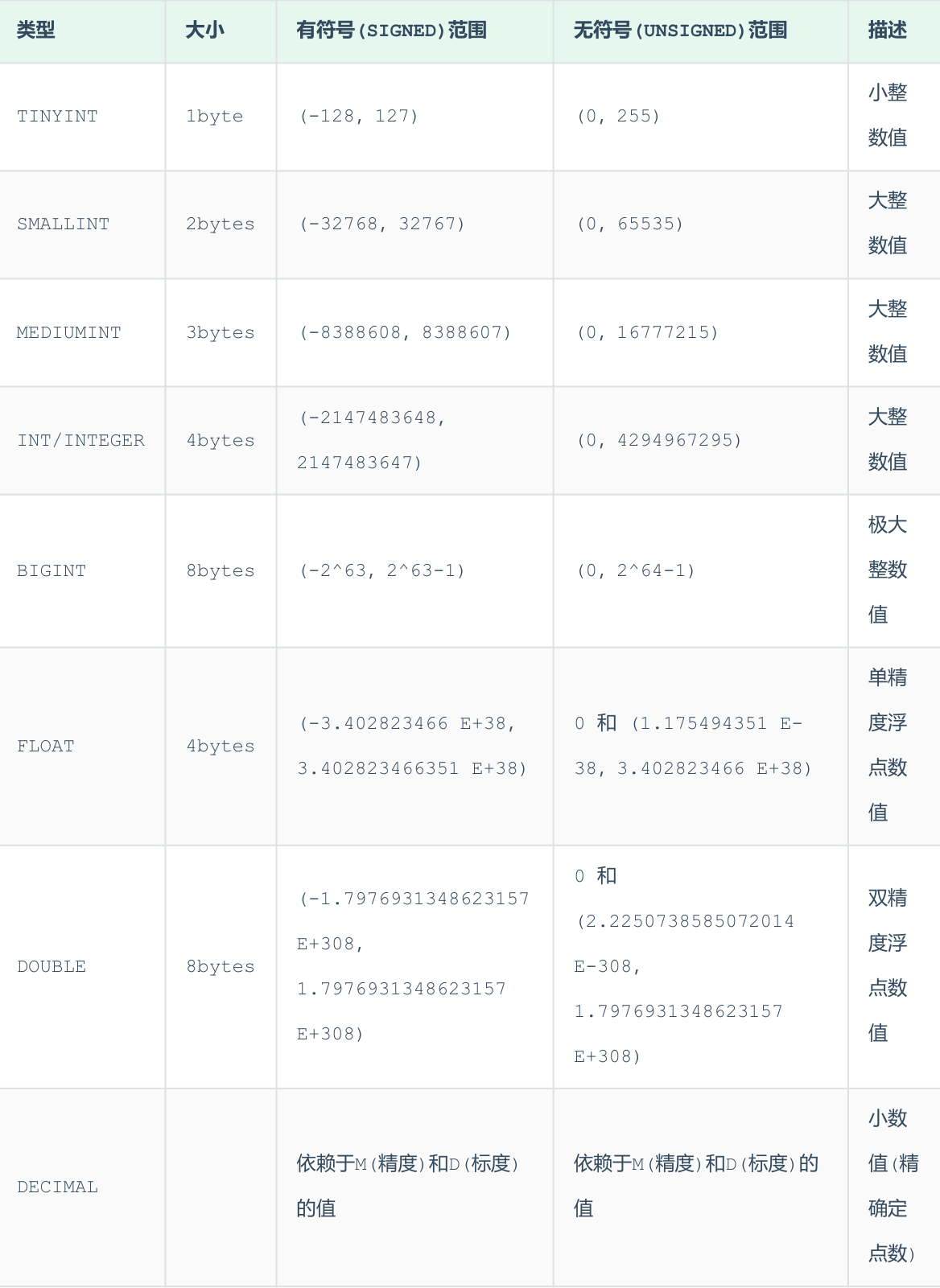
数据类型
-
- 还具有一些附加参数
- 声明为无符号
age tinyint unsigned - 声明(总最大位数,小数部分位数)
score double(4,1)
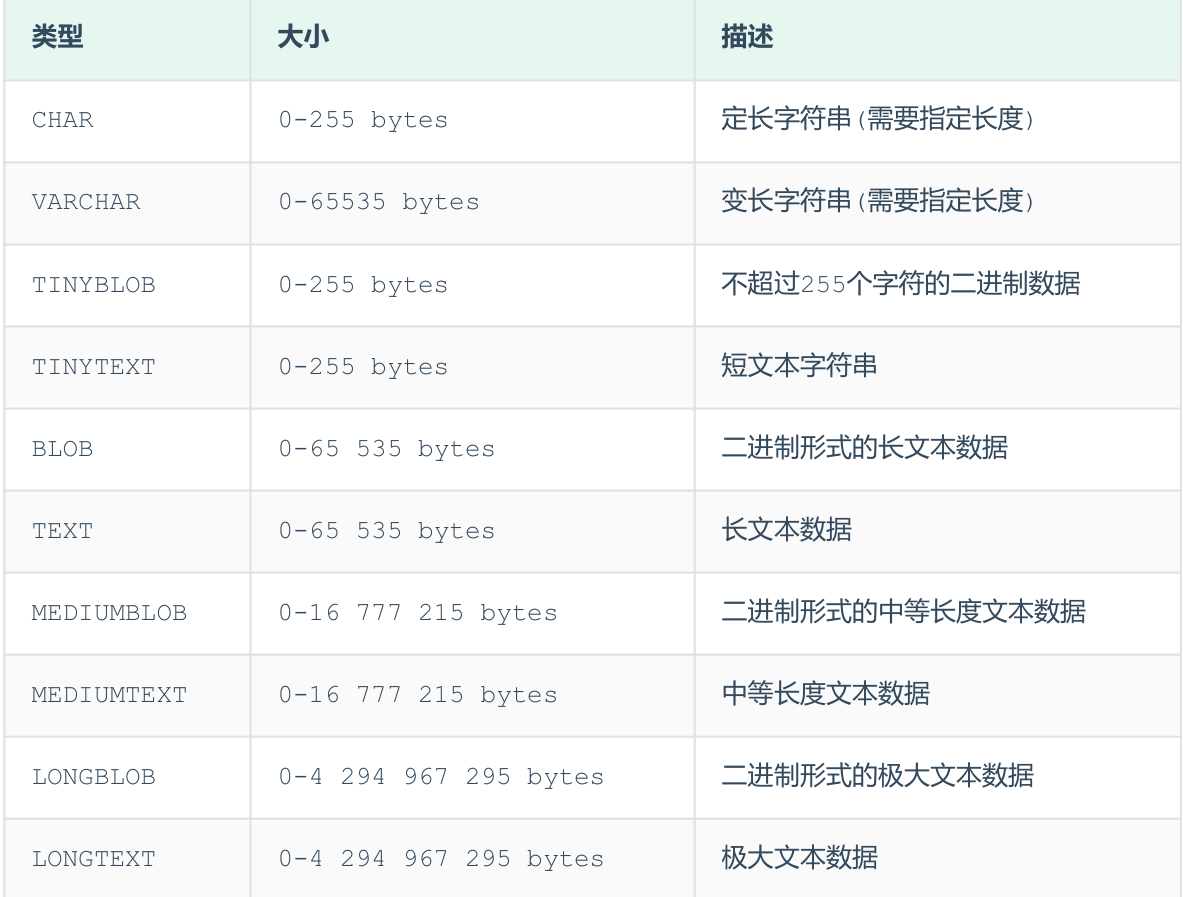
- char是定长字符串,指定长度多长,就占用多少个字符,和字段值的长度无关 。而varchar是变长字符串,指定的长度为最大占用长度
-
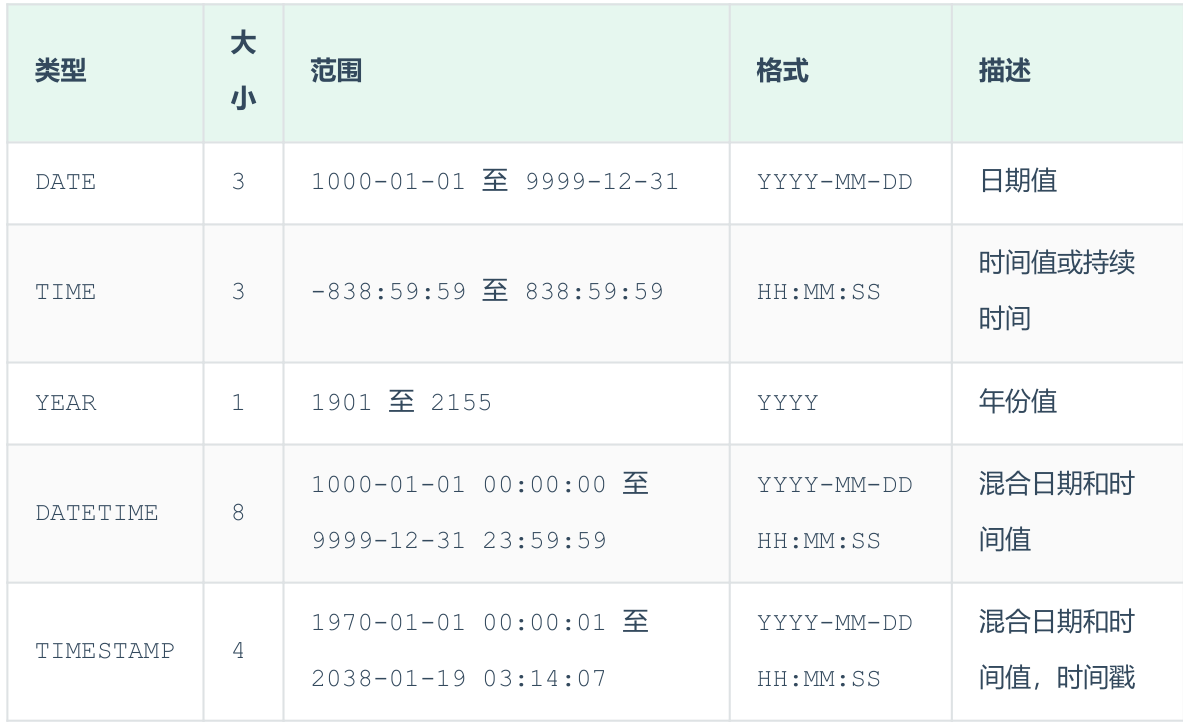
-
修改
- 添加字段
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD 字段名 类型 (长度) [ COMMENT 注释 ] [ 约束 ];ALTER TABLE employee ADD weight INT(4) DEFAULT 120 AFTER age;ALTER TABLE employee ADD test INT(10) DEFAULT 11 FIRST;- 通过约束指定新增列的放置位置
- 修改数据类型
ALTER TABLE 表名 MODIFY 字段名 新数据类型 (长度); -
修改字段名和字段类型
ALTER TABLE 表名 CHANGE 旧字段名 新字段名 类型 (长度) [ COMMENT 注释 ] [ 约束 ]; -
删除
ALTER TABLE 表名 DROP 字段名; -
修改表名
ALTER TABLE 表名 RENAME TO 新表名; -
修改表
DROP TABLE [ IF EXISTS ] 表名;
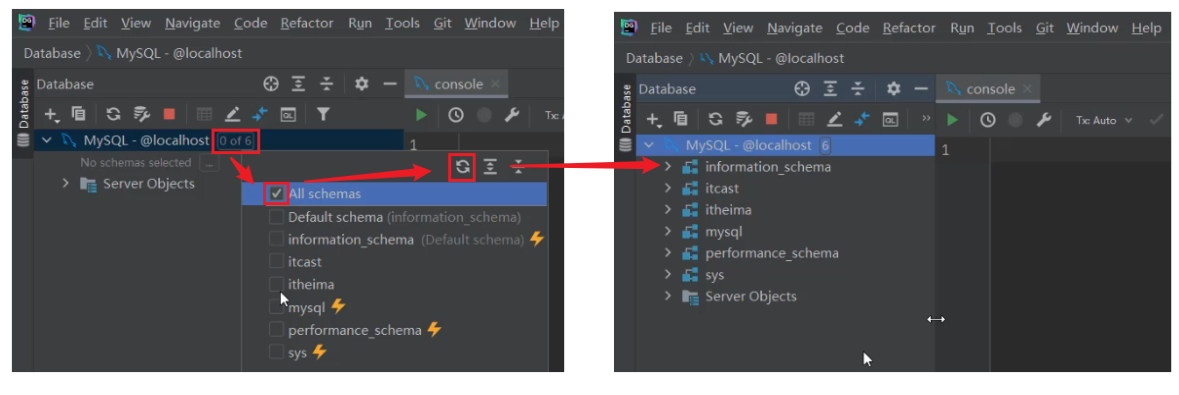
图形界面操作(DataGrip)¶
- 展示所有数据库
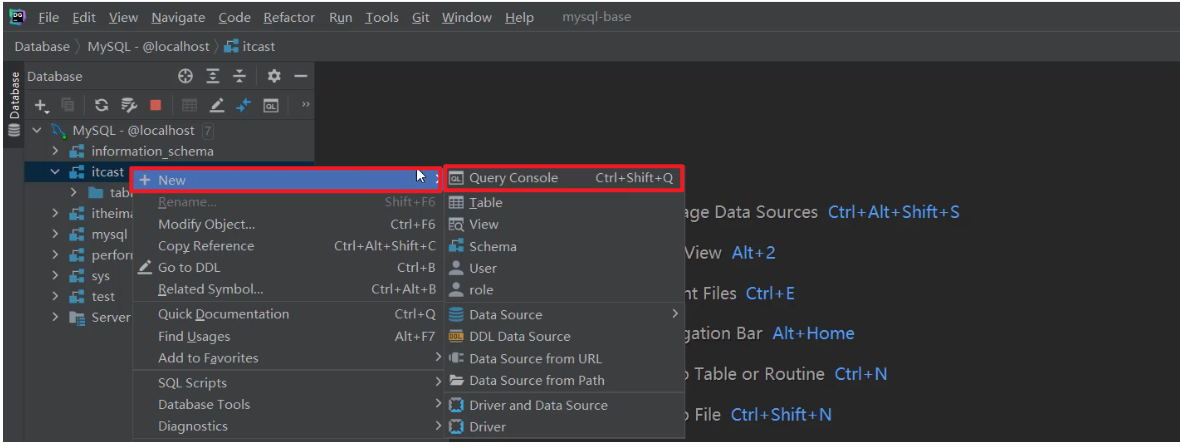
- 在DataGrip中执行SQL语句
DML¶
- 给指定字段添加数据
INSERT INTO 表名 (字段名1, 字段名2, ...) VALUES (值1, 值2, ...); - 为全部字段添加
INSERT INTO 表名 VALUES (值1, 值2, ...); - 支持批量添加
INSERT INTO 表名 (字段名1, 字段名2, ...) VALUES (值1, 值2, ...), (值1, 值2, ...), (值1, 值2, ...) ; - 修改数据
UPDATE 表名 SET 字段名1 = 值1 , 字段名2 = 值2 , .... [ WHERE 条件 ] ; update employee set name = '小昭' , gender = '女' where id = 1;- 省略条件时对整张表进行操作
- 删除数据
DELETE FROM 表名 [ WHERE 条件 ] ; delete from employee where gender = '女';- 删除的是整条记录
- 特殊:连接删除
DELETE p1 FROM Person p1, Person p2 WHERE p1.Email = p2.Email AND p1.Id > p2.Id - DELETE p1 表示对 p1 表进行删除,具体删除哪些条目由 where 决定
- 删除重复的电子邮箱
DQL¶
- 基本查询(不带任何条件)
SELECT 字段1, 字段2, 字段3 ... FROM 表名 ;- * 号代表查询所有字段
- 为字段设置别名
SELECT 字段1 [ 别名1 ] , 字段2 [ 别名2 ] ... FROM 表名; - 过滤重复结果
SELECT DISTINCT 字段 FROM 表名;
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] <目标列表达式>[,<目标列表达式>]…
FROM <表名或视图名>[,<表名或视图名>]…
[WHERE <条件表达式>]
[GROUP BY <列名> [HAVING <条件表达式>]]
[ORDER BY <列名> [ASC|DESC]…]
SELECT * FROM Student
WHERE Id>10
GROUP BY Age HAVING AVG(Age) > 20
ORDER BY Id DESC
- 条件查询(WHERE)
SELECT 字段列表 FROM 表名 WHERE 条件列表 ;- 逻辑运算 (多个条件):AND、OR、NOT
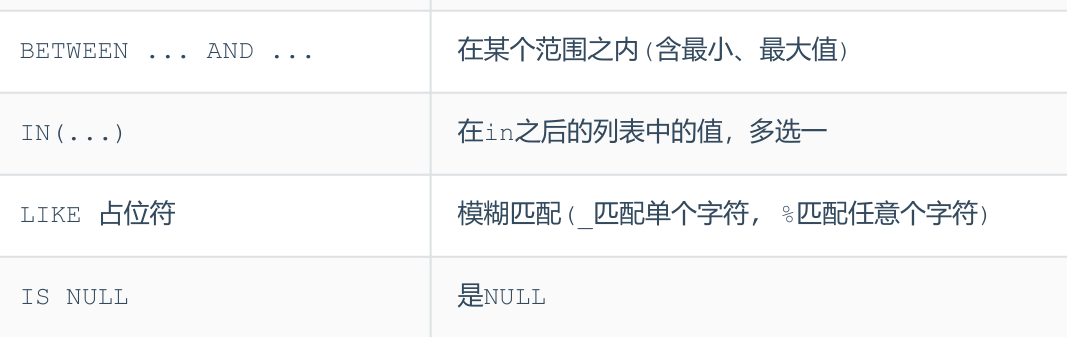
- LIKE 子句通过通配符来将一个值同其他相似的值作比较,百分号代表零个、一个或者多个字符。下划线则代表单个数字或者字符。两个符号可以一起使用。
SELECT FROM table_name WHERE column LIKE '%XXXX%' ELECT FROM table_name WHERE column LIKE 'XXXX_' select * from emp where idcard is null; select * from emp where age = 18 or age = 20 or age =40; select * from emp where age in(18,20,40); select * from emp where idcard like '%X'; -
注意:MySQL 使用三值逻辑 —— TRUE, FALSE 和 UNKNOWN。因此对于 x!=y 如果其中有为 null 的则不会返回 true。需要对 null 单独处理
SELECT name FROM customer WHERE referee_id <> 2 OR referee_id IS NULL;而不应该使用= null -
聚合函数(count、max、min、avg、sum)
- 将一列数据作为一个整体,进行纵向计算 。
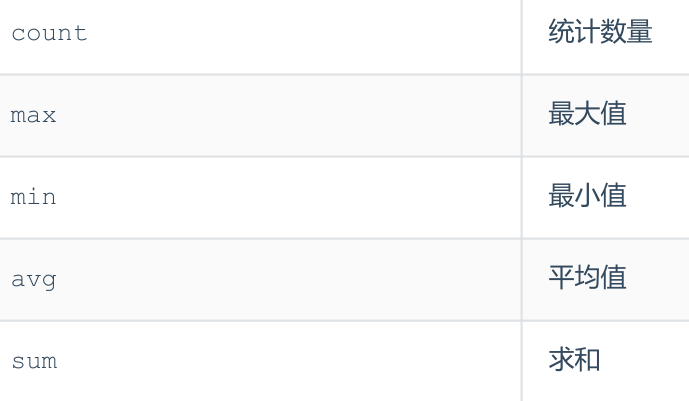
SELECT 聚合函数(字段列表) FROM 表名 ;- 例:统计西安地区员工的年龄之和
select sum(age) from emp where workaddress = '西安'; - 统计记录的总数目
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employee_tbl ; - 分组查询(group by)
-
SELECT 字段列表 FROM 表名 [ WHERE 条件 ] GROUP BY 分组字段名 [ HAVING 分组后过滤条件 ];SELECT ID, NAME, AGE, ADDRESS, SALARY FROM CUSTOMERS GROUP BY age HAVING COUNT(age) >= 2; -
执行顺序:where > 聚合函数 > having
-
可以根据多维条分组,用
,分隔select workaddress, gender, count(*) '数量' from emp group by gender , workaddress;
-
排序查询(order by)
SELECT 字段列表 FROM 表名 ORDER BY 字段1 排序方式1 , 字段2 排序方式2 ;- ASC : 升序(默认值);DESC: 降序
-
例子:查询所有年龄小于等于35岁员工的姓名和年龄,并对查询结果按年龄升序排序,如果年龄相同按入职时间降序排序。
select name , age from emp where age <= 35 order by age asc , entrydate desc;
-
分页查询(limit)
ELECT 字段列表 FROM 表名 LIMIT 起始索引, 每页查询记录数 ;-
起始索引从0开始
- 如果查询的是第一页数据,起始索引可以省略
-
例子:查询性别为男,且年龄在20-40 岁(含)以内的前5个员工信息,对查询的结果按年龄升序排序,年龄相同按入职时间升序排序。
select * from emp where gender = '男' and age between 20 and 40 order by age asc ,entrydate asc limit 5 ;select * from emp where gender = '男' and ( age between 20 and 40 ) and name like '___';
-
执行顺序
-
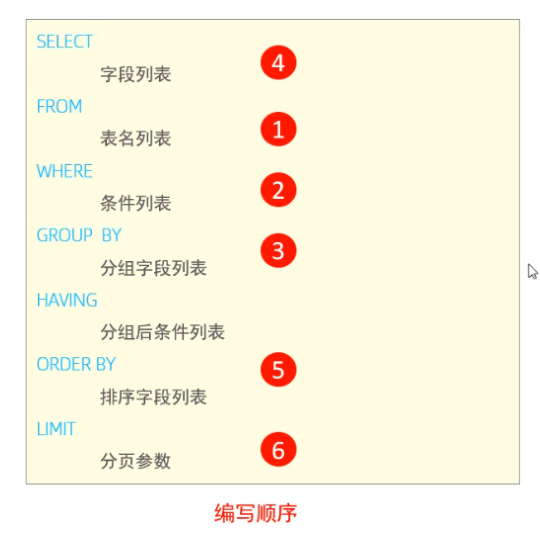
-
DISTINCT
-
同 SELECT 语句一起使用,可以去除所有重复记录,只返回唯一项。
-
SELECT DISTINCT... -
UNION
- 将两个或者更多的 SELECT 语句的运算结果组合起来。
SELECT Txn_Date FROM Store_Information
UNION
SELECT Txn_Date FROM Internet_Sales;
- INTERSECT
-
用于组合两个 SELECT 语句,但是只返回两个 SELECT 语句的结果中都有的行。
-
EXCEPT 子句
-
组合两个 SELECT 语句,并将第一个 SELECT 语句的结果中存在,但是第二个 SELECT 语句的结果中不存在的行返回。
-
索引
- 在使用 SELECT 语句查询的时候,语句中 WHERE 里面的条件,会自动判断有没有可用的索引。使用索引可以实现对查询的加速。
-
创建索引
CREATE [UNIQUE] [CLUSTER] INDEX <索引名> ON <表名>(<列名>[<次序>][,<列名>[<次序>]]…);-- 建立学生表索引:单一字段Id索引倒序 CREATE UNIQUE INDEX INDEX_SId ON Student (Id DESC); -- 建立学生表索引:多个字段Id、Name索引倒序 CREATE UNIQUE INDEX INDEX_SId_SName ON Student (Id DESC,Name DESC); -- 另一种语法 ALTER TABLE employee ADD INDEX idx_id (id); -
删除索引
-- 删除学生表索引 INDEX_SId DROP INDEX INDEX_SId; -
视图:一种虚拟的表,以预定义的 SQL 查询的形式存在的数据表的成分
- 以用户或者某些类型的用户感觉自然或者直观的方式来组织数据;
- 限制对数据的访问,从而使得用户仅能够看到或者修改(某些情况下)他们需要的数据
- 它不包含数据,只是保存了一个SQL查询的结果。因为视图是基于底层的真实表创建的,所以当真实表的数据发生变化时,视图也会相应地呈现出最新的数据。
CREATE VIEW view_name AS SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name WHERE condition; CREATE VIEW v_emp (v_name,v_age,v_phone) AS SELECT name,age,phone FROM employee;
DCL¶
管理用户¶
- 查询用户列表
select * from mysql.user; - 创建用户
CREATE USER '用户名'@'主机名' IDENTIFIED BY '密码';- 通过主机限制用户只能通过特定的主句访问数据库,使用
%表示允许从任意的主机进行访问 create user 'itcast'@'localhost' identified by '123456';
- 通过主机限制用户只能通过特定的主句访问数据库,使用
- 修改用户密码
ALTER USER '用户名'@'主机名' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY '新密码' ; - 删除用户
DROP USER '用户名'@'主机名' ;
权限控制¶
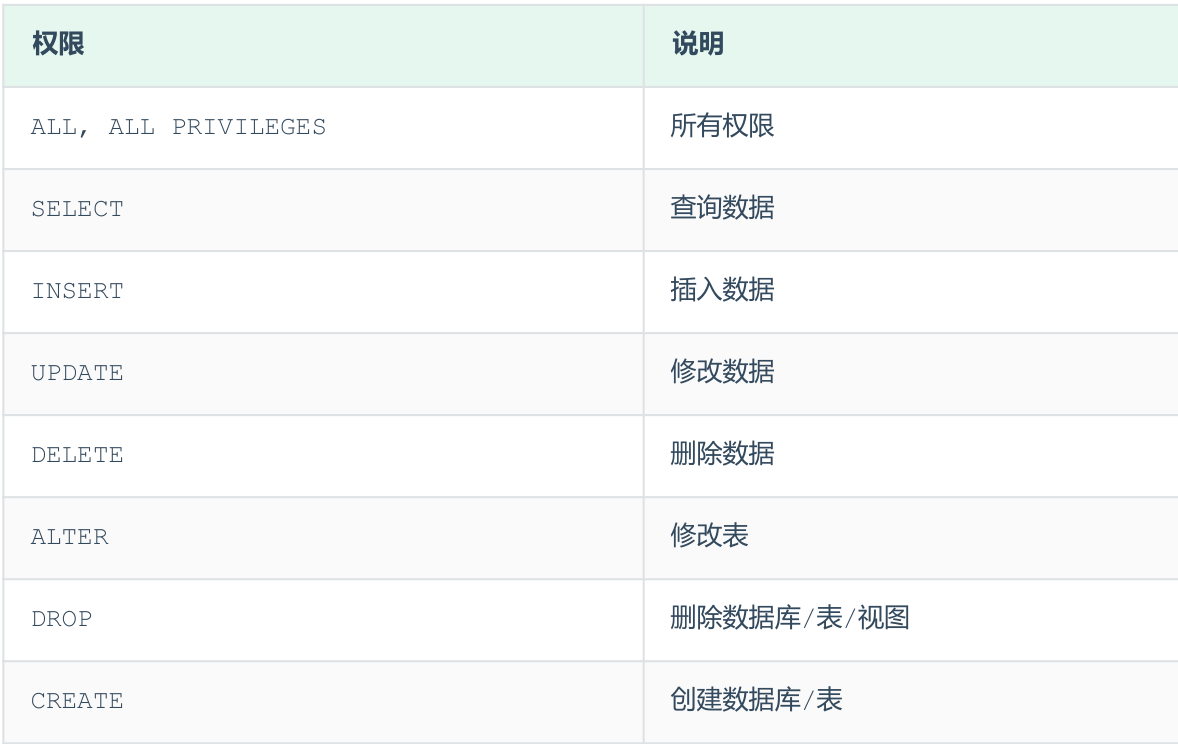
- 查询权限
SHOW GRANTS FOR '用户名'@'主机名' ; - 授予权限
GRANT 权限列表 ON 数据库名.表名 TO '用户名'@'主机名'; - 撤销权限
REVOKE 权限列表 ON 数据库名.表名 FROM '用户名'@'主机名' - 多个权限之间,使用逗号分隔
- 授权时, 数据库名和表名可以使用 * 进行通配,代表所有。
补充¶
函数¶
字符串函数¶
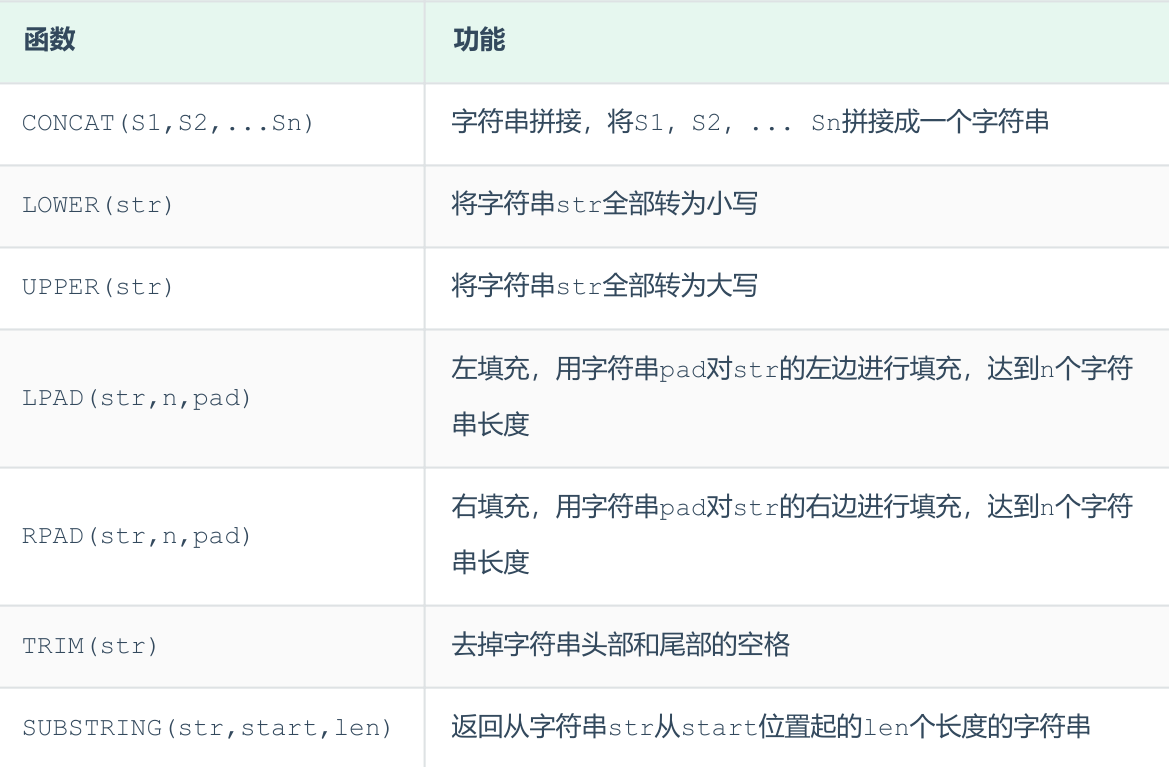
- select 可以用于在不涉及具体表的时候调用函数
select concat('Hello' , ' MySQL'); - 在特定字段前补 0
update emp set workno = lpad(workno, 5, '0');
数值函数¶
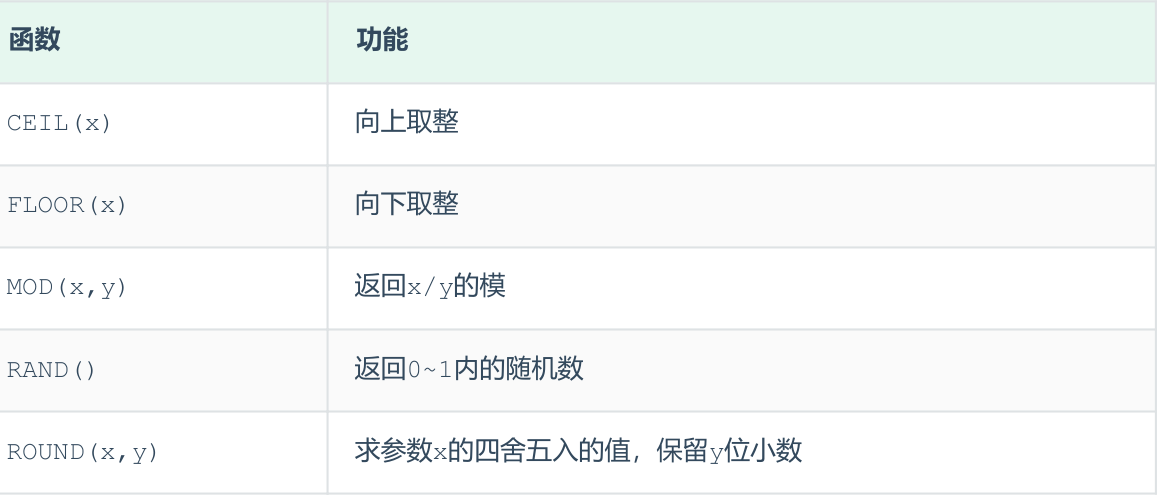
select lpad(round(rand()*1000000 , 0), 6, '0');
日期函数¶
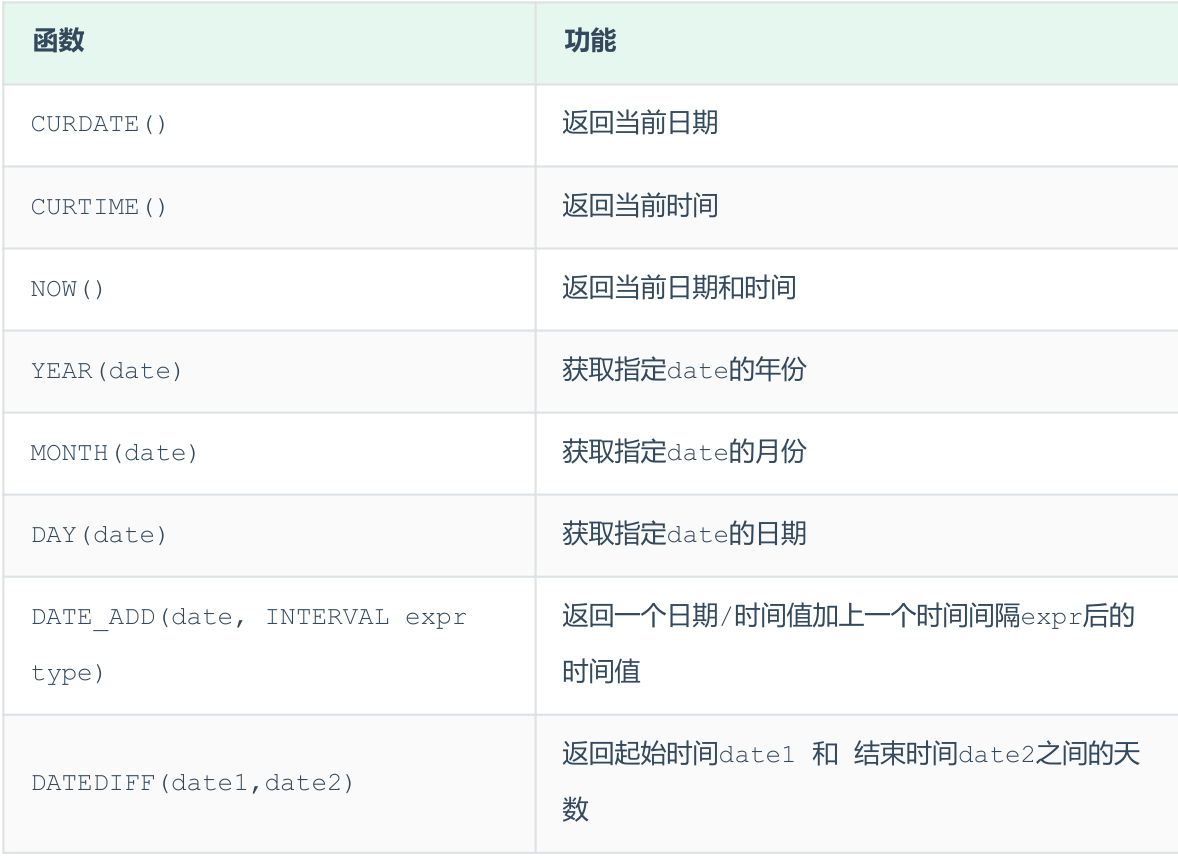
-
select curdate(); -
查询所有员工的入职天数,并根据入职天数倒序排序。
select name, datediff(curdate(), entrydate) as 'entrydays' from emp order by entrydays desc;
流程函数¶
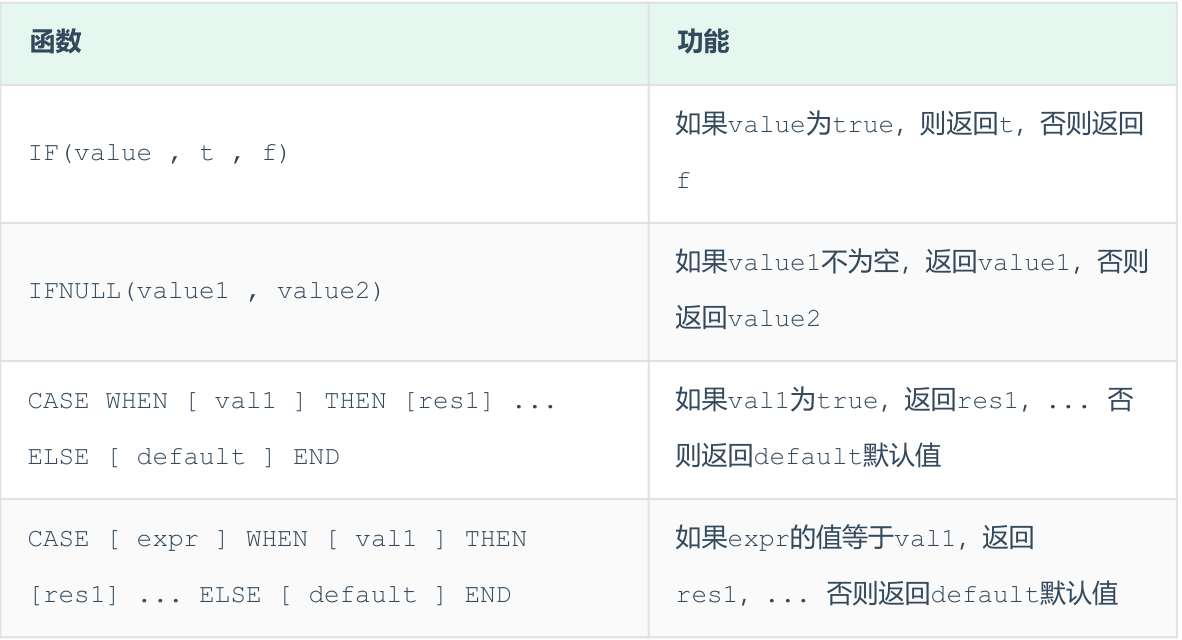
select if(false, 'Ok', 'Error');
select
id,
name,
(case when math >= 85 then '优秀' when math >=60 then '及格' else '不及格' end )'数学',
(case when english >= 85 then '优秀' when english >=60 then '及格' else '不及格'end ) '英语',
(case when chinese >= 85 then '优秀' when chinese >=60 then '及格' else '不及格'end ) '语文'
from score;
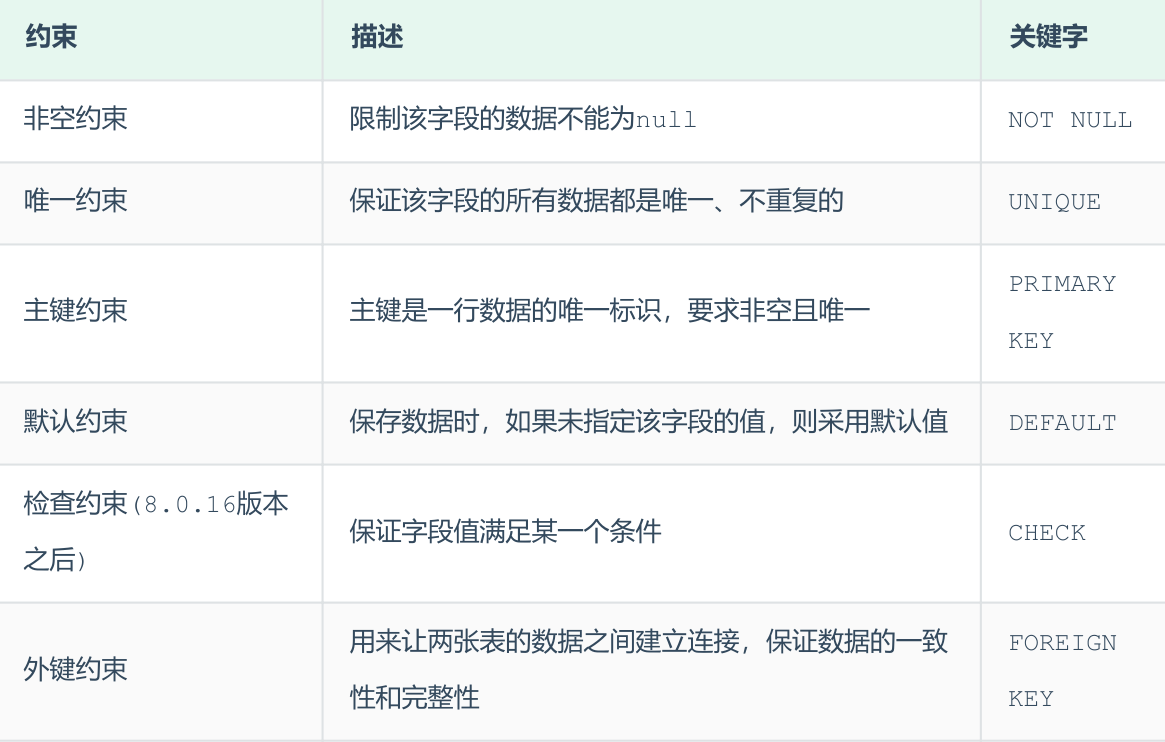
约束¶
-
作用于表中字段上的规则,用于限制存储在表中的数据。
-
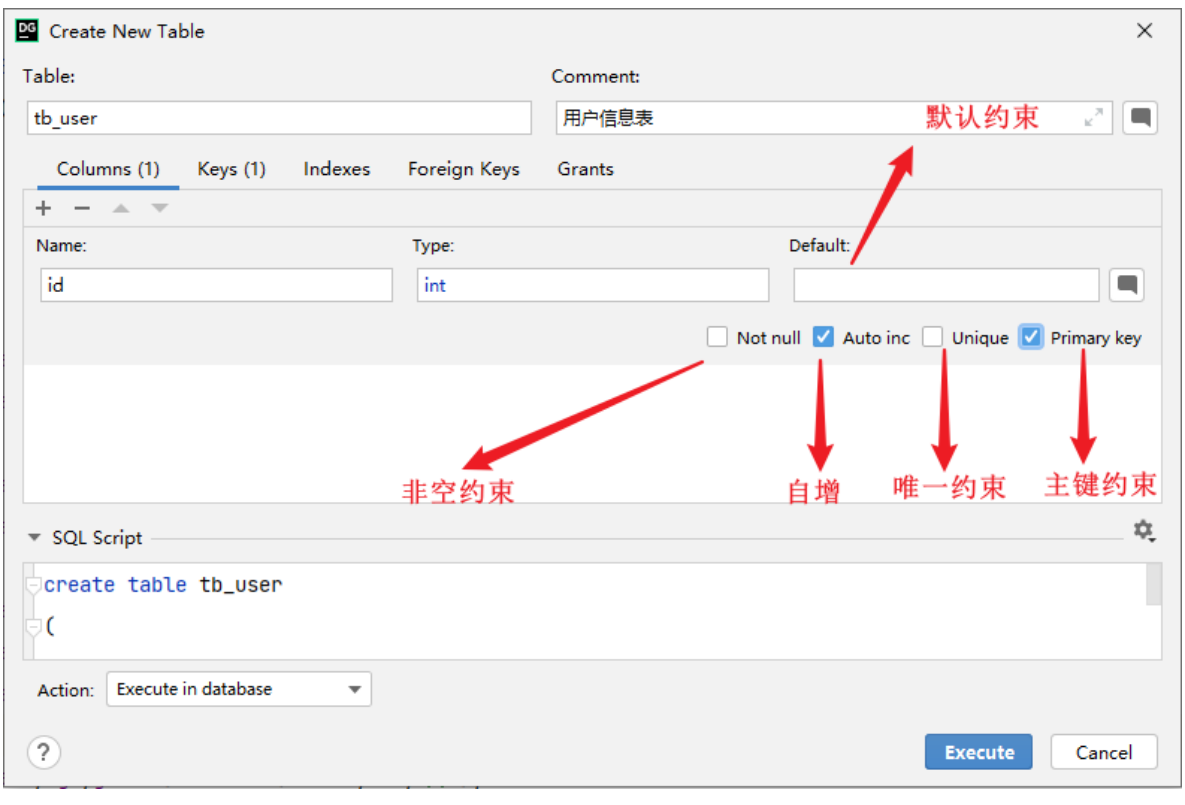
-
AUTO_INCREMENT 约束:自动增长
CREATE TABLE tb_user( id int AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY COMMENT 'ID唯一标识', name varchar(10) NOT NULL UNIQUE COMMENT '姓名' , age int check (age > 0 && age <= 120) COMMENT '年龄' , status char(1) default '1' COMMENT '状态', gender char(1) COMMENT '性别' ); -
创建时在字段后加上约束关键字
id int AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY COMMENT 'ID唯一标识', -
-
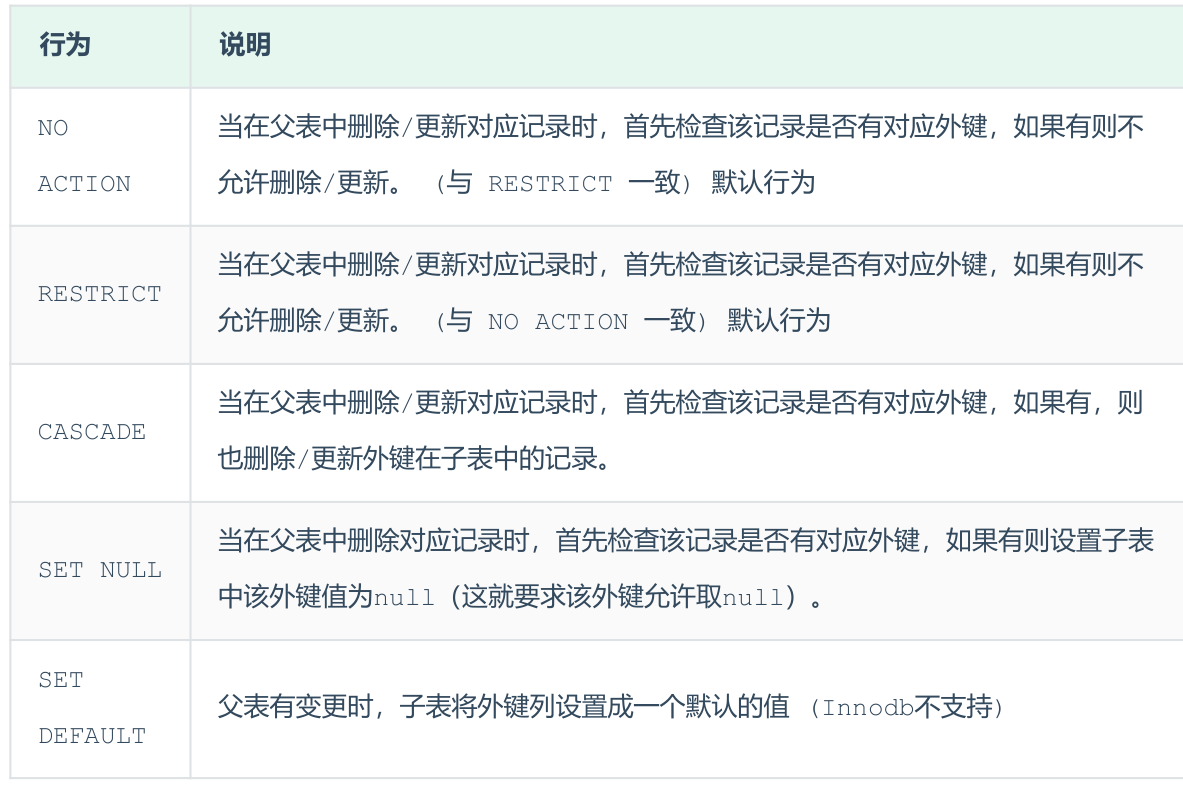
外键约束:用来让两张表的数据之间建立连接,从而保证数据的一致性和完整性。
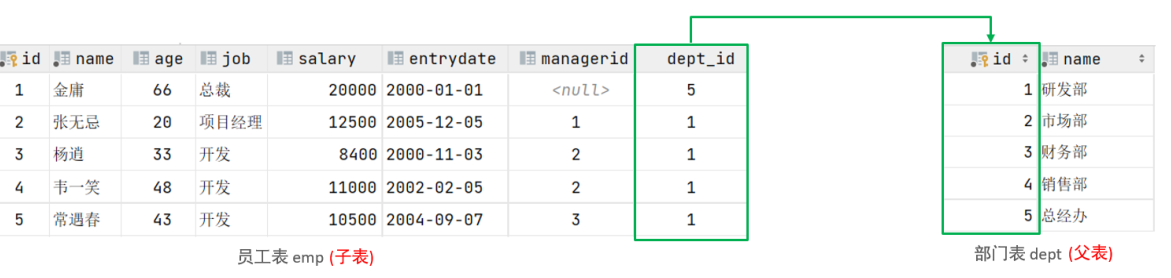
-
创建表时设置约束
CREATE TABLE 表名( 字段名 数据类型, ... [CONSTRAINT] [外键名称] FOREIGN KEY (外键字段名) REFERENCES 主表 (主表列名) ); -
添加约束
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD CONSTRAINT 外键名称 FOREIGN KEY (外键字段名)REFERENCES 主表 (主表列名) [ON UPDATE 更新行为 ON DELETE 删除行为]; -
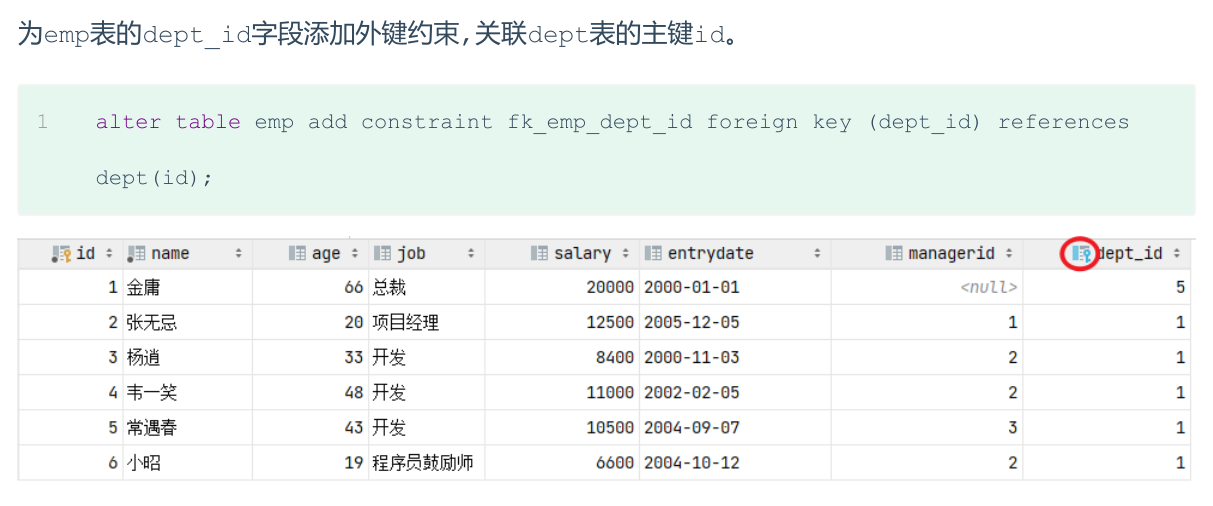
-
删除
ALTER TABLE 表名 DROP FOREIGN KEY 外键名称; -
外键的作用
- 参照完整性约束:外键的主要目的是防止无效数据的输入。如果一个字段是另一个表中主键的外键,则不能添加或修改该字段的值,除非这个值在主表中存在。例如,如果在学生表中有一个字段是课程 ID,这个课程 ID 在课程表中是主键,那么在学生表中,就不能输入不存在的课程 ID。
- 关联和联接表格:外键也可以用于关联两个表的数据。通过在 SQL 查询中使用 JOIN 语句,可以获取到两个或多个表中相关联的数据。
- 级联操作:有时,当在一个表中更新或删除一个记录时,你可能希望自动更新或删除另一个表中与之相关联的记录。这是通过定义级联更新或级联删除的外键来实现的。例如,如果在学生和课程两个表之间存在一个外键关系,那么删除课程表中的一门课程时,会连带删除选修了这门课程的所有学生的选课记录,以保持数据的一致性。
- 主次之分:假设我们有两个表,一个是学生表,一个是课程表。在课程表中,课程代码是主键,在学生表中,选课代码是外键。在这个例子中,课程表就是主表,学生表是从表。
-
添加了外键之后,再删除父表数据时产生的约束行为,我们就称为删除/更新行为
-
ALTER TABLE 表名 ADD CONSTRAINT 外键名称 FOREIGN KEY (外键字段) REFERENCES 主表名 (主表字段名) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE; -
示例
CREATE TABLE student( sid int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, sname varchar(20) NOT NULL, gender varchar(10) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(sid) ); CREATE TABLE course( cid int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, cname varchar(20) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(cid) ); CREATE TABLE mark( mid int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, sid int NOT NULL, cid int NOT NULL, score int NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY(mid), FOREIGN KEY(sid) REFERENCES student(sid), FOREIGN KEY(cid) REFERENCES course(cid) );
多表查询¶
- 多表关系
- 一对多:一个部门对应多个员工
- 在多的一方建立外键,指向一的一方的主键
- 多对多:一个学生可以选修多门课程,一门课程也可以供多个学生选择
- 建立第三张中间表,中间表至少包含两个外键,分别关联两方主键
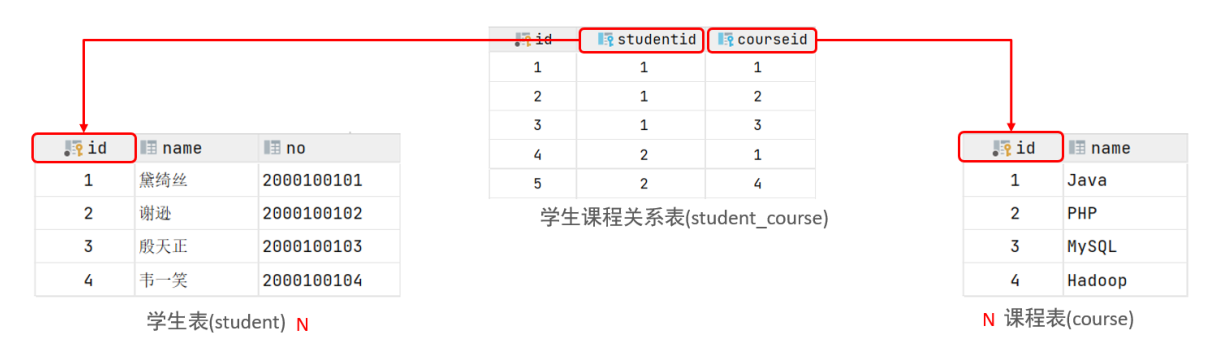
- 一对一:用户与用户详情的关系
- 在任意一方加入外键,关联另外一方的主键(相当于对一个表进行了拆分合并)
- 查询多个表
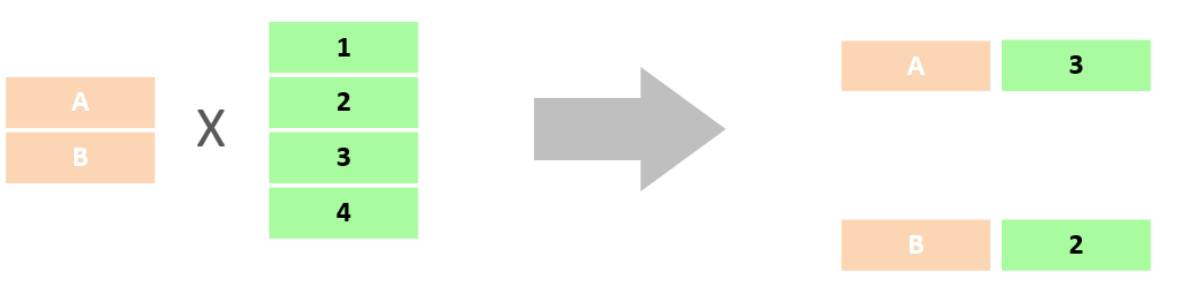
select * from emp , dept;使用逗号分隔 - 默认返回表的笛卡尔积
- 同样可以附加条件
select * from emp , dept where emp.dept_id = dept.id
链接¶
- 分类
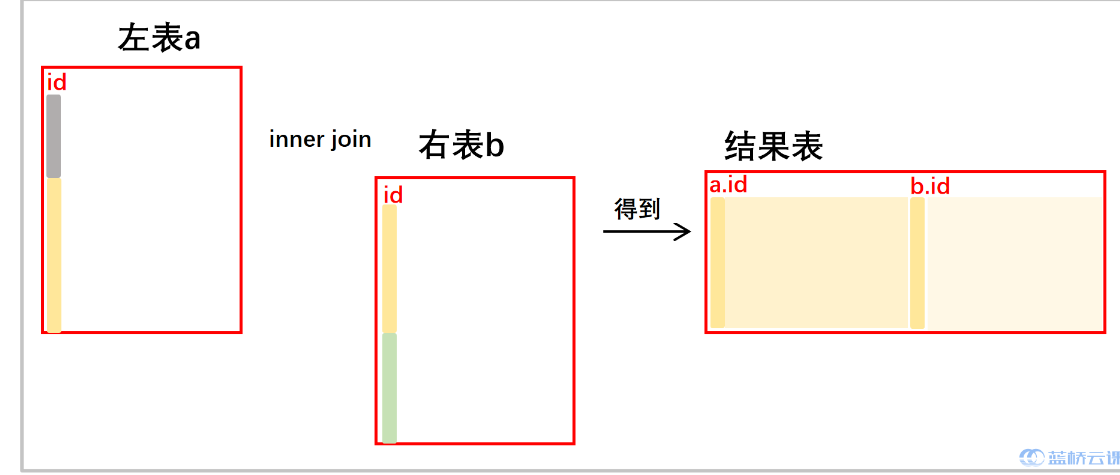
- 内连接(INNER JOIN):当两个表中都存在匹配时,才返回行。
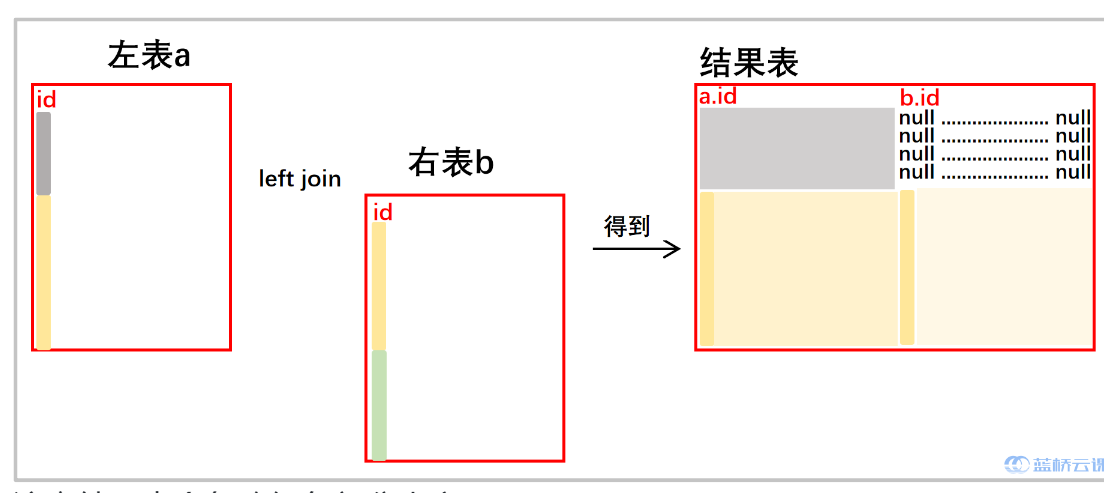
- 左连接(LEFT JOIN):返回左表中的所有行,如果左表中行在右表中没有匹配行,则结果中右表中的列返回空值。
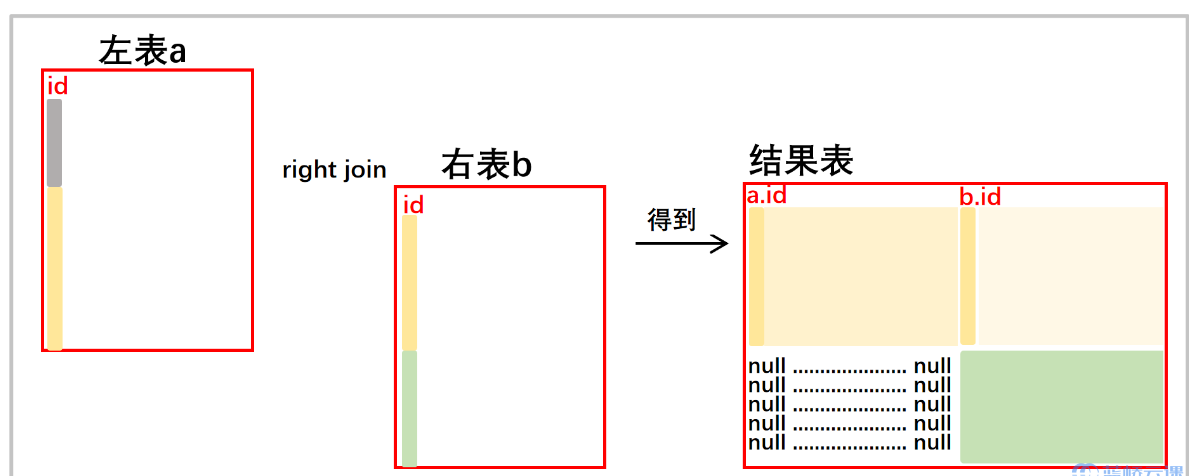
- 右连接(RIGHT JOIN):恰与左连接相反,返回右表中的所有行,如果右表中行在左表中没有匹配行,则结果中左表中的列返回空值。
-
全连接(FULL JOIN):返回左表和右表中的所有行。当某行在另一表中没有匹配行,则另一表中的列返回空值
- 如果所用的数据库不支持全连接,比如 MySQL,那么你可以使用 UNION ALL 子句来将左连接和右连接结果组合在一起
-
内连接
SELECT 字段列表 FROM 表1 , 表2 WHERE 条件 ... ;-
显示语法
select e.name, d.name from emp e join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;- 为表设置别名
tablea 别名1 , tableb 别名2 - 一旦为表起了别名,就不能再使用表名来指定对应的字段了,此时只能够使用别名来指定字段。
- 为表设置别名
-
外连接
- 左外连接
SELECT 字段列表 FROM 表1 LEFT [ OUTER ] JOIN 表2 ON 条件 ... ; - 右外连接
SELECT 字段列表 FROM 表1 RIGHT [ OUTER ] JOIN 表2 ON 条件 ... ; -
查询 emp 表的所有数据, 和对应的部门信息
select e.*, d.name from emp e left outer join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id; -
自链接
SELECT 字段列表 FROM 表A 别名A JOIN 表A 别名B ON 条件 ... ;- 自连接必须对同一个表设置不同的别名
-
查询所有员工 emp 及其领导的名字 emp , 如果员工没有领导, 也需要查询出来
select a.name '员工', b.name '领导' from emp a left join emp b on a.managerid = b.id; -
联合查询
UNION运算符选择的各个SELECT语句必须拥有相同的数量的列,列也必须拥有相似的数据类型,同时在相同的顺序上。- union all 会将全部的数据直接合并在一起,union 会对合并之后的数据去重。
SELECT 字段列表 FROM 表A ... UNION [ ALL ] SELECT 字段列表 FROM 表B ....; select * from emp where salary < 5000 union all select * from emp where age > 50;
子查询(嵌套查询)¶
-
SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE column1 = ( SELECT column1 FROM t2 ); -
标量子查询(子查询结果为单个值)
- 查询返回的结果是单个值(数字、字符串、日期等)
-
查询 "销售部" 的所有员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '销售部'); -
列子查询 (子查询结果为一列)
- 子查询返回的结果是一列(可以是多行,挑选字段)
- 查询 "销售部" 和 "市场部" 的所有员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id in (select id from dept where name = '销售部' or name = '市场部'); -
查询比研发部其中任意一人工资高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > any ( select salary from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '研发部') ); -
行子查询 (子查询结果为一行)
- 子查询返回的结果是一行(可以是多列)
- 由于只有一行,因此通常直接使用=
-
查询与 "张无忌" 的薪资及直属领导相同的员工信息:
select * from emp where (salary,managerid) = (select salary, managerid from emp where name = '张无忌'); -
表子查询 (子查询结果为多行多列)
- 子查询返回的结果是多行多列,这种子查询称为表子查询。
- 通常使用 in
- 查询与 "鹿杖客" , "宋远桥" 的职位和薪资相同的员工信息:
select * from emp where (job,salary) in ( select job, salary from emp where name = '鹿杖客' or name = '宋远桥' ); select e.*, d.* from (select * from emp where entrydate > '2006-01-01') e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id ;
事务¶
- 事务是一组操作的集合,它是一个不可分割的工作单位 ACID 属性
- 原子性(Atomicity):事务是不可分割的最小操作单元,要么全部成功,要么全部失败。
- 一致性(Consistency):事务完成时,必须使所有的数据都保持一致状态。
- 隔离性(Isolation):数据库系统提供的隔离机制,保证事务在不受外部并发操作影响的独立环境下运行。
- 持久性(Durability):事务一旦提交或回滚,它对数据库中的数据的改变就是永久的。
-
事务是一个或多个 SQL 语句组成的一个执行单元。只有当该单元内的所有操作都成功完成时,该事务才会被提交。如果其中任何操作失败,事务将被回滚,所有的操作都不会生效。
-
查看/设置事务提交方式
SELECT @@autocommit ; SET @@autocommit = 0 ; -
把默认的自动提交修改为了手动提交, 此时我们执行的 DML 语句都不会提交, 需要手动的执行 commit 进行提交。
-
控制事务
- 开启事务
START TRANSACTION- 具体操作语句在开启与提交之间
- 提交事务
COMMIT - 回滚事务
ROLLBACK;
-- 开启事务
start transaction
-- 1. 查询张三余额
select * from account where name = '张三';
-- 2. 张三的余额减少1000
update account set money = money - 1000 where name = '张三';
-- 3. 李四的余额增加1000
update account set money = money + 1000 where name = '李四';
-- 如果正常执行完毕, 则提交事务
commit;
-- 如果执行过程中报错, 则回滚事务
-- rollback;
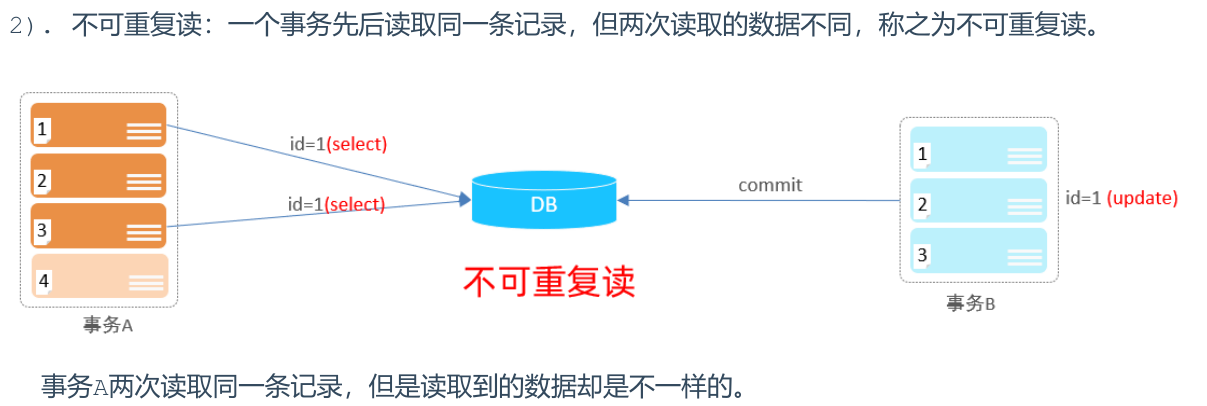
- 并发问题
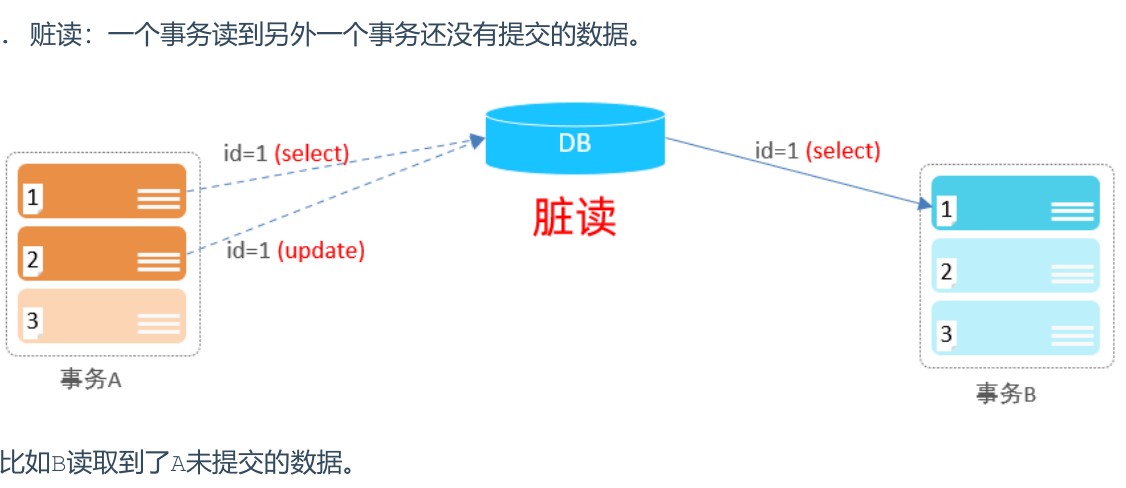
- 事务A修改了一条记录,但还没有提交这个修改。此时,事务B读取了同一条记录。如果事务A回滚,事务B读到的数据实际上是错误的。
事务隔离级别¶
-
-
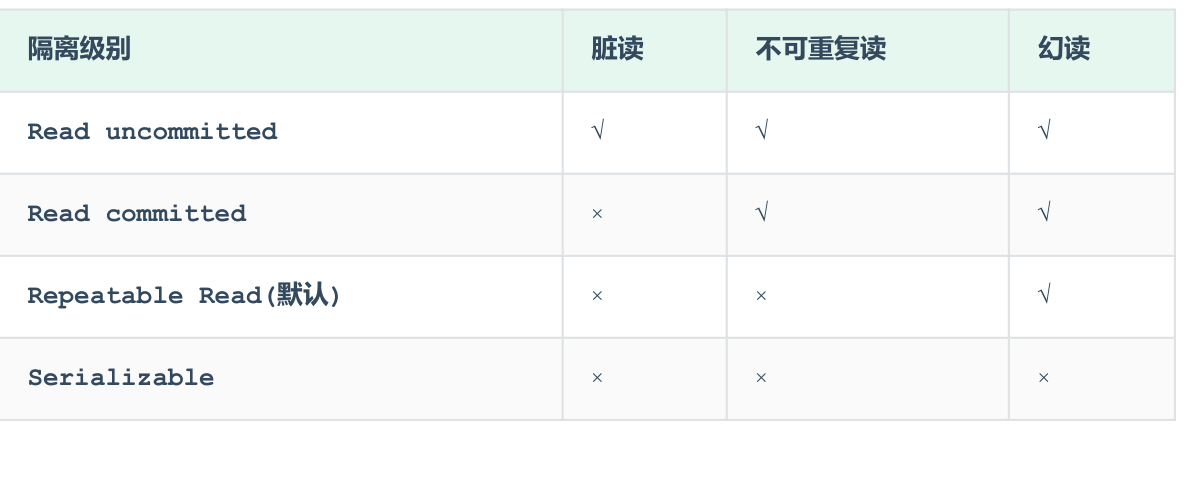
读未提交(Read Uncommitted):
- 最低的隔离级别,事务间相互影响最大。
- 允许一个事务读取另一个事务尚未提交的数据。
-
可能导致脏读(Dirty Read),即读取到未提交的数据。
-
读已提交(Read Committed):
- 保证一个事务只能读取到已提交的数据。
- 事务在执行过程中看到的数据是稳定的,不会读取到其他事务已提交的数据变化。
-
可能导致不可重复读(Non-repeatable Read),即同一事务内两次读取同一数据,结果不一致。(强调单条数据的修改)
-
可重复读(Repeatable Read):
- 保证一个事务多次读取同一数据时结果始终一致。
- 在事务执行期间,其他事务对该数据进行修改也不会影响到当前事务的读取。
-
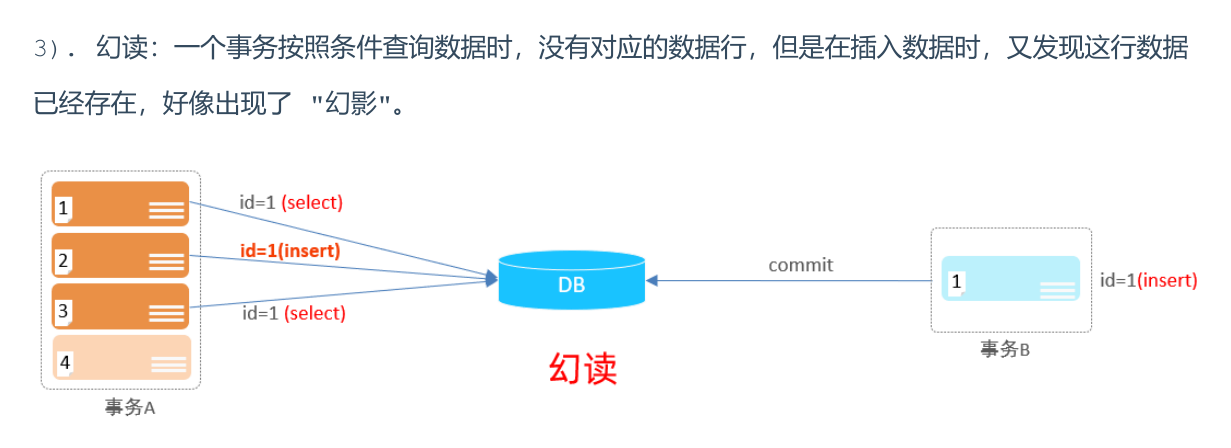
可能导致幻读(Phantom Read),即同一事务内两次查询结果集不一致。(强调数据总条数的增减,而不局限于单条的变化)
-
串行化(Serializable):
- 最高的隔离级别,完全串行化执行每个事务,确保不会发生并发问题。
- 通过锁机制来实现事务的完全隔离。
-
避免了脏读、不可重复读和幻读的问题,但性能较低,一次只能执行一个事务。
-
查看事务隔离级别
SELECT @@TRANSACTION_ISOLATION; - 设置事务隔离级别
SET [ SESSION | GLOBAL ] TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL { READ UNCOMMITTED | READ COMMITTED | REPEATABLE READ | SERIALIZABLE }
死锁¶
- 当两个或者多个事务无限期地等待一个资源时,就会发生死锁。解决死锁的常见方法包括:
- 预防死锁:例如,设定锁的超时时间。
- 死锁检测和恢复:定期检查死锁,一旦检测到,挑选一个事务进行回滚。
逻辑语句¶
case-when¶
CASE
WHEN condition1 THEN result1
WHEN condition2 THEN result2
...
ELSE default_result
END
SELECT
name,
age,
CASE
WHEN age < 18 THEN 'Minor'
WHEN age >= 18 AND age <= 65 THEN 'Adult'
ELSE 'Senior'
END AS age_group
FROM
people;
if(month=1,amount,0) as a
CTE 子查询语句¶
- 用于化简多层嵌套的复杂子查询问题
with 临时表名1 as ( select 语句1 ), 临时表名2 as ( select * from 临时表名1 ), 。。。。。。 select * from 临时表名n 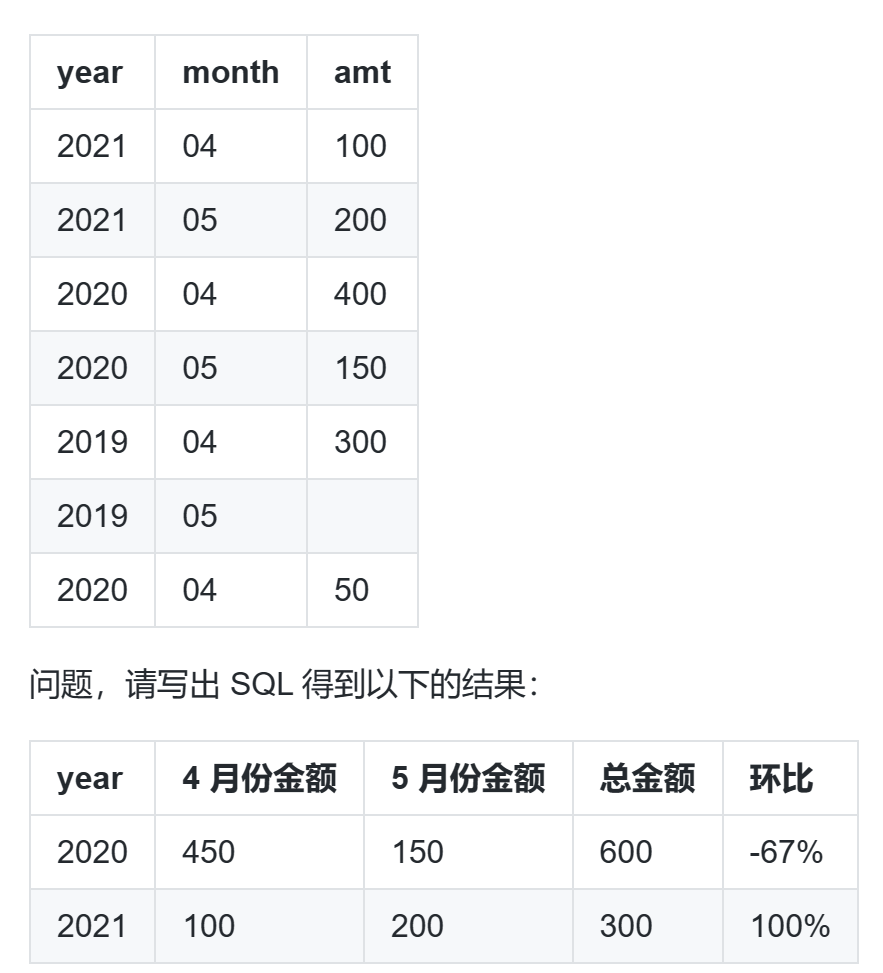
-- 先行变列再提取并计算比例 select year,amt_4,amt_5,amt_all, concat(rate*100,'%') as rate from ( select *, round((amt_5 - amt_4) / amt_4, 2) as rate -- 环比 from ( -- 行转列的套路,就是用sum(case when或if) select year, sum(if(month = '04', amt, 0)) as amt_4, -- 4月份金额 sum(if(month = '05', amt, 0)) as amt_5, -- 5月份金额 sum(amt) as amt_all -- 总金额 from sales group by year ) t1 ) t2; -- 使用CTE优化 with t1 as ( select year, sum(if(month = '04', amt, 0)) as amt_4, sum(if(month = '05', amt, 0)) as amt_5, sum(amt) as amt_all from sales group by year ), t2 as ( select *, round((amt_5 - amt_4) / amt_4, 2) as rate from t1 ) select year, amt_4, amt_5, amt_all, concat(rate * 100,'%') as rate from t2 ;
功能函数¶
- 时间
select year('2023-05-20') as year1, month('2023-05-20') as month1, day('2023-05-20') as day1; -- 按照年月日提取,分别得到2023,05,20 - 日期运算 data_sub&data_add
- DATE_ADD(date,interval expr type)、DATE_SUB(date,interval expr type) 其中常用的 type 的类型有:second、minute、hour、day、month、year 等。
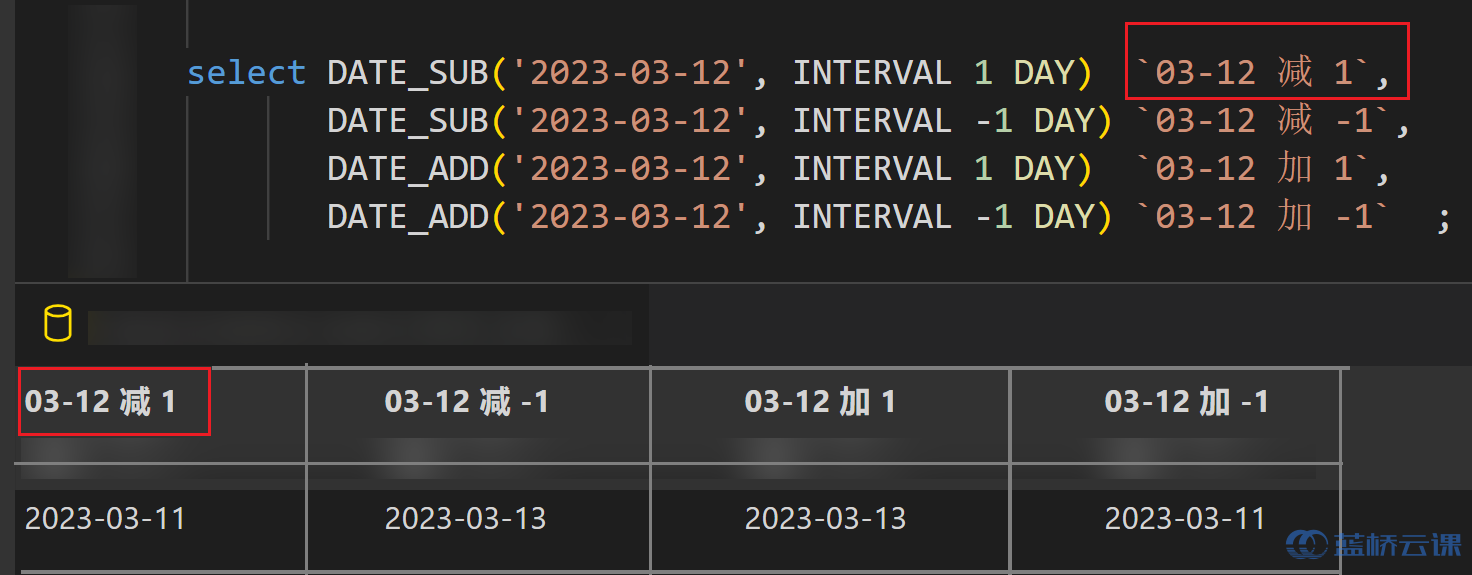
- 格式转化,如年月日转化为年月:
SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2018-12-18', '%Y-%m') AS year_month;
字符串函数¶
- 拼接
CONCAT_WS(separator,string1,string2,...), (以指定的字符拼接)select concat_ws('_','小王','男',30) as x;得到小王_男_30- 直接拼接两个字符串
concat(str1,str2)
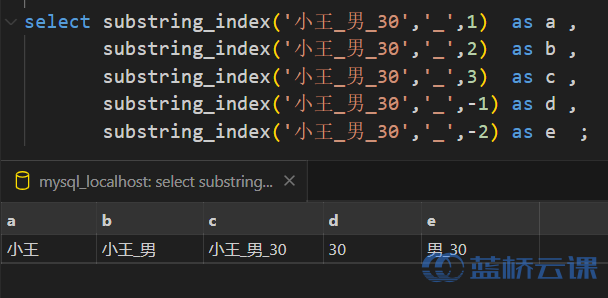
- 截取字符串
- substring_index (str, delim, number)
- str: 要处理的字符串
- delim: 分隔符
- number: 指定分隔符位置
- 如果 number 是正数,那么就是从左往右数,第 N 个分隔符的左边的全部内容,
- 相反,如果是负数,那么就是从右边开始数,第 N 个分隔符右边的所有内容。
- 获取字符串长度
LENGTH(column)
数学¶
- 近似值
round(num,len)
其它¶
nvl(字段名 , 默认值)如果字段名是 null,则返回指定的默认值COALESCE(expression1, expression2, ..., expressionN)从它的参数列表中返回第一个非NULL值。
SQL 实战¶
- 书写 sql 时最好按对层级书写而不是顺序书写
- 如
-- 先写 select from table1 -- 逐步填入内容 select case end as `新字段名` from table1 select *, -- a是伪列,是我们自己造的。 case when month=1 then amount else 0 end as a from table1;
行转列问题¶
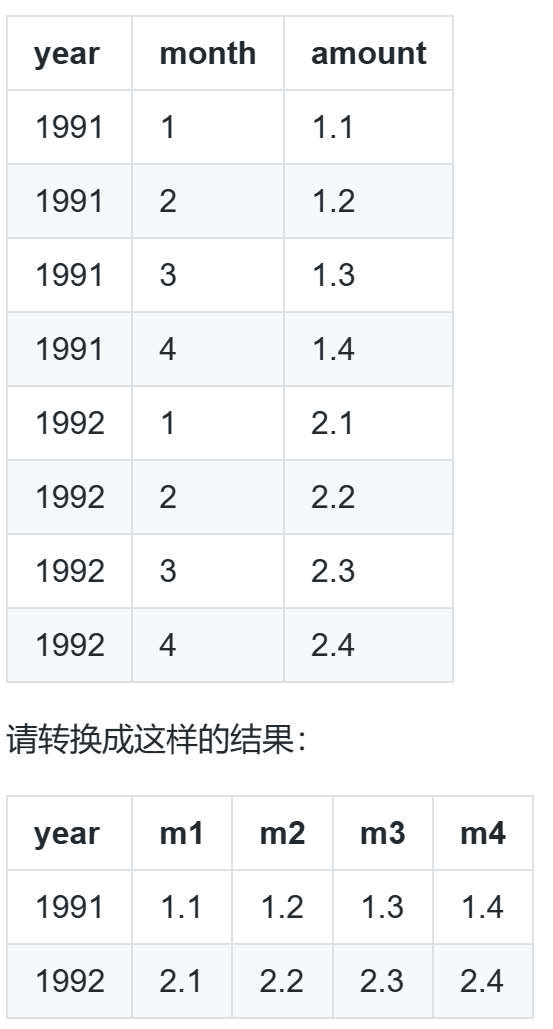
select DDate, sum(a) as `胜`, sum(b) as `负` from (select DDate, case when shengfu = '胜' then 1 else 0 end as a, case when shengfu = '负' then 1 else 0 end as b from table2) t group by DDate; -- 简化 select year, sum(if(month=1,amount,0)) m1, sum(if(month=2,amount,0)) m2, sum(if(month=3,amount,0)) m3, sum(if(month=4,amount,0)) m4 from table1 group by year;- 创建新列
if(month=1,amount,0)提取出提取出特定月份的数值,再按年份 group 就得到了每一列
行转列多指标¶
列转行问题¶
窗口函数问题¶
窗口函数名(参数) over(partition by 分组字段 order by 排序字段 rows between 起点 and 终点) as 新字段名rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following表示最前面到最后面current row表示当前行between 1 preceding and 1 following更加精确的范围控制rows between unbounded preceding and current row这是省略时的默认行为select *, -- 班级内总分是多少 -- 写法1 sum(score) over(partition by class_id order by score rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following) as sum1, -- 简化写法2 sum(score) over(partition by class_id) as sum2, -- 班级内分数小于等于自己的同学的总分是多少 -- 写法1 sum(score) over(partition by class_id order by score rows between unbounded preceding and current row) as sum3, -- 简化写法2 sum(score) over(partition by class_id order by score) as sum4, -- 班级内每个学生,比他分数高1名,低1名,和自己3人的总分是多少 sum(score) over(partition by class_id order by score rows between 1 preceding and 1 following) as sum5 from student;
- 分类
- 聚合类的窗口函数
sum/count/avg/max/min(其实就是聚合函数,同名) - 排序类的窗口函数
row_number/rank/dense_rank - 偏移、跨行类的
lag/lead - 获取第一/最后/第 N 个
first_value/last_value/nth_value - 分组
ntile - 分布函数
percent_rank/cume_dist
- 聚合类的窗口函数
聚合类¶
count(1)填入任何一个常量都不是创建一个伪列(常量列),返回值是行数(count (*)也是这个意思)- 对于表中存在的列,返回的是不为空的列有几个
- 加上
distinct关键字表示去重的数目count(distinct city)
- 加上
- count、avg、max、min 都符合上面的用法
排序类¶
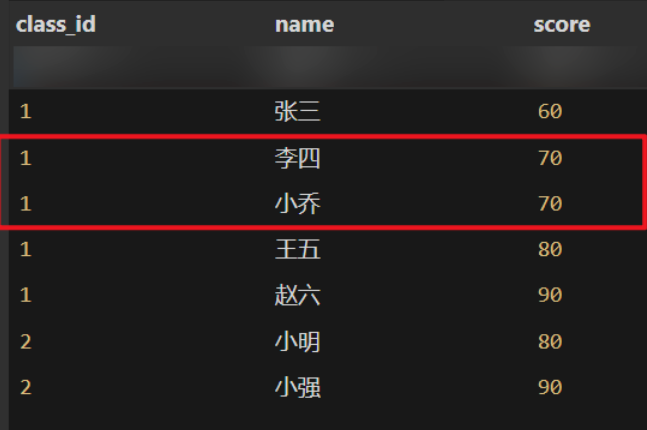
- 如果考试分数有 60、70、70、80,(注意有 2 个并列 70 分,假设最低分排在第一名)。
- 则按 row_number 排名时,名次是 1、2、3、4 ;
- 若按 rank 排名时,名次是 1、2、2、4 ;
- 若按 dense_rank 排名时,名次是 1、2、2、3。
-- 排序类的窗口函数 select *, -- 用row_number连续排序 row_number() over(partition by class_id order by score) rn, -- 用rank并列排序,考虑并列且序号不连续 rank() over(partition by class_id order by score) rk, -- 用dense_rank并列排序,考虑并列且序号连续 dense_rank() over(partition by class_id order by score) drk from student;row_number() over(order by score)就表示对全表(全局)排序
偏移窗口¶
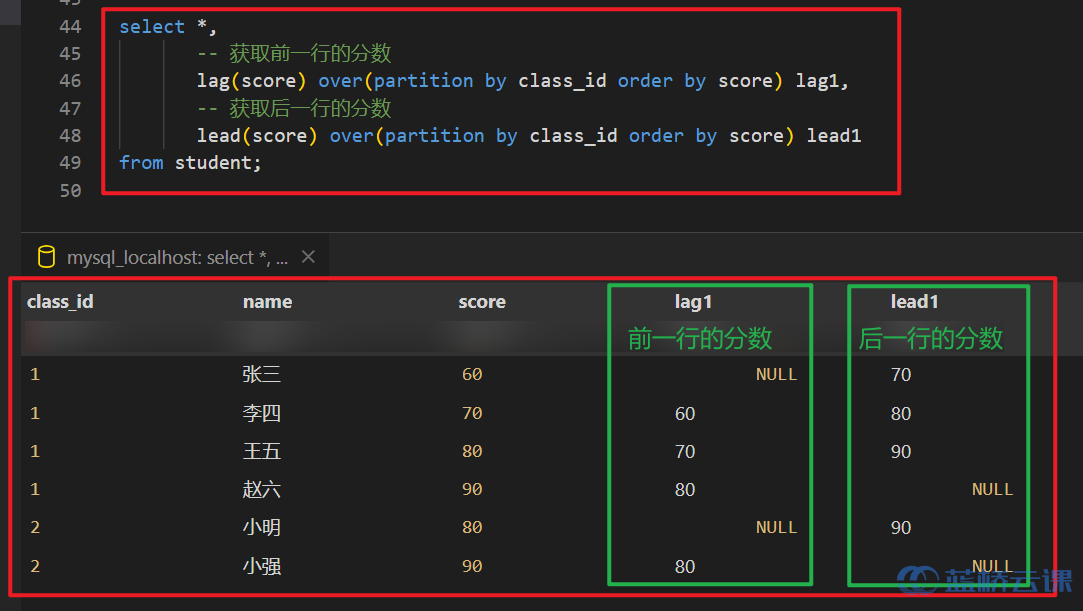
lag和lead都有三个参数,第一个参数是列名(需要被偏移的字段),第二个参数是偏移的offset(偏移量),第三个参数是超出记录窗口时的默认值(默认为 null,可以设置为 0 )。- 当偏移量是 1 时,
offset可以省略不写。default_value默认是null - lag 是向下偏移,lead 是向上偏移
LAG(expression,offset,default_value) OVER ( PARTITION BY expr,... ORDER BY expr [ASC|DESC],... )
- 当偏移量是 1 时,
其它窗口¶
- 获取第 N 行的值
first_value():返回窗口中第 1 个值。last_value():返回窗口中最后的值。nth_value(expr,n):返回窗口中第 N 个值。
- 分组 ntile
NTILE(n)函数用于将一组分区中的有序数据再尽量平均划分为 n 个小组。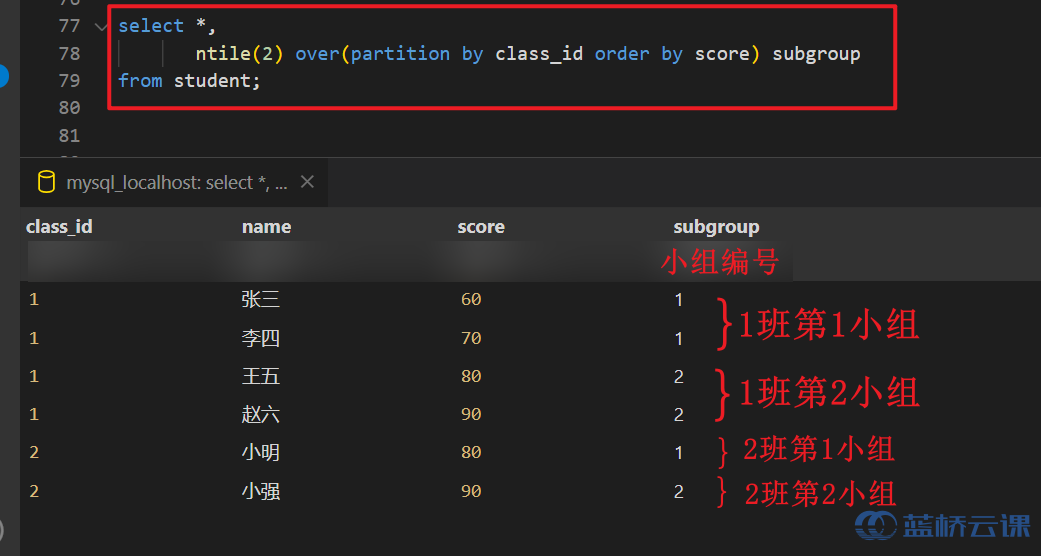
- 分布函数
- percent_rank():计算方式
- (rank - 1) / (rows - 1) - cume_dist():分组内小于等于当前 rank 值的行数/分组内总行数
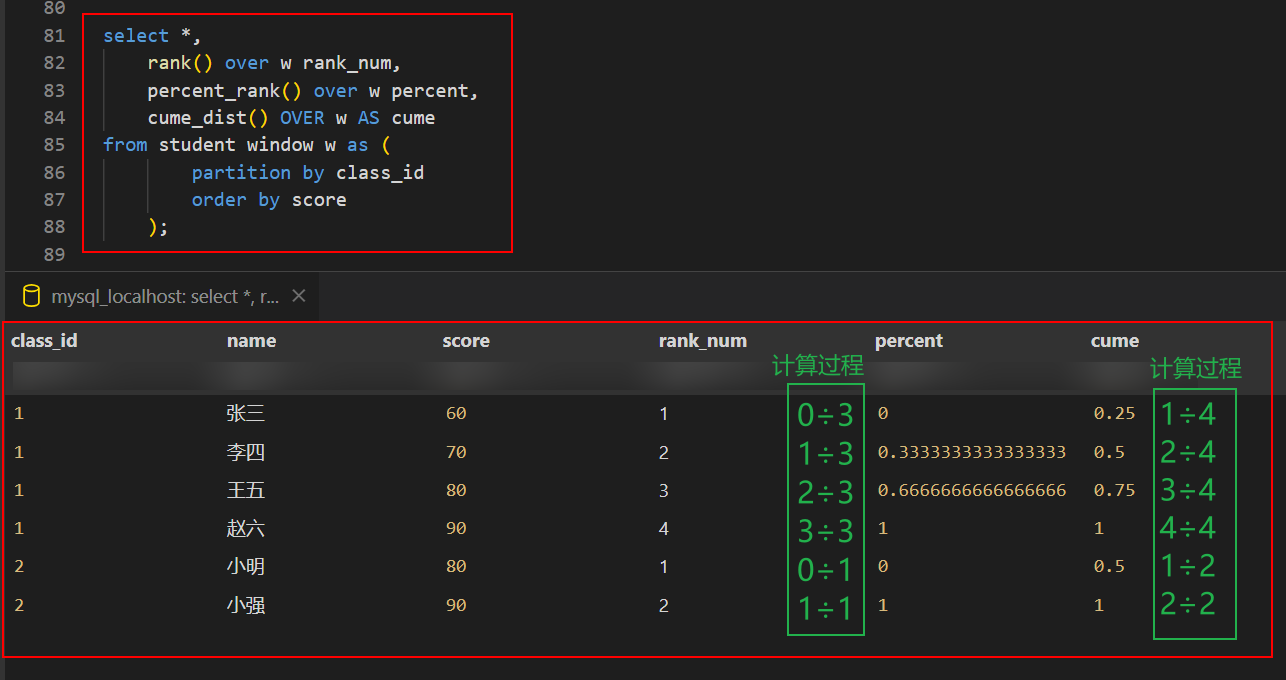
SELECT *, rank() over w as rank_num, percent_rank() over w as percent, cume_dist() over w as cume FROM student WINDOW w AS ( PARTITION BY class_id ORDER BY score );
- percent_rank():计算方式
实例¶
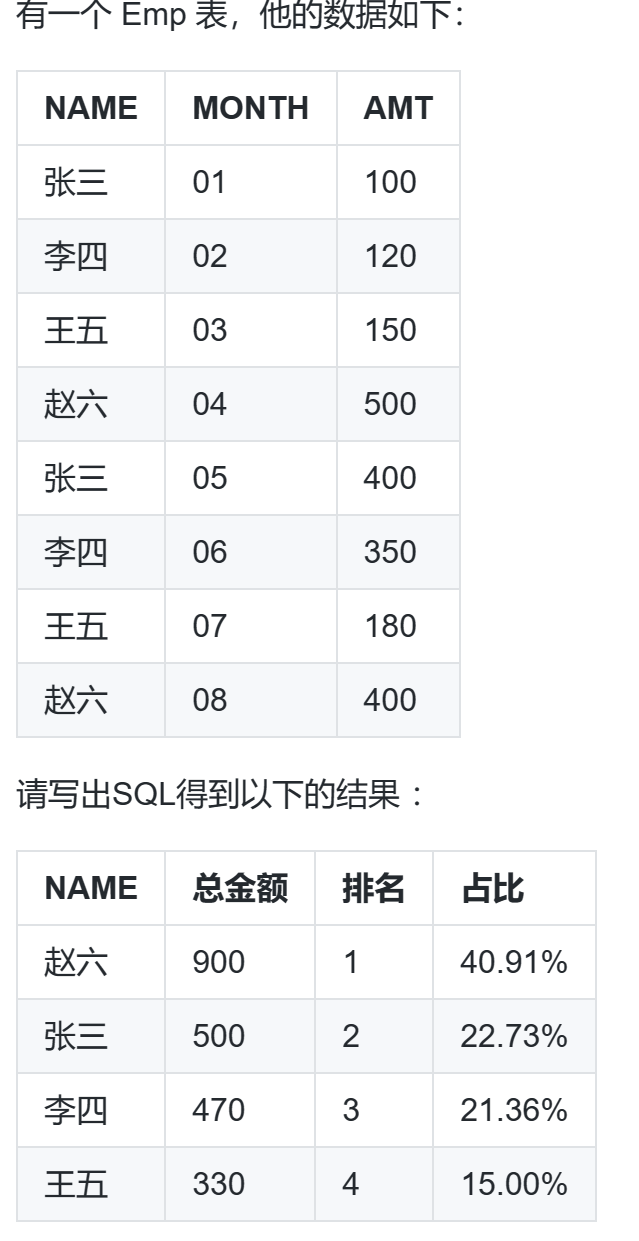
with t1 as ( select name, sum(amt) as sum_amt from emp group by name ), t2 as ( select name, sum_amt, row_number() over (order by sum_amt desc ) as rn, sum(sum_amt) over () as total_amt from t1 ) select name,sum_amt,rn, concat(round(sum_amt/total_amt*100,2),'%') as rate from t2;
数据重复问题¶
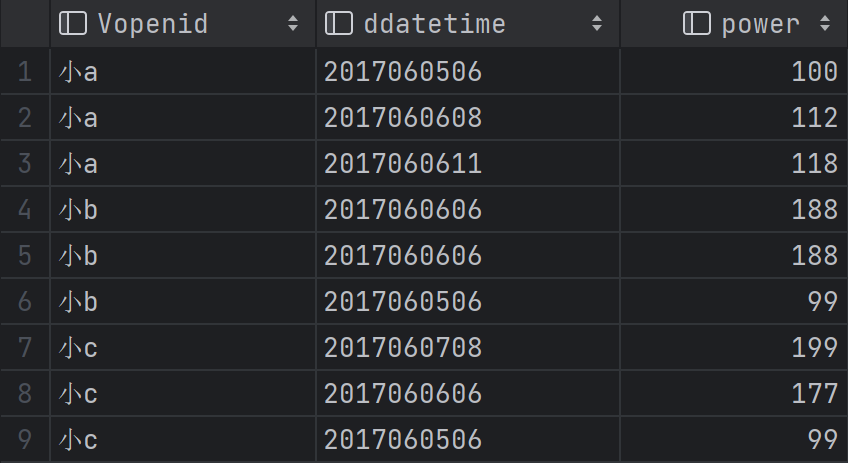
- 对一列去重
- distinct:
select distinct Vopenid from play_power; - group by:
select Vopenid from play_power group by Vopenid;
- distinct:
- 对组合(两列)去重
- 同样使用 distinct
select distinct Vopenid,substr(ddatetime,1,8) ddate from play_power;distinct后可以接多个字段,表示联合去重- 实现原理
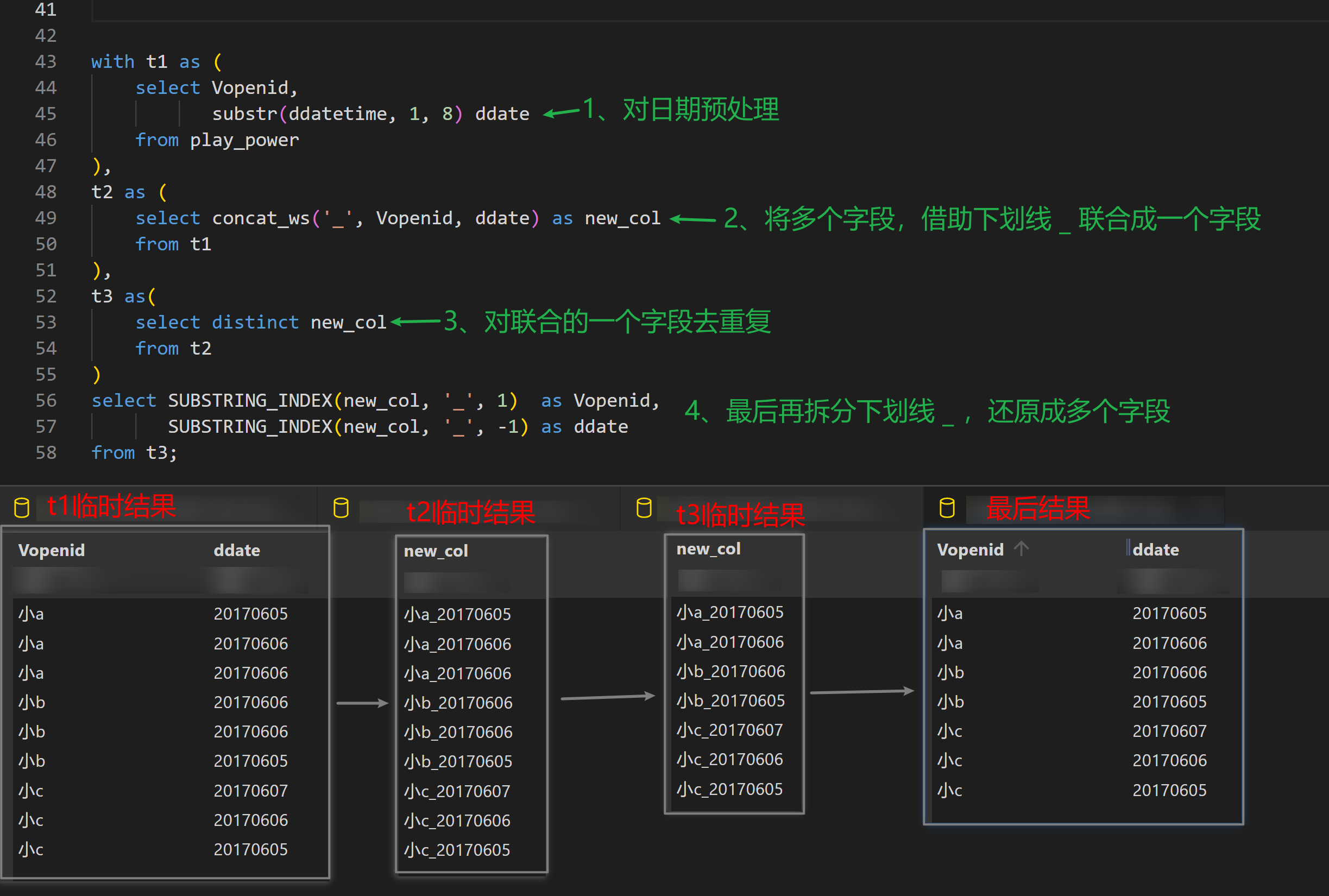
- 使用 group by
select Vopenid, substr(ddatetime, 1, 8) ddate from play_power group by Vopenid, substr(ddatetime, 1, 8);
- 同样使用 distinct
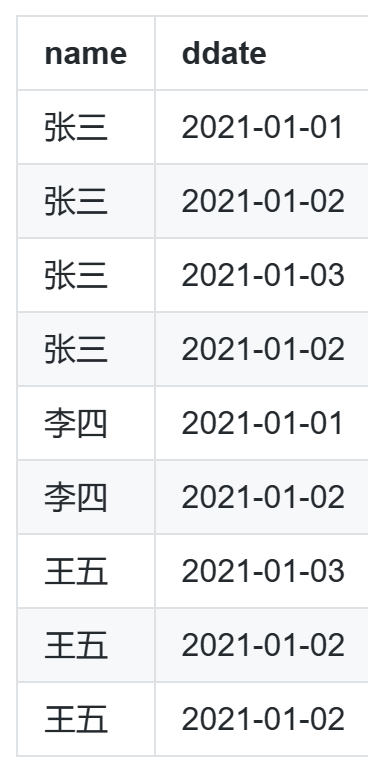
- 6 月 6 日每个玩家的最后一条战力值,由于要求保留最后一条数据,使用 row_number 实现 (以一列为指标对表进行去重也使用这种方法)
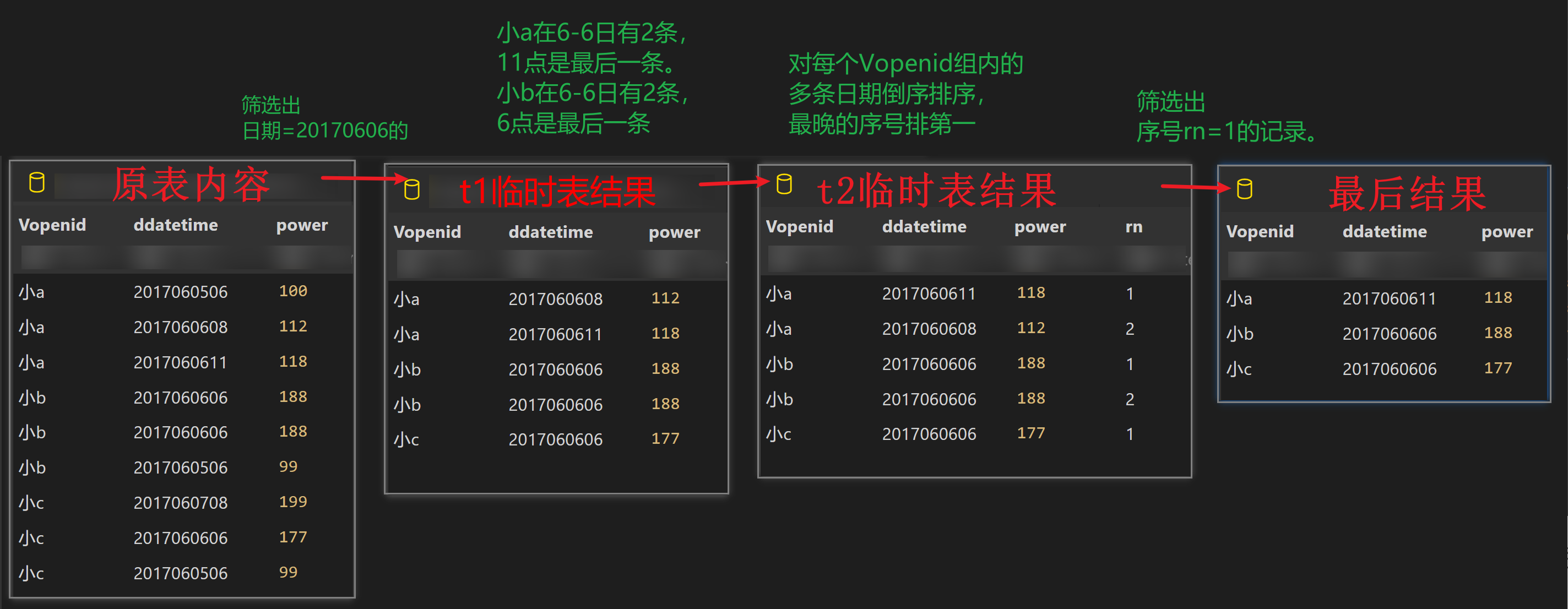
with t1 as ( select * from play_power where substr(ddatetime, 1, 8) = "20170606" ), t2 as ( select Vopenid, ddatetime, power, row_number() over (partition by Vopenid order by ddatetime desc) as rn from t1 ), t3 as ( select Vopenid, ddatetime, power from t2 where rn = 1 ) select * from t3; -- 进一步化简 select Vopenid, ddatetime, power from (select Vopenid, ddatetime, power, row_number() over (partition by Vopenid order by ddatetime desc ) as rn from play_power where substr(ddatetime, 1, 8) = "20170606") t where rn = 1;
连续 n 天登录问题¶
- 查询连续三天登录的人员姓名
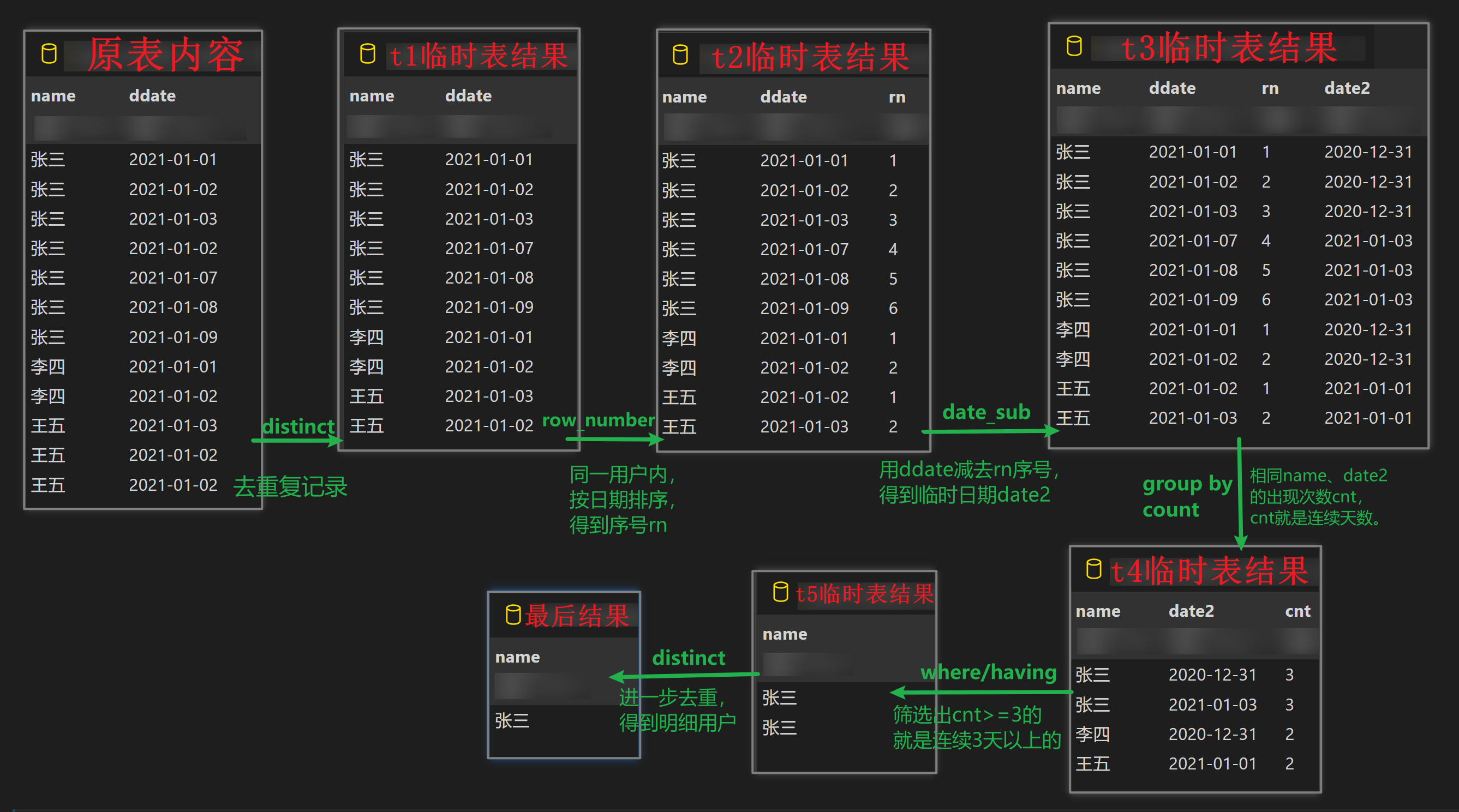
with t1 as( select distinct name,ddate from game), t2 as ( select *, row_number() over (partition by name order by ddate) rn from t1), t3 as ( select *, date_sub(ddate,INTERVAL rn DAY ) date2 from t2), t4 as ( select name, date2, count(1) cnt from t3 group by name,date2), t5 as(select name from t4 where cnt>=3), t6 as ( select distinct name from t5) select * from t6;- 第二种方法,使用窗口
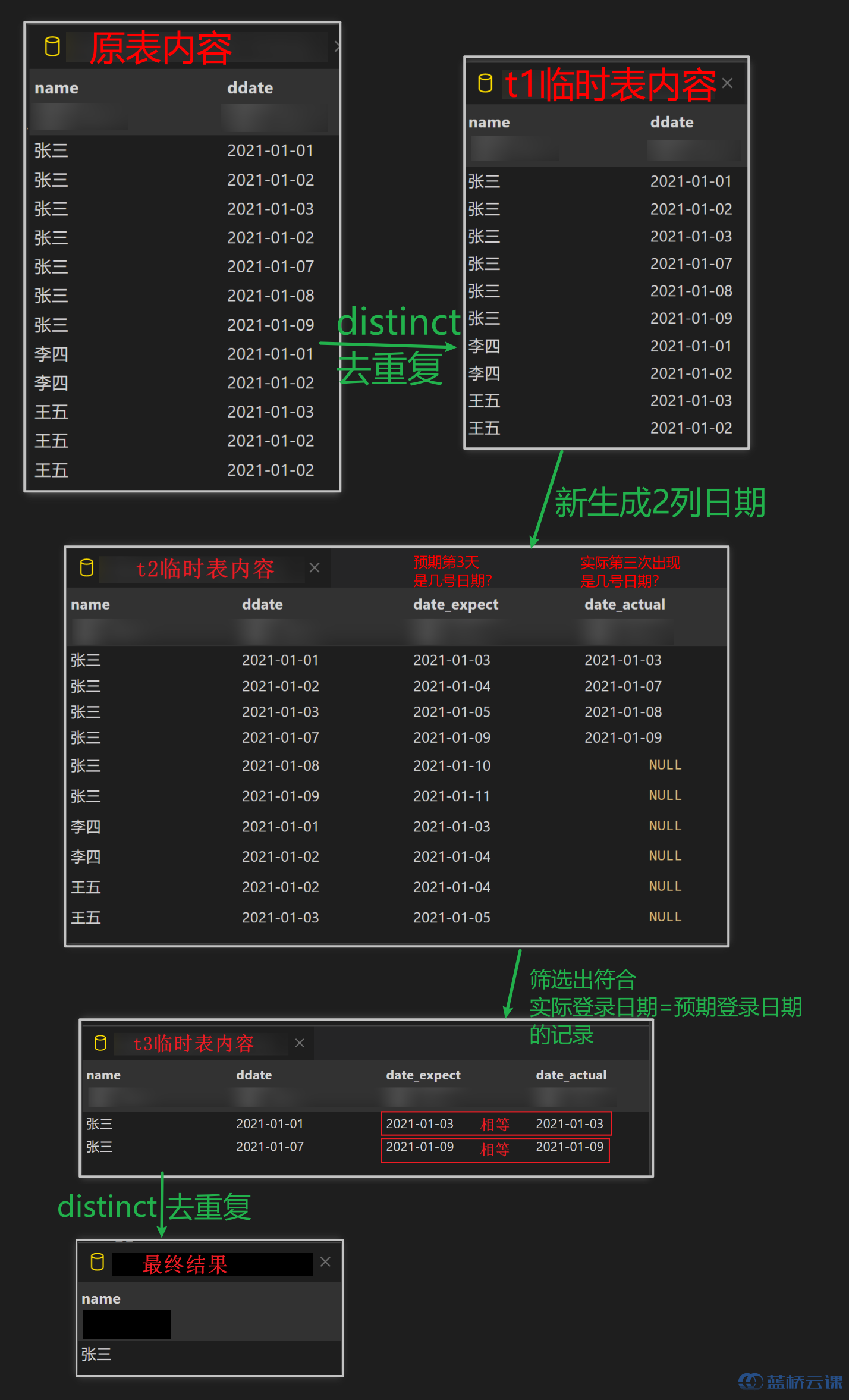
with t1 as ( select distinct name,ddate from game ), t2 as ( select *, date_add(ddate,INTERVAL 2 DAY) as date_expect, lead(ddate,2) over(partition by name order by ddate) as date_actual from t1 ), t3 as ( select * from t2 where date_expect=date_actual ), t4 as (select distinct name from t3) select * from t4 -- 更简洁的写法 with t1 as ( select distinct name,ddate from game ), t2 as ( select *, lead(ddate,2) over(partition by name order by ddate) as date_actual from t1 ) select distinct name from t2 where datediff(date_actual,ddate)=2
分组内求 topN 问题¶
- 先通过窗口函数分组排序,然后对排名序号进行筛选
select zzz from (select *, row_number() over (partition by xxx order by yyy) as rn from employee) t1 where rn<=n;
join 问题¶
- [inner]join:
- left join
- right join
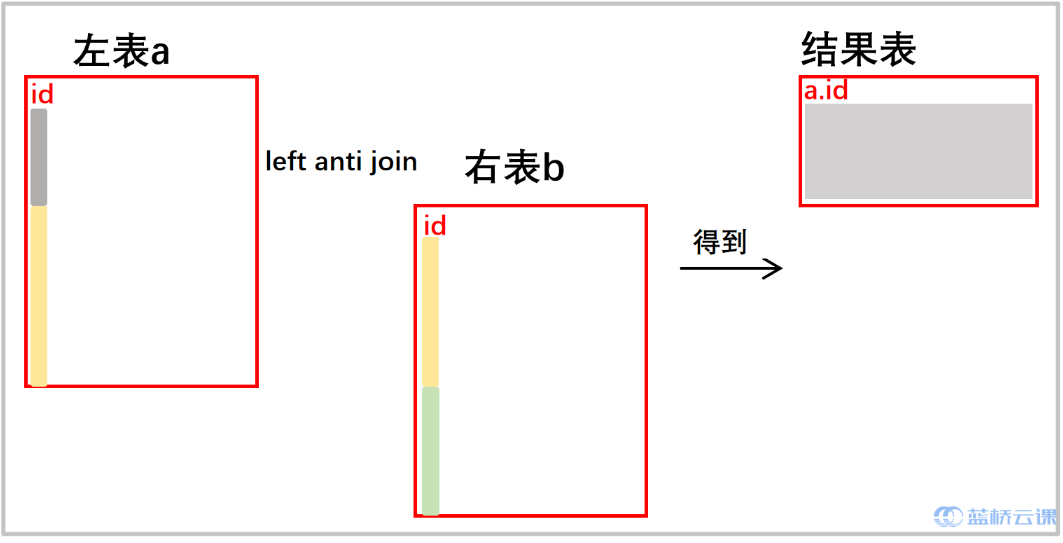
- left semi join
- MySQL 不支持 semi、anti,用于 Hive、SparkSQL
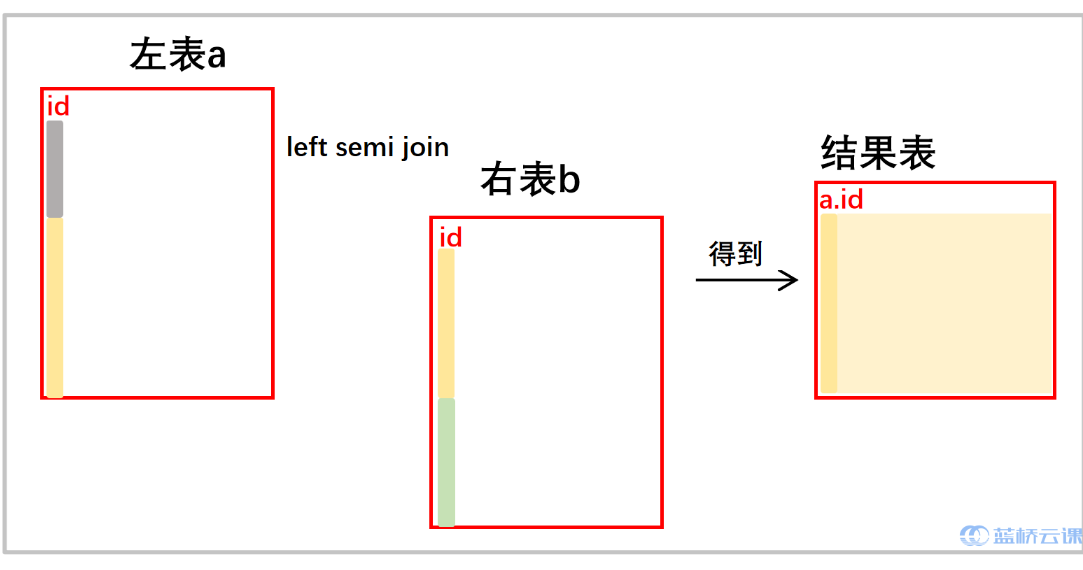
- 只保留 a 的指标,相当于只是将 b 用于 a 的筛选
- left anti join
- full join
- 会保留左右两个表的所有信息。也可以理解是
left join和right join的结合体。(MySQL 同样不支持) 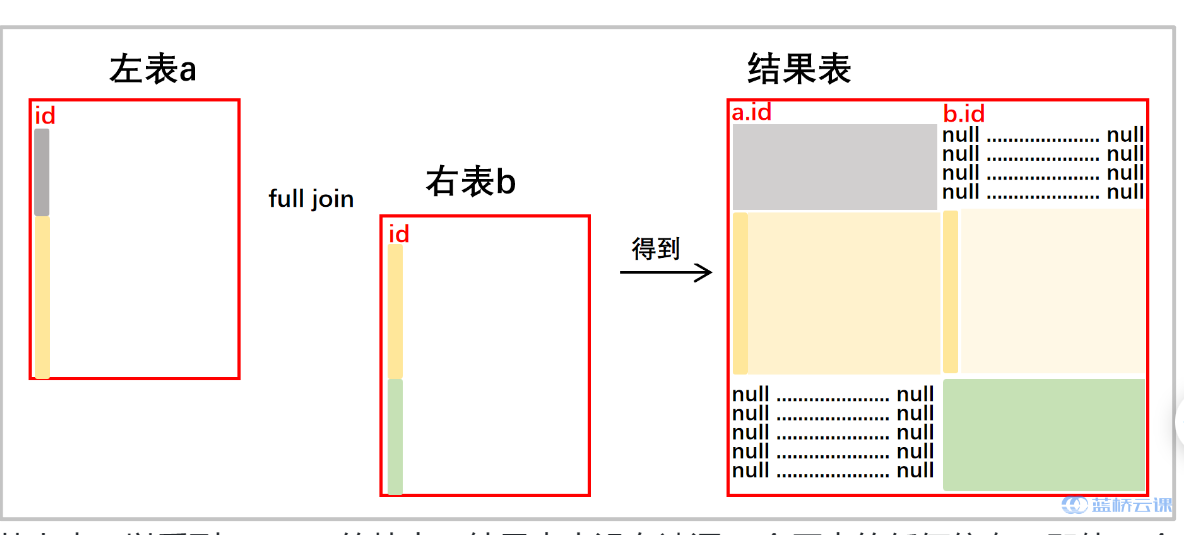
-- 间接实现 SELECT 。。 FROM A LEFT JOIN B ON A.key = B.key UNION ALL SELECT 。。 FROM A RIGHT JOIN B ON A.key = B.key WHERE A.key IS NULL
- 会保留左右两个表的所有信息。也可以理解是
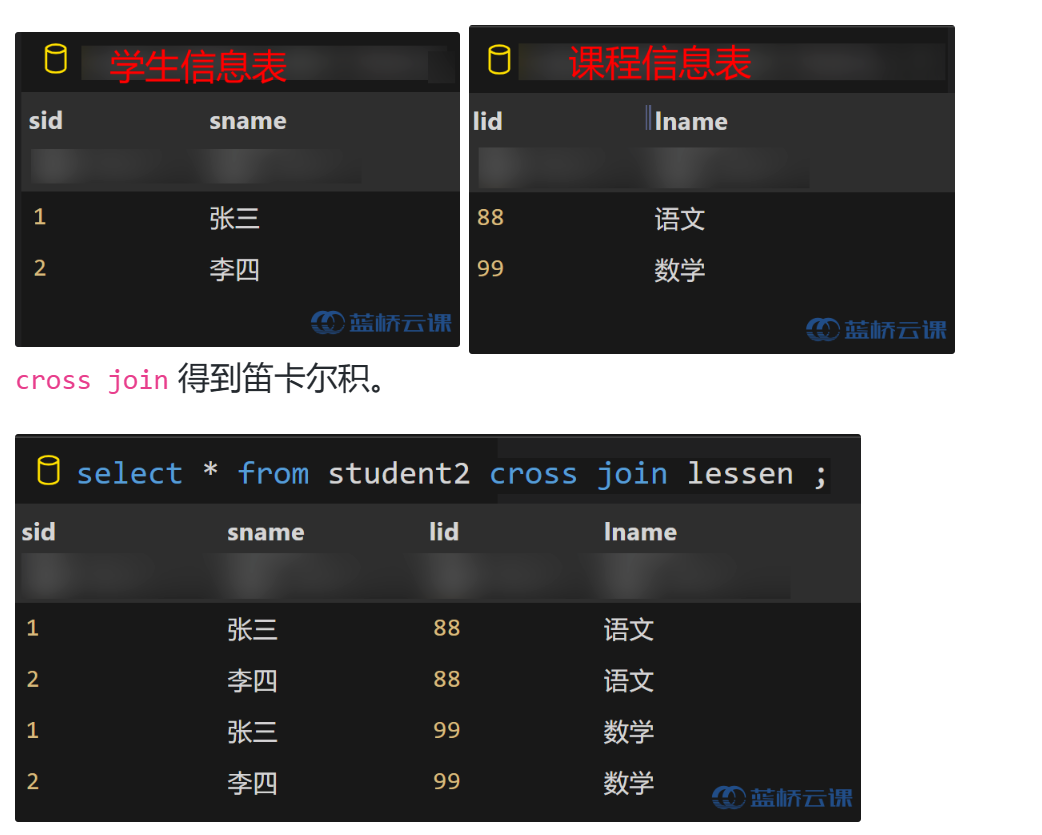
- cross join
- 笛卡尔积
示例¶
- full join 拼接数据并处理空缺值
with a as ( select p_date, server_id, role_id, sum(cost) cost from dm_paid_buy where p_date >= '2021-01-01' and p_date <= '2021-01-07' group by p_date, server_id, role_id ), b as ( select p_date, server_id, role_id, sum(cost) cost from dm_free_buy where p_date >= '2021-01-01' and p_date <= '2021-01-07' group by p_date, server_id, role_id ), c as ( select a.p_date p_date_a, a.server_id server_id_a, a.role_id role_id_a, nvl(a.cost, 0) cost_a, b.p_date p_date_b, b.server_id server_id_b, b.role_id role_id_b, nvl(b.cost, 0) cost_b from a full join b on a.p_date=b.p_date and a.server_id=b.server_id and a.role_id=b.role_id ), t as ( select coalesce(p_date_a, p_date_b) p_date, coalesce(server_id_a, server_id_b) server_id, coalesce(role_id_a, role_id_b) role_id, round(cost_a / cost_b, 3) as rate from c ) select * from t;
join 优化问题¶
- 普通方案,先提取所有需要的参数进行拼接然后再进行筛选
select count(distinct T1.ci_no) as cnt from T1 join T2 on T1.ci_no=T2.ci_no where month(T1.cre_dt)=9 and T1.cus_sts='Y' and bal>0; - 优化先筛选缩小范围再做合并
select count(T1.ci_no) as cnt from (select * from T1 where month(cre_dt)=9 and cus_sts='Y') T1 join (select ci_no,sum(bal) from T2 group by ci_no having sum(bal)>0) T2 on T1.ci_no=T2.ci_no;
N 日留存率¶
- 比如首日注册 10000 人,一周之后还剩下 6000 活跃用户,那么留存率为 60%
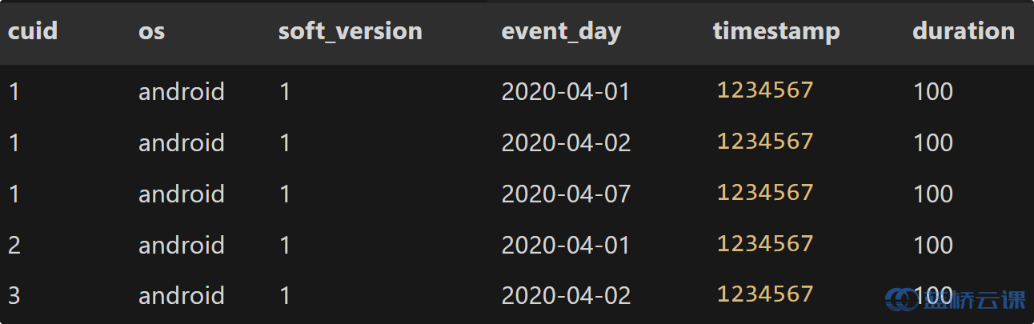
- 求出 4.1 在 4.2 的留存 uv 以及留存率、4.1 在 4.7 的留存 uv 留存率
- pv 表示页面浏览量,uv 是独立访客数(就是要去掉一个用户的多次访问)
- join 方法,效率较低
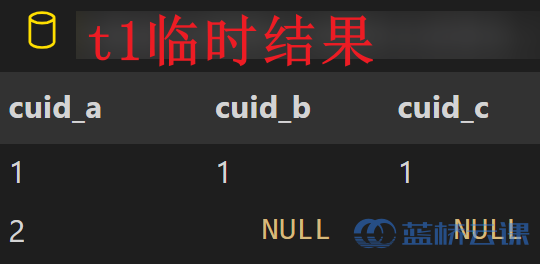
- 即提取每一天的用户并通过左连接追踪
with t1 as ( select a.cuid as cuid_a, b.cuid as cuid_b, c.cuid as cuid_c from (select distinct event_day, cuid from tb_cuid_1d where event_day='2020-04-01') as a left join (select distinct event_day, cuid from tb_cuid_1d where event_day='2020-04-02') as b on a.cuid=b.cuid left join (select distinct event_day, cuid from tb_cuid_1d where event_day='2020-04-07') as c on a.cuid=c.cuid ) select count(cuid_a) uv, count(cuid_b) uv2, count(cuid_c) uv7, count(cuid_b)/count(cuid_a) as `次日留存率`, count(cuid_c)/count(cuid_a) as `7日留存率` from t1;
- 行转列方法
- 不适用 join 性能好
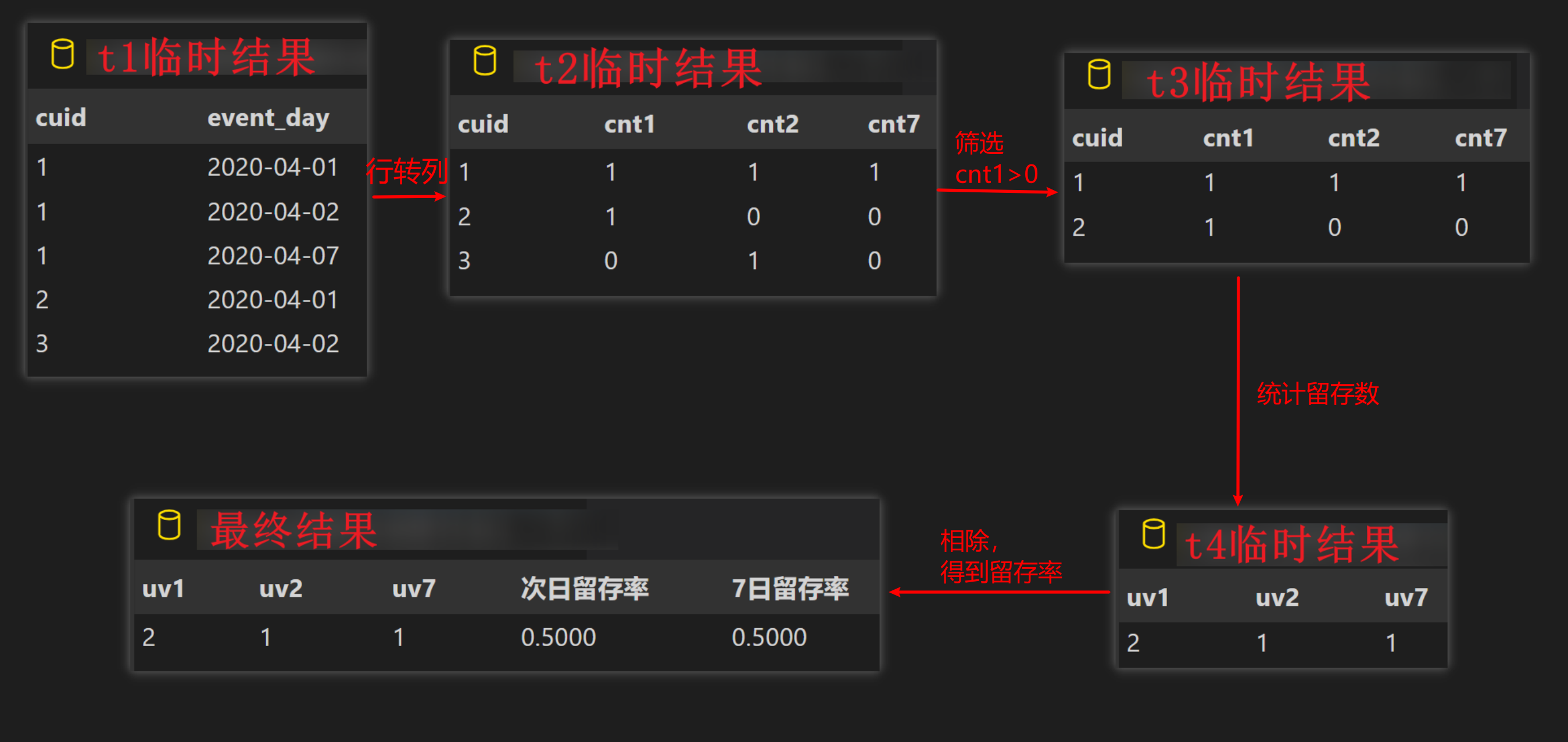
with t1 as (
select cuid,
event_day
from tb_cuid_1d
where event_day in ('2020-04-01','2020-04-02','2020-04-07')
),
t2 as (
select cuid,
count(if(event_day='2020-04-01',1,null)) as cnt1,
count(if(event_day='2020-04-02',1,null)) as cnt2,
count(if(event_day='2020-04-07',1,null)) as cnt7
from t1
group by cuid
),
t3 as (
select cuid,
cnt1,
cnt2,
cnt7
from t2
where cnt1 >0
),
t4 as (
select count(cuid) as uv1,
count(if(cnt2 > 0, 1, null)) as uv2,
count(if(cnt7 > 0, 1, null)) as uv7
from t3
),
t5 as (
select *,
uv2 / uv1 as `次日留存率`,
uv7 / uv1 as `7日留存率`
from t4
)
select * from t5;